Blepharoplasty (surgical "reconstruction" of the eyelid) may involve fat removal, fat transfer, and other manipulations. Whatever the approach, it is not the change in the contour of the eyelid gap that remains universal and important, but the possibility of avoiding possible complications and achieving a quick recovery of the patient. This article focuses on performing lower eyelid blepharoplasty in a patient requiring hernial fat removal using a mini-incision technique using a radiofrequency device. The transconjunctival approach to lower eyelid blepharoplasty has gained popularity over the past few years. This was partly due to increased patient awareness of the complications associated with the percutaneous technique. At the same time, the interest of people in carrying out blepharoplasty remains very high,
The main source of concern for modern patients planning blepharoplasty is the postoperative scar, which should remain invisible, if any, as well as the fastest possible return to work and an active lifestyle after the operation. In order to smoothly achieve the above result, a certain surgical technique has been developed and there are special tools.Blepharoplasty techniques for hernial fat removal
There is quite a lot of interest in the use of lasers in making eyelid tissue incisions, as they do less harm than electrocoagulation. Traditional electrocoagulation uses a platinum wire heated to a high temperature by an electric current, which can lead to noticeable tissue damage. Lasers may also not be safe enough, because they can increase tissue trauma due to excessive heating and even cause burns.
Many specialists prefer to use ultrasonic frequency radiosurgical instruments, which results in minimal skin damage. Soft tissue resistance to these radio waves causes the fluid in the cells to heat up. An electrode attached to the handpiece is used to make an incision in the skin and muscle, and to remove orbital fat. The incision is obtained without pressure, without blood, smooth and with minimal thermal damage to the skin.
High frequencies in surgical procedures have been a long-standing subject of research among medical professionals, stating that 4.0 megahertz is the optimal frequency for incision of skin tissue. The use of radio frequency allows the surgeon to work in different modes:
- filtered mode: for a smooth micro-incision with little tissue damage and associated coagulation;
- cut-coagulation mode: well suited for operations on vascular areas, such as the eyelid, while avoiding tissue trauma;
- hemostasis mode: designed to stop bleeding that occurs during surgery.
Features of percutaneous and transconjunctival blepharoplasty
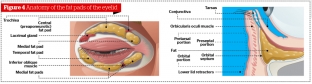
Historically, the percutaneous technique has been used to remove hernial fat, which could result in a visible scar, eversion or retraction of the lower eyelid. The last phenomenon was the most terrifying result of blepharoplasty.
- removal of too large areas of skin;
- swollen canthus;
- Insufficient fat removal resulting in damage to the optical focus, diplopia and hemorrhage.
- canthal gaping,
- eyelid retraction,
- hemorrhage,
- double vision, etc.
Benefits of Blepharoplasty with RF Devices
The instrument used for this operation is a radio frequency surgical device that delivers high frequency waves at 4.0 MHz, the optimum frequency for soft tissue incision. The Surgitron is capable of transmitting various forms of radio waves, and its micro-radio electrodes require less energy, resulting in a significant reduction in thermal effects on tissues.
Cosmetic surgery, and especially the ophthalmic branch, requires great skill and deep knowledge of the anatomy of the eyelid in order to avoid complications and undesirable results during recovery. Transconjunctival blepharoplasty helps to achieve a positive result. When using the Chadley method, it became much easier to remove hernial fat. The retractor completely exposes the eyeball, which allows you to easily get to the fat collected in one of the three folds of the eyelid. Fast and painless recovery is due to the radiosurgical handpiece, with which the surgeon makes quick, painless and easy to heal incisions.







Add a comment