Age-related changes in the skin are an important problem in modern cosmetology, and most programs related to rejuvenation are aimed at correcting them. In order to choose the right set of procedures and methods of correction, it is necessary to take into account many anatomical and physiological aspects associated with the skin – such as its structure at different age periods, functions performed, probable factors influencing aging. Read about these and other facts that allow you to better understand the mechanisms of our skin at estet-portal.com.
Age features of facial skin related to its functions
The common idea of the skin as a special covering for the body that protects the human body from external influences is not entirely correct, since this organ makes up approximately 16% of the total body mass and performs, in addition to protective, & nbsp; number of vital functions:
- homeostatic – regulates temperature and prevents water loss, helps to maintain the constancy of the internal environment of the body;
- excretory – removes many metabolic products from the body through the sweat glands, including helping to maintain the water-salt balance;
- endocrine – secretes a number of hormones, including such important for women as estrogen;
- secretory – contributes to the formation of vitamin D under the action of sunlight and its absorption by the body;
- touch – has temperature, pain, tactile sensitivity, transmits information to the body through a system of receptors.
Some experts also distinguish a diagnostic function, since many internal disorders and diseases can be reliably determined by the condition of the skin in their early stages.
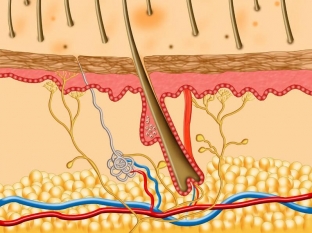
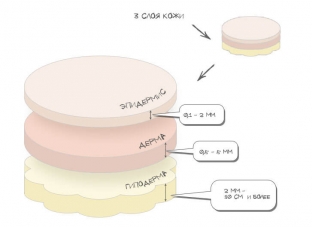
The structure of the skin: what should be considered in terms of the age characteristics of the face
Human skin consists of three layers, and this is very important to take into account when calculating the cosmetic effect on the age-related features of the face, since each procedure is designed for a certain depth of drug administration. So, when working with the skin, the impact can be carried out on the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis.
The outer layer of the skin – The epidermis is a stratified squamous keratinized epithelium, which is firmly connected to the underlying dermis through the basement membrane. The structure of this membrane is determined by the interaction of keratinocytes – from the epidermis and fibroblasts – from the dermis. The basement membrane serves as a kind of support for the cells of the epidermis, it takes part in regulating the intake of nutrients and the excretion of metabolic products.
Connective tissue layer of the skin – The dermis consists of papillary and reticular layers, one of which performs a trophic function due to the loose fibrous structure, and the other is responsible for the strength and elasticity of the skin due to the content of collagen fibers. The dermis provides strength to the skin.
Inner layer of leather – the hypodermis consists mainly of lobules of mature fat cells, which are separated from each other by thin connective tissue layers, along which nerve endings, blood and lymphatic vessels pass.
Each of the layers of the skin reacts differently to the processes occurring in the body, including those associated with aging, therefore, competent cosmetic treatment for the purpose of rejuvenation should be carried out on each of them.
Dependence of age-related features of the skin on external and internal factors
There are various theories explaining the onset of age-related skin changes. By and large, all the reasons why its age-related features appear can be divided into internal and external. On the one hand, chronoaging plays a role in the manifestation of age-related changes, which is manifested by thinning of the dermis and hypodermis in combination with a thickening of the stratum corneum, a decrease in the production of hyaluronic acid, collagen and other important elements responsible for skin elasticity, thinning of capillary walls, gravitational ptosis. On the other hand, there is an age-related accumulation of chronic diseases, the effects of stress and other factors that negatively affect the state of the body as a whole and affect the condition of the skin.
Experts say that 70% of age-related changes in the skin are caused not by internal factors of aging of the body, but by exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation.
Both internal and external factors that cause skin aging lead to approximately the same consequences – a decrease in the content of collagen, an increase in the activity of melanocytes, a deterioration in the ability of the skin to regenerate, which becomes the first manifestations of age-related features of the skin, leading patients to a cosmetologist.







Add a comment