Every year, about 10,000 people die from tuberculosis in our country. The main feature, and at the same time, the danger of the disease is that tuberculosis infection can affect almost all body systems. The defeat of tuberculosis of the genitourinary organs is in the first place, among the extrapulmonary forms of tuberculosis. The risk group is young women of reproductive age. Untreated genital tuberculosis can lead to serious consequences, among which infertility is one of the main complications.
Classification and causes of genital tuberculosis
Genital tuberculosis develops as a secondary infection, due to the penetration of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the primary focus into the genitals, against the background of a decrease in the body's immune abilities. The infection can spread throughout the body by the hematogenous or lymphogenous route. It is impossible to become infected with tuberculosis through sexual contact, since the epithelium of the mucous membranes of the female genital organs is resistant to the pathogenic effects of mycobacteria. The fallopian tubes and endometrium are most often affected, tuberculosis of the ovaries, cervix, vagina and external genital organs is much less frequently diagnosed. In the classification of genital tuberculosis, the following forms are distinguished:
- chronic genital tuberculosis with a mild clinical picture;
- subacute form of tuberculosis with significant involvement;
- caseous form of genital tuberculosis with severe and acute processes;
- resolved tuberculous process with calcification of foci.
Symptoms of genital tuberculosis: the main complaints of patients
The most common complaint among female patients resulting in a diagnosis of genital TB is the inability to conceive a child. Moreover, infertility until the process becomes chronic may remain the only complaint. Only in half of the patients, at the same time, menstrual function is disturbed, in the form of the appearance of irregular, rare, scanty and painful menstrual bleeding. In the case of the development of a chronic tuberculous process, in addition to infertility, patients complain of fever, weakness, fatigue, weight loss, the appearance of night sweats, as well as severe aching pain in the lower abdomen, which develops due to the formation of adhesions in the small pelvis . Rarely, and only in very young patients, genital TB may present with "acute abdomen" symptoms.
Difficulties in diagnosing the tuberculous process of the genitals
Diagnosis of genital tuberculosis is indeed a very difficult process, since the clinical picture of the disease is blurred, non-specific, and resembles a large number of other diseases of the pelvic organs, which are also characterized by infertility.
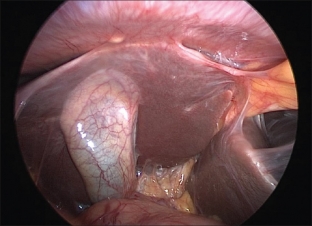
Only a carefully collected anamnesis, from which it will be known about the patient's contact with tuberculosis patients or an already established diagnosis of tuberculosis of another localization, can suggest the idea of a tuberculous process. There is a special tuberculin test, the essence of which is the subcutaneous injection of small doses of tuberculin, which provoke the appearance of general focal reactions of the body, confirming the diagnosis of tuberculosis. But the most accurate methods are microbiological studies, such as PCR and bacteriological cultures of secretions, which detect the growth of tuberculous microflora. With the help of diagnostic laparoscopy followed by biopsy and histological examination of tissues, it is possible not only to confirm tuberculosis of the genitals, but also to assess changes in the pelvis, formed against the background of the tuberculous process, as well as to eliminate the immediate cause of infertility during the operation. Ultrasound and hysterosalpingography also visualize changes in the affected organs.
Treatment of genital tuberculosis: chemotherapy and surgery
Like any other TB process, genital TB must be treated with a special chemotherapy regimen. Without fail, treatment should be carried out in anti-tuberculosis dispensaries or special sanatoriums - outpatient therapy is strictly prohibited. First-line chemotherapy drugs include the well-known rifampicin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol, isoniazid, and streptomycin. In the case of established resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to them, it is necessary to use second-line drugs - fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides. The treatment of tuberculosis is very long, the destruction of mycobacteria takes from 6 to 24 months. In the treatment regimen for genital tuberculosis, in addition to chemotherapy, it is also necessary to include immunomodulators, vitamins, antioxidants, drugs for symptomatic treatment - analgesics, antipyretics. Surgical intervention in genital tuberculosis is indicated when there are pronounced changes in the pelvic organs that disrupt their function and cause infertility, as well as when conservative treatment is ineffective. It must be remembered that the timely administration of the TB vaccine in childhood can protect against the occurrence of any TB process, including genital TB.






Add a comment