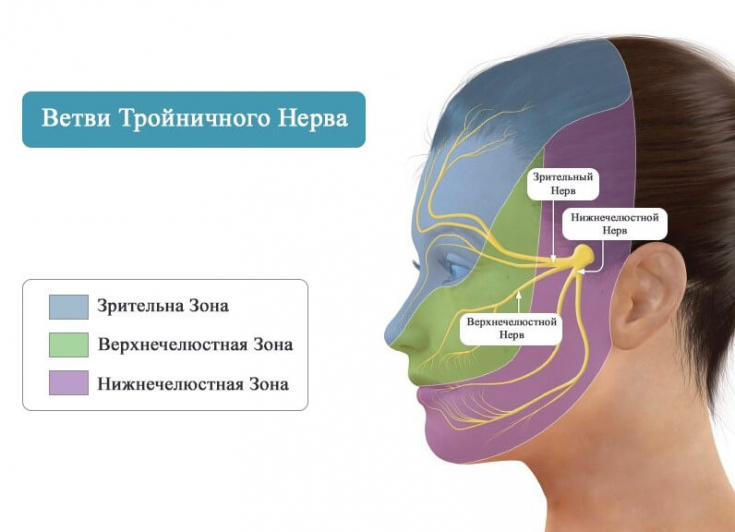
Trigeminal nerve − largest of all cranial nerves.
It is mixed: it has a thin motor and thick sensory roots.
GASER (trigeminal) ganglion is located in the trigeminal fossa of the temporal bone.
It contains sensory fibers that perceive pain, temperature and mechanical stimuli on the face.
Peripheral processes of neurons form three branches of the trigeminal nerve (frontal, maxillary and mandibular).
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com by which symptoms a cosmetologist can recognize lesions of the trigeminal nerve, and what changes on the face this pathology manifests itself.
- Characterization of pain in trigeminal neuralgia
- Trigger factors for attacks of trigeminal neuralgia
- Approaches to the treatment of trigeminal neuralgiava
Characteristics of pain in trigeminal neuralgia
Patients can finely localize their pain.
It usually runs along the line of division into the mandibular and maxillary branches of the nerve or the maxillary and ophthalmic.
60% of patients complain of shooting pain from the corner of the mouth to the corner of the mandible; 30% .minus; from the upper lip to the eye and eyebrow, without involving the orbit.
In less than 5% of cases, pain occurs along the ophthalmic branch of the facial nerve.
Follow us on Instagram!
Pain is usually intense, paroxysmal, stabbing.
It begins with a sensation of electric shock in a certain area, then rapidly builds up in less than 20 seconds to a discomfort "deep in the face", often distorting the patient's facial expression.
Then fades away over a few seconds, followed by burning pain that can last from a second to several minutes.
During attacks, patients may perform various head movements or "grimaces"; to reduce the severity of pain, thus a condition similar to pain typeto.
A terrible poison or an invaluable medicine: botulinum therapy in the treatment of migraine
Trigger factors for attacks of trigeminal neuralgia
Trigger or hypersensitivity areas are often located near the nose/mouth in most patients.
Chewing, talking, smiling, or drinking cold/hot liquids can trigger a pain attack.
Touching, shaving, brushing your teeth, or blowing cold air from an open car window can also cause pain.
Physical examination usually helps in differential diagnosis with other diseases.
However, remember that pain occurs after trigger point stimulation; thus, some patients may restrict vision due to fear of irritation of these areas.
The diagnosis of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia is likely only if there is no objective evidence of dysfunction of the fifth pair of cranial nerves.
Gluten intolerance: modern day troubles or serious illness
Sensitivity disturbance is observed immediately after an attack of pain; the presence of permanent numbness in any area rules out the diagnosis.
Loss of the corneal reflex also excludes the diagnosis of idiopathic TN unless a prior rhizotomy of the trigeminal branches has been performed.
Weakness of the muscles in the lower jaw or other part of the face, difficulty swallowing indicate a different etiology of the disease.
In patients with multiple sclerosis or organic disease and TN, there is loss of sensation on examination.
Although facial hypesthesia or dysesthesia may occur transiently in classic TN, they should be considered part of the symptomatic forms.
However, the absence of these signs does not rule out the presence of an underlying cause, i.e. does not rule out a symptomaticform of TN.

Trigeminal neuralgia treatment approaches
includes:
pharmacological therapy;- percutaneous interventions (e.g. percutaneous rhizotomy);
- surgical interventions (e.g. microvascular decompression);
- radiotherapy (stereotactic radiosurgery using a gamma knife).
- Pharmacological considerations: At the beginning of treatment, it is recommended that pharmacological therapy be given before invasive treatments, as it is effective in 75% of cases.
One-time therapy can help relieve pain immediately after an attack occurs.Carbamazepine
is the most studied drug for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia and the only drug approved by the FDA. Because there is a chance of spontaneous cessation of seizures after 6-12 months, patients may be able to stop taking medication in the first year after diagnosis.
Trigeminal neuralgia can progress, so patients will need to take additional drugs to control pain in the future, up to surgical treatment.
Some risks of injecting under eye fillers
Lamotrigineand baclofen are second line drugs. Sufficient evidence for
combination therapyis available for only two drugs − lamotrigine and carbamazepine, in case of failure of the latter it is recommended to prescribe gabapentin, which has been shown to be effective in trigeminal neuralgia, especially in patients with multiple sclerosis.






