Breast cancer is the leading cause of malignant death among the female population. The approach to surgical treatment of breast cancer has undergone many changes throughout the history of oncology - from the classical radical mastectomy, which was developed at the end of the 19th century by Halsted, to organ-preserving operations. These changes are associated with the development and implementation of new methods of combined and complex treatment.
Breast cancer treatment methods.
The use of neoadjuvant treatments for breast cancer in the form of chemotherapy and radiation therapy given before surgery reduces the biological activity of the tumor and reduces or prevents lymphogenous dissemination. But these methods are able to delay the timing of the radical operation, since the appearance of radiation epitheliitis and leukopenia is possible.
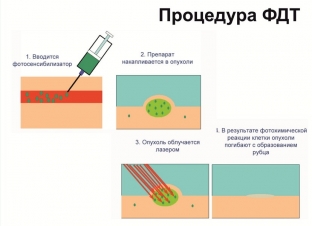
Photodynamic therapy is a organ-preserving method of treating breast cancer due to the accumulation of photosensitizer substances in the cells of malignant neoplasms. The basis of this method is the photochemical destruction of the photosensitizer with the release of a large amount of "singlet oxygen".
This is done by the action of light radiation of a certain power and wavelength. These waves, together with other radicals, provoke the process of destruction in the cell and lead to necrobiosis and necrosis of cellular structures, basement membranes of tumor vessels and endothelium.
Mechanism of action of photodynamic therapy on a tumor
In addition, photodynamic therapy (PDT) activates the complement system and immunologically active blood cells that are in the tumor.
The most important thing in the action of photodynamic therapy is the triggering of cell apoptosis. This greatly reduces the biological activity of neoplasm cells and the risk of metastasis. Therefore, the possibility of combining photodynamic therapy with a surgical method has been studied. PDT is used in the treatment of malignant formations that are accessible to laser exposure.
The positive effect of photodynamic therapy for various oncological processes ranges from 70% to 92%.
Evidence base for the successful use of photodynamic therapy
In many cases of early detection of breast cancer, patients refuse surgery. Therefore, the question arises about the possibility of using photodynamic therapy as an independent type of treatment.
In this regard, studies were conducted to develop a technique for interstitial photodynamic therapy of breast cancer and evaluate the effectiveness of this method with Photosens, which is a second-generation photosensitizer.
The study involved 14 patients aged 40 to 65 who voluntarily agreed to undergo PDT.
Patients who were diagnosed with breast cancer (T1-2NхM0), mononodular form, who had a tumor diameter of not more than 3 cm, PDT was used as a preoperative therapy.
The essence of the study using PDT in the treatment of breast cancer
Photosensitizer Photosens (PS) was used in a study of breast cancer treatment by PDT. This drug was administered intravenously over 30 minutes at a dosage of 0.5 mg / kg 1-1.5 hours before irradiation with preliminary dilution in saline.
In order to detect and determine the concentration of a substance in the tumor, a LESA-6 device with a laser operating at a wavelength of 630 nm was used. At the same time, the energy density that he created never provoked photodynamic damage to the tissue under study.
For photodynamic therapy in the treatment of breast cancer, a diode laser LD680-2000 was used, which has a power of 1.5 W and laser radiation with a wavelength of 670 nm. A metallized light guide with a diameter of up to 1 mm was used to supply the laser light. In this case, the laser irradiation power at the output of the quartz fiber was 300 mW/cm2. The energy density during interstitial irradiation was 100-500 J/cm3 from one position.
Photodynamic therapy was carried out 7-10 days before the mastectomy with a radical method.
Women underwent interstitial irradiation for the treatment of breast cancer. When the tumor node exceeded more than 2.5 cm (in 6 cases), the light guide was brought to the neoplasm from 4 points. In the remaining 8 patients, light was supplied from one point, which was located in the center of the tumor. This confirmed the ultrasonic orientation correction.
In order to reduce the photosensitivity of the skin, women after the introduction of photosensitizers avoided direct sunlight for 4-6 weeks. Patients took antihistamines and antioxidants for a month, and also used sunscreen and glasses.
Results of a photodynamic therapy study
During the spectrometry in the removed preparation, the concentration of PS in the neoplasm tissue was 3.35-4.1 times higher than in the calibration sample. This is a necessary condition for PDT. But in the skin and in the surrounding breast tissue, it did not exceed 1.8 units.
Histological examination of the removed mammary gland tissues showed the process of necrosis of the tumor node in absolutely all cases.
In 11 cases out of 14, this necrosis after photodynamic therapy was total, and the structure of the tumor was not determined. In 3 people the necrosis was partial.
This points to the shortcomings in the technique of photodynamic therapy for large tumors, which require multifocal supply of light energy.
Effectiveness of photodynamic therapy in the treatment of breast cancer
Results and conclusions on the advisability of using photodynamic therapy in the treatment of breast cancer:
- Photodynamic therapy allows to obtain complete tumor necrosis with the replacement of its tissue with scar tissue.
- In all cases of breast cancer treatment, FS accumulated significantly, which allowed PDT to be performed with a good local effect.
- In cases of refusal of surgical treatment of breast cancer, the method can be used in combination with X-ray and chemotherapy.
- No adverse reactions were observed after administration of Photosens at the recommended doses.
- It is possible to conduct repeated sessions without the administration of the drug due to the long delay of the photosensitizer in the tissues.
- With the use of the recommended power modes, photodynamic therapy proceeds with pain, which requires the preliminary administration of analgesics.
Of the negative aspects of the use of photodynamic therapy, it is worth highlighting pain in the area of application of energy of the highest density, as well as an increase in skin photosensitivity. The pain that occurred during the sessions was stopped by non-narcotic painkillers.
The skin was photosensitive for 2-3 months, which indicated a significant content of PS in it. Local phototoxic reaction on the hands and on open areas of the skin in the form of itching and hyperemia was observed in 3 patients. In 8 patients, after the first day, swelling of the mammary gland was observed, in 3 patients the temperature rose to subfebrile numbers.
In general, photodynamic therapy is one of the few effective treatments for breast cancer that are used today.






Add a comment