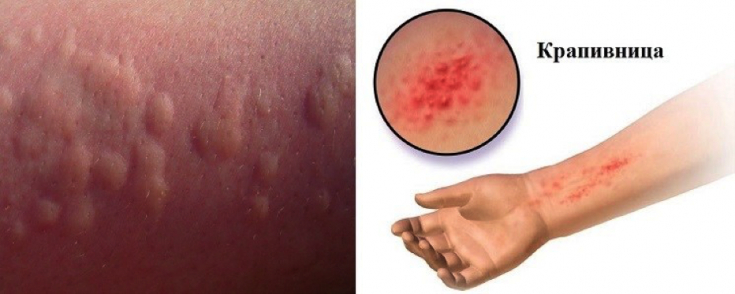
The skin reaction in urticaria is usually associated with edema. Since histamine, which is released by mast cells, is the basic mediator of the pathogenesis of urticaria, H1-antihistamines (AHP) of the 2nd generation are considered the basis of modern therapy, but standard doses of AHP are not always sufficient to eliminate the skin symptoms of urticaria.
- studying the effectiveness of bilastine in the treatment of chronic urticaria
- bilastine and other antihistamines in the treatment of urticaria
- bilastine and cold urticaria
An important test for determining the effectiveness of antihistamines is the test for
the ability to relieve the symptoms of chronic urticaria, when other antihistamines, such as loratadine, cetirizine, rupatadine, ebastine, fexofenadine and desloratadine, have proven ineffective. Such a study was also carried out for bilastine.
Subscribe to our page on Facebook!
Bilastine was studied in chronic urticaria at doses of 10, 20, and 30 mg versus placebo in a phase II study (n = 222).Reduction of rash and pruritus was taken as primary endpoints. The results in all dosage groups of bilastine were statistically different from placebo, confirming its effectiveness in comparison with other drugs.
Although there was a dose-related trend, there were no statistically significant differences between the results in groups of patients with urticaria treated with different doses of bilastine.An important aspect of the review was the safety of treatment with bilastine, including at high doses. The conclusion is that bilastine has favorable profiles of both efficacy and safety. Bilastine is a highly effective antihistamine even when taken at a dose of 20 mg per day.
Bilastin practically does not penetrate the BBB, does not have a sedative and hypnotic effect. Moreover, in practice, these statements can be extrapolated to increased doses of the drug - 40 and 80 mg.
Sex hormone dysfunction in the development of acne
Being able to safely use bilastine even at 4x the dose as outlined in the EAACI/GA2LEN/EDF/WAO guidelinesfor the treatment of severe urticaria whose symptoms are not ameliorated by standard doses of antihistaminesis a significant advantage bilastine before other antihistamines.
Bilastin and other antihistamines in the treatment of urticariaWhat can trigger an exacerbation of atopic dermatitis?
Recently, in a multicenter study in Europe and Argentina involving 525 patients with urticaria, bilastine 20 mg was compared with levocetirizine 5 mg and placebo. The drugs were prescribed daily for 28 days.Bilastin significantly (p <0.001) reduced the total number of symptoms already from the second day of administration. The results were significantly different from placebo. The Dermatological Quality of Life Index (DLQI) was also significantly improved. Bilastine and levocetirizine were equally effective and safe, both were well tolerated by patients.
The second study compared the effects of bilastine 20mg hydroxyzine 50mg in 24 healthy volunteers admitted to fly as pilots. Assessments were made before taking the drugs and 6 hours later. For assessment, we used tasks on attentiveness and concentration, the Stanford sleepiness scale. The results showed that,
, unlike hydroxyzine, bilastine 20mg did not cause drowsiness or deterioration in the performance of flight-related tasks. These results suggest that bilastine may provide an effective antiallergic therapy for pilots suffering from allergic
The results showed that urticaria that developed at 4 °
C, completely leveled with bilastine. Doses of the drug 40 and 80 mg completely eliminated the symptoms.
increase in efficacy with increasing dosage of the drug in the absence of drowsiness
. The secondary endpoint in the study was the level of itching. With treatment with bilastine 20 mg daily, the mean pruritus score was significantly reduced, with 13 of 20 patients reporting that itching had stopped.Emollients and food allergies: what's the connection?More useful information on our YouTube channel







Add a comment