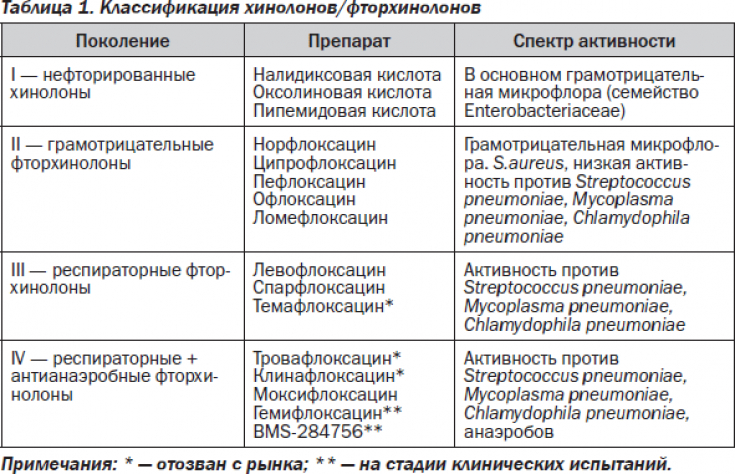
Ofloxacin – one of the most effective representatives of the second generation fluoroquinolones due to its high bactericidal activity against a large number of pathogenic microorganisms.
Ofloxacin, as a fluoroquinolone, destabilizes bacterial DNA by directly inhibiting the DNA hydrase enzyme. As a result of DNA damage, irreversible metabolic processes in the cell lead to the death of bacteria.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com for which infectious diseases fluoroquinolones are most effective, in particular, the representative of the second generation - ofloxacin.
Spectrum of action and pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin
The spectrum of action of ofloxacin extends to bacteria that produce beta-lactamase, staphylococci that produce and do not produce penicillinase, streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae and E. coli, Shigella, Salmonella, meningococci, enterococci, legionella and intracellular microbes, namely chlamydia, mycoplasma and ureaplasma.
Follow us on Instagram!
Microbial resistance to ofloxacin is rarely detected. Ofloxacin is rapidly absorbed in the digestive tract (within 1-2 hours), has the highest bioavailability among fluoroquinolones (more than 95%) and forms high concentrations in tissues and body fluids (sometimes higher than in the blood). The drug is excreted by the kidneys and liver.
Indications, contraindications and side effects of ofloxacin
Bactericidal antimicrobial activity and a small number of adverse reactions have led to the widespread use of ofloxacin in modern uronephrology. The drug is used to treat patients with almost all acute and chronic infectious and inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system, namely: microbial lesions of the upper and lower urinary tract, urethritis, prostatitis, orchitis and epididymitis.
Gonorrhea in men: what is important to know about sexually transmitted disease
Side effects of ofloxacin are noted in 1.5-3% of patients, as a rule, these are reactions from the nervous system (impaired reaction rate, sleep, vision), dyspeptic symptoms (diarrhea, dyspepsia), skin manifestations (photodermatitis, edema ), blood reactions (leuko-, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis), reversible liver and kidney dysfunction, tendinitis, cardiotoxic and allergic reactions.
Contraindications to the appointment of fluoroquinolones are pregnancy, lactation, individual sensitivity to fluoroquinolones, epilepsy, damage to the central nervous system with convulsions and age.
Clinical efficacy of fluoroquinolones
In the presence of acute or exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis, ofloxacin and ciprofloxacin − most effective among fluoroquinolones and antimicrobial therapies. They form a very high therapeutic concentration both in the parenchyma and directly in the urine. In the presence of intoxication and hyperthermia in patients with pyelonephritis, it is necessary to administer ofloxacin intravenously.
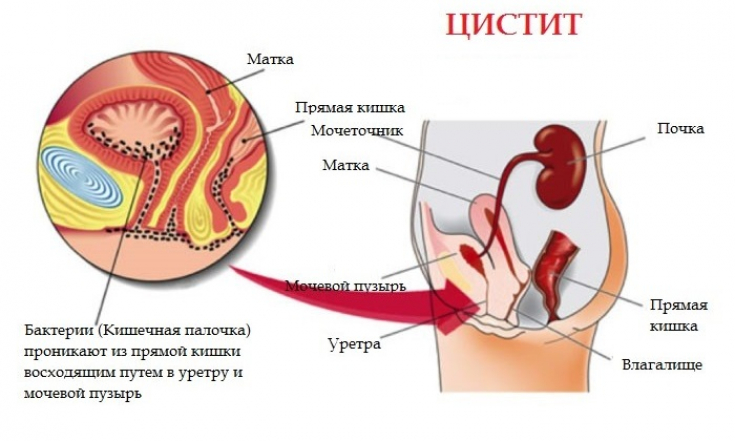
In the presence of acute cystitis, ofloxacin, like ciprofloxacin and, to a lesser extent, lomefloxacin among the fluoroquinolones, are very effective drugs for monotherapy. As a rule, in patients with uncomplicated cystitis, it is not possible to prescribe a drug in accordance with the sensitivity of the detected pathogen, since it is necessary to quickly reduce the severity of the symptoms of the disease.
In most cases, fluoroquinolones exhibit high antimicrobial activity in cystitis. This is due to the fact that most often the causative agents of cystitis (E. coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Gardnerella, gonococcus) are highly sensitive to the bactericidal action of fluoroquinolones.
Urinary syndrome: as evidenced by changes in urine values
Ofloxacin is the first-line fluoroquinolone treatment for intracellular infections. In patients with urogenital chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis), ofloxacin is prescribed 300-400 mg 2 times a day for 10-28 days, which allows you to influence 3-7 cycles of microbe development.
In the presence of Ureaplasma urealiticum, the duration of treatment at 200-400 mg 2 times a day is 14 days. As with urogenital chlamydia, patients with cystitis should have instillations.
Recovery of patients is determined by the results of sowing immediately after the end of treatment, by titers of antibodies of class G - after 3-6 months; after therapy, this figure reaches 95%.
In the treatment of mycoplasmal infection, the tactics do not differ from those for ureaplasmosis. The effectiveness of therapy is 40-60%. In the case of intracellular infections, mandatory examination and treatment, in the presence of an appropriate pathogen, requires a partner. In the treatment of patients with acute prostatitis, ofloxacin is the first-line drug due to its high concentration in the anatomical structures of the prostate.

It should be noted that ofloxacin − a more active drug compared to other fluoroquinolones and macrolides in the treatment of patients with urogenital chlamydia and ureaplasmosis. We also note that macrolides do not belong to bactericidal drugs, with the exception of azalides - sumamed, which also indicates the advisability of prescribing fluoroquinolones.
Treatment of ureaplasmosis in men: all the features of therapy
Representatives of the latest generations of fluoroquinolones (grepafloxacin, trovafloxacin, etc.) do not show high activity against pathogens of urogenital infections, including chlamydia.
So, among the second-generation fluoroquinolones, ofloxacin is the optimal first-line drug for acute and chronic urinary tract infections.
Symptoms and aspects of treatment of urogenital candidiasis







Add a comment