Prolapse of the uterus is a phrase that sounds very menacing in itself. This gynecological pathology occupies one of the leading places in the structure of anomalies in the position of the internal female genital organs. The main reason for the development of uterine prolapse is traumatic childbirth: an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and a weakening of the fixing apparatus of the uterus are key factors necessary for the development of this pathology. Uterine prolapse very often occurs in young women of reproductive age and significantly impairs their quality of life, while posing a threat of serious complications. A careful approach to the diagnostic process and treatment of uterine prolapse will help restore the normal position of the internal genital organs of a woman.
Methods for diagnosing and treating uterine prolapse
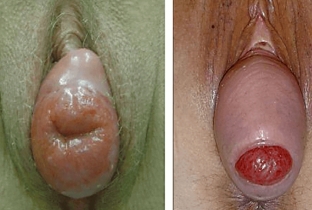
Since the clinical picture of uterine prolapse is quite specific, it is often possible to diagnose diseases easily and in a timely manner. However, this pathology develops gradually and in the early stages of the disease, the only symptom that bothers a woman may be the sensation of a foreign body in the vagina. In some cases, women may not seek medical help for a long time and sound the alarm only when the internal genital organs fall outside the genital gap. At the same time, irreversible pathological processes can already develop in the tissues of organs. That is why the diagnosis and treatment of uterine prolapse must be timely.
Treatment of uterine prolapse:
- basic diagnostic methods for uterine prolapse;
- conservative treatments for uterine prolapse;
- surgical treatments for uterine prolapse.
Basic diagnostic methods for uterine prolapse
The diagnostic process of uterine prolapse and prolapse is based on the patient's complaints, as well as on examination and palpation of the woman's genitals. After a gynecological examination, the prolapsed genitals are set back and a bimanual gynecological examination is performed to assess the condition of the pelvic floor muscles, the ligamentous apparatus of the uterus and its appendages. Ulcerations visualized on the walls of the vagina and cervix must be differentiated from oncopathology. To do this, perform colposcopy, cytological examination and, if necessary, targeted biopsy. Be sure to conduct a rectal examination to determine the condition of the anal sphincter. If there are complaints about the functioning of the urinary system, additional methods are used to help investigate its condition.
Conservative treatments for uterine prolapse
The choice of treatment for uterine prolapse depends on the following factors:
- degrees of prolapse of the internal genital organs of a woman;
- patient's age;
- the presence of concomitant gynecological pathology;
- desire to restore and preserve reproductive function;
- the presence of disorders of the functions of the large intestine and rectal sphincter;
- concomitant extragenital pathology.
If a woman is diagnosed with a slight prolapse of the internal genital organs, that is, they do not descend to the level of the vestibule of the vagina, and also if there are no violations of the functions of neighboring organs, conservative treatment of uterine prolapse is possible. For this purpose, patients are recommended to wear special bandage underwear, as well as a course of physiotherapy exercises.
Surgical treatment of uterine prolapse
In more severe cases, surgical treatment of uterine and vaginal prolapse is recommended. For this purpose, the following groups of surgical interventions are used:
- operations aimed at strengthening the pelvic floor: colpoperineolevathoroplasty;
- operations aimed at correcting the suspensory apparatus of the uterus: shortening and strengthening of the ligaments;
- operations aimed at strengthening the fixing apparatus of the uterus: stitching, transposition of ligaments;
- surgeries with rigid fixation of prolapsed organs to the pelvic walls;
- surgeries in which alloplastic materials are used to fix the uterus;
- operations with partial obliteration of the vagina;
- radical operations: vaginal hysterectomy.






Add a comment