Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are one of the most common causes of the development and manifestation of chronic dermatoses. Celiac disease is a genetically determined autoimmune enteropathy, characterized by gluten intolerance, affecting the small intestine, which leads to atrophy of the intestinal villi of its mucosa. Impairment of the permeability of the small intestine, as well as its absorption and digestion functions, the presence of specific autoantibodies in case of gluten intolerance is directly related to various dermatological manifestations. Let's talk on estet-portal.com about
Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis: clinical picture- Gde connection between dermatitis and celiac disease:
- etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis
Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis: clinical presentation
Dermatitis herpetiformis or Dühring-Brock disease is an inflammatory skin disease characterized by a chronic relapsing course, typical histopathological and immunopathological features.
Skin lesions in this disease are symmetrical clustered elements characterized by true polymorphism.
In dermatitis herpetiformis rashes include erythema, urticarial plaques, papules, localized mainly on the extensor surface of the elbows, knees, palms and soles, as well as on the shoulders, buttocks, in the sacral region, on the neck , face and scalp.
Follow us onInstagram!
Herpetiform vesicles may appear later and are often eliminated immediately, leaving behind erosions, crusts, and areas of post-inflammatory dyschromia. petechial lesions of the skin in the palmar-plantar zone can also be observed. The mucous membranes remain intact.
Read also: Dermatitis herpetiformis: treatment features
Nikolsky's symptom is negative. Patients diagnosed with dermatitis herpetiformis experience intense itching that is resistant to antihistamine therapy, pain and burning.
Diagnosis of 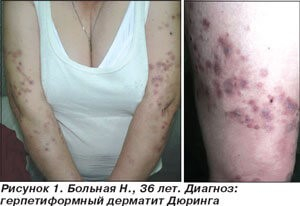 Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis
Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis
How dangerous is Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis
During histological examination of dermatitis herpetiformis, pyoepidermal bullae are observed. Indirect immunofluorescence determines
IgAin the dermoepidermal junction area and the papillary dermis. Where is the connection between dermatitis and celiac disease: etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis
is the most common
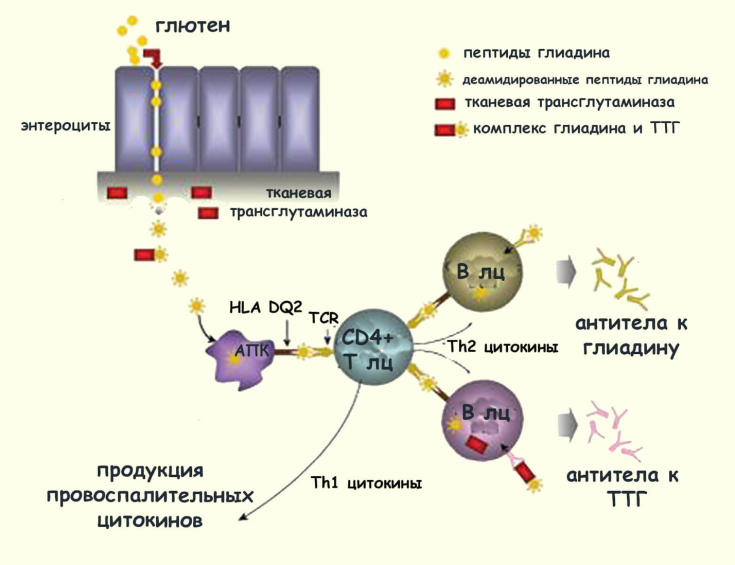
extraintestinal manifestation of celiac diseasein> 85% of cases. In fact, dermatitis herpetiformis and celiac disease share the same HLA haplotypes, DQ2 and DQ8. For all patients with this diagnosis, such changes in the mucous membrane of the small intestine, as in celiac disease, as well as circulation of high-affinity antitransglutaminase
IgA– autoantibodies of two types: intestinal and epidermal. Such antibodies are specific serological biomarkers that are characteristic of both celiac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis. Epidermal transglutaminase is an important enzyme that triggers pathological reactions in a genetically predisposed organism. It activates
cellulartransformation
at the stage of keratinocyte differentiation and is a autoantigen that affects the skin.
 Follow us on
Follow us on
As a result of these processes, in dermatitis herpetiformis, dermal deposits of immune complexes are deposited in the dermis, including Ig
Ato tissue transglutaminase (TSH) . Read also: Possible complications of gluten intolerance
The most reliable theory for the development of Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis is a genetic predisposition associated with gluten load, which contributes to the formation of antibodies
IgAto gluten – TSH - complex with further deposition of tissue deposits IgA. Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis is a serious chronic skin disease with a clear association with celiac disease. When following a gluten-free diet – strict exclusion of all gluten-containing foods from the diet – helps to reduce clinical manifestations, that is, reduce intense itching, pain and burning sensation vesicular -
erythematouspapules, and hence the achievement of remission. Therefore, screening for celiac disease in patients suffering from chronic skin conditions is warranted. More interesting stuff on our YouTube channel:







Add a comment