Granuloma – a delayed complication of contouring, which is included in the list of phenomena insufficiently studied in aesthetic medicine. From the point of view of histology, these formations are the reaction of the body to a foreign body with tissue infiltration by giant cells and macrophages. There are three types of granulomas that can appear after the introduction of fillers: cystic, nodular and sclerosing. Red firm papules, nodules or plaques may form months or even years after injections of permanent and temporary dermal fillers, most commonly – hyaluronic acid and bovine collagen.
Description of the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of granulomas after fillers by Dr. Beata Cybulska is given in the article estet-portal.com.
- Glulomas after filler injections
- Diagnosis and treatment of granulomas after fillers
- Clinical and histological features of granulomas after contouring
- Differential diagnosis of granulomas after fillers
- Granuloma treatment after dermal filler injections
Formation of granulomas after filler injections
A granuloma is formed as a result of a non-allergic chronic inflammatory reaction to a foreign body after the injection of a filler or other foreign material. This tumor is made up of immune cells such as macrophages. They coalesce into chaotically distributed giant cells containing more than 20 nuclei.
Stages of granuloma formation:
- Protein absorption;
- macrophage adhesion;
- macrophage fusion;
- cross interactions.
Patients with chronic sinusitis, dental disease, or other infections are more likely to develop infection after periorbital or central facial fillers. Such patients may also be prone to developing biofilms around or within the implant due to trauma caused by previous
Diagnosis and treatment of granulomas after the introduction of dermal fillers cause certain difficulties. For successful therapy, it is necessary to collect a comprehensive medical and aesthetic history, as well as conduct a thorough examination of the patient. It is important to differentiate between granulomas and nodules formed by fillers.
| Granuloma
| Filler knot
| Late allergic reaction
| Infection
|
|
| Clinical presentation and symptoms
| Cystic, nodular, indurated plaques of a bluish tint with congested capillaries, the size of which exceeds the volume of the injected filler. Appear simultaneously in different places.
| Uniform white-colored masses, firmer than granulomatous nodules
| Erythema, edema, indurated papules, nodules with or without itching
| Erythema, swelling, swelling, induration and/or tenderness
|
| Reason
| Filler: type and amount of drug injected.
Subject: infection and biofilm. Injectionist: skin cleanliness and patient choice.
| Injectionist: incorrect insertion technique (overcorrection or too shallow insertion), massage not performed.
Subject: failed massage (L-polylactic acid).
| Filler: HA or bovine collagen
| Subject: Bacterial, viral, fungal, parasitic infections.
Injectionist: Wrong choice of patient, inadequate skin cleansing.
|
| Start
| Months or years after filler injection
| Early – up to two weeks after filler injection
| One month after filler injection with spontaneous resolution one year
| Immediate or later
|
. 1: granuloma differential diagnosis
In case of late complicationssuch as granuloma after fillers , you should ask the patient about:
time of onset of symptoms;- signs of inflammation – pain and redness;
- history of filler injections;
- type, volume and site of filler injection;
- presence of skin infections;
- presence of skin diseases;
- presence of immunodeficiency.
- Filler injections are contraindicated in active infections:
bacterial (caused by streptococci and staphylococci causing impetigo);
- parasitic (caused by mites such as demodex folliculorum
- , causative agents of rosacea); fungal;
- viral, such as herpes simplex virus or papillomavirus infection in the perioral region;
- Pityrosporum folliculitis.
Late allergic reactions to hyaluronic acid fillers Also
before contouring, therapy must be completed:
sinusitis;- periodontal diseases;
- ENT infections;
- flux.
- There is evidence that such infections can spread to the injected filler and trigger the formation of biofilms, which in turn are a
trigger of allergic reactions. Clinical and histological features of granulomas after contouring
Depending on histological properties, there are four types of granulomas after dermal fillers:
cystic (HA, bovine collagen);
- nodular lipogranulomas (silicone, polyacrylamide);
- sclerosing;
- mixed.
| Intralesional injections
| Systemic Therapy
| Surgical methods
|
| Bleomycin 5-fluorouracil | Antibiotics Prednisolone Allopurinol | Laser removal Opening and drainage Excision and grafting of fat tissue or flap |
2: Granuloma treatment methods
Clinically, granulomas appear as red indurated papules, nodules, or plaques that may appear months or years after
Differential diagnosis of granulomas after fillers It is sometimes difficult to differentiate between
granulomas
, nodules that form for other reasons, and abscesses. So, nodules can appear after contouring if the drug was injected using the wrong injection technique, in case of infection or the development of a late allergic reaction. Granulomas should be differentiated from nodules that form as a result of incorrect insertion technique, infection, or a late allergic reaction. Investigations that may help in making a diagnosis:
C-reactive protein;
number of white blood cells;
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
- microscopic examination and culture;
- hybridization in
- situ
- ; computed tomography; magnetic resonance imaging;
- biopsy and histological
skin examination. - Treatment of granulomas after dermal filler injections
- Treatment of nodules after filler injections is recommended based onthe cause of their appearance : most often these are infections, improper injection technique, less often – hypersensitivity to material and other product dependent factors.
If the problem occurs after
hyaluronic acid injection, resort to 6
intralesional hyaluronidase injections;extraction of the contents of the nodule with a 16G needle under negative pressure;
subsequent intralesional administration of 5 fluorouracil (5 FU);- laser lysis;
- surgical excision (last resort).
- Antibiotic therapy – the first step in the management of complications of presumably infectious origin. Intralesional steroid injections given prior to a course of antibiotics may exacerbate the problem.
| Late start |
| |
|
Other fillers |
| Hyaluronidase|
| Massage Lidocaine + Saline |
Intralesional steroids in small amounts |
Fractional laser (eyelids and lips)
Fig. 3: management of non-inflammatory nodules after the introduction of dermal fillers – palpable and visible nodules occurring 2-4 weeks after injections |
:
avoid overcorrecting;do not inject fillers too superficially;
Use medicines as directed;- Massage the treated area to spread the gel evenly.
- Intralesional injections
- Treatment of
that form without an inflammatory response can be done with:
intralesional steroids, then – 5FU;
surgical excision.- Such formations do not require urgent removal, the patient can be examined after 2 weeks.
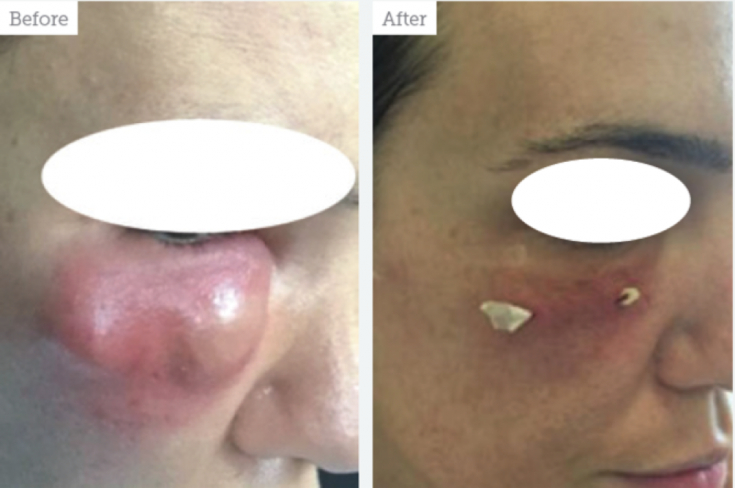 Before and after photos of a patient with a nodular inflammatory lesion that appeared a few weeks after HA injections into the nasolacrimal trough. Culture is positive for coagulase-negative staphylococcus aureus. Treatment: injections of hyaluronidase, ciprofloxacin 500 twice a day for 2 weeks, followed by surgical incision and drainage +
Before and after photos of a patient with a nodular inflammatory lesion that appeared a few weeks after HA injections into the nasolacrimal trough. Culture is positive for coagulase-negative staphylococcus aureus. Treatment: injections of hyaluronidase, ciprofloxacin 500 twice a day for 2 weeks, followed by surgical incision and drainage +
Fillers based on polymethylacrylate can be "melted" first; laser and then removed. In some cases, intralesional steroids are needed during the course of antibiotics. Steroid injections are done carefully because of the risk of local atrophy. High doses of triamcinolone (35-40mg) mixed with 2% lidocaine are recommended to be administered with a 0.5-1ml insulin syringe with a 30G intralesional needle. Best Injection Technique – introduction of small amounts from the periphery to the center.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics are given if painful nodules with signs of inflammation are present despite negative cultures. Therapy also includes other substances (bleomycin, colchicine, cyclosporine, immiquimod or etanercept) that are traditionally used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. Isoretinoin can be used alone or in combination with steroids.
Systemic TherapySystemic therapy is recommended if local treatment fails. High doses of steroids, such as oral prednisolone 30 mg/day (initial dose) and 60 mg/day (maintenance dose), are given to prevent recurrence of granulomas after fillers. The oral antibiotic minocycline alone or in combination with oral or intralesional steroids is effective in the treatment of inflammatory or silicone granulomas.
Read also:
Filler overcorrection: why it happens and how to fix it
Surgical removal Surgical excision involves the removal of the foreign body and biofilm. But this procedure carries the risk of complications such as scarring and deformities due to potential invasive growth of granulomas and irregular borders that make their complete removal impossible.
In addition, surgical excision of silicone-induced granulomas carries the risk of abscess or fistula formation. Localized sclerosing granulomas can be excised, followed by deformity correction with fat grafts or flaps. Efficacy is demonstrated by incision followed by drainage of a sterile abscess. Follow us on
!
Biofilm| Erythematous indurated area appearing anytime after filler injection
Granuloma | Sterile abscess, redness, indurated area after a few months – years after filler injections
|
|
If no result, switch to clindamycin 600 mg twice daily po + tetracycline 500 mg twice daily po. If improved, remove the nodule material with a 16G negative pressure needle. Consider: injections of 0.5 ml of 5FU monthly x 4; laser lysis, incision and irrigation of the cavity with antibiotics or surgical excision.
Intrafocal or systemic steroids: triamcinolone, betamethasone, or prednisolone. If no response, add 5 FU, bleomycin, colchicine, ciclosporin. | If no response, consider surgical excision with flap technique or fat grafting.
Fig. |
| Adapted from Aesthetics. |
YouTube
-channel







Add a comment