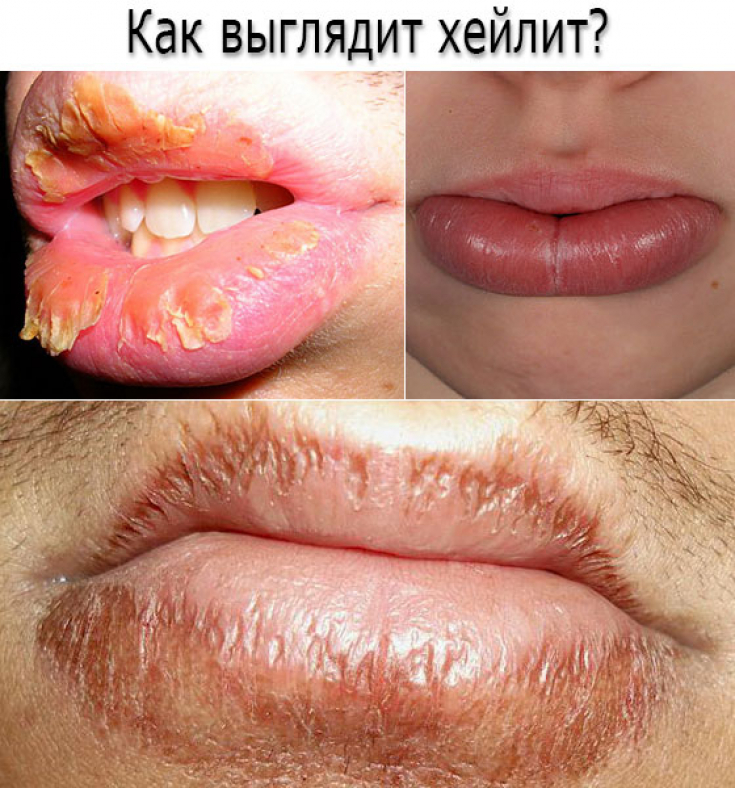
Chailitis – This is a group of diseases in which the inflammatory process is localized only on the lips: on the red border or mucous membrane of the lips. Lip damage is a manifestation of allergic, infectious or oncological diseases.
Heilites are divided into two groups – independent and symptomatic. The independent group includes meteorological, exfoliative, glandular, contact and actinic cheilitis.
Symptomatic cheilitis includes atopic, eczematous, candidal, plasma cell, macrocheilitis (Rossolimo-Rosenthal syndrome), cheilitis associated with ichthyosis and beriberi.
On estet-portal.com read about the types, symptoms and differential diagnosis of independent cheilitis.
Meteorological cheilitis: consequences of climatic factors
Meteorological cheilitis – an inflammatory disease of the lips, provoked by the physical influence of meteorological factors (dryness, wind, humidity, cold).
Most often, the entire lower lip is affected, which is covered with small peeling. There is also dryness of the lips and the occurrence of painful erosions when the scales are removed. The skin and mucous membranes of the lips are not changed.
Meteorological cheilitis must be differentiated from allergic, actinic, atopic cheilitis and dry form of exoflative cheilitis.
Read us also on Facebook
Dry and exudative cheilitis: features of the course of each form
Exfoliative cheilitis – a chronic disease in which only the red border of the lips is affected. There are dry and exudative forms of cheilitis.
The exudative form is characterized by the appearance of gray-yellow scales on the red border of the lips, accompanied by pain and burning, especially when the lips are closed. After removing the crusts, a moist, smooth, bright red surface of the lips is exposed, while there is no erosion.
In the dry form of exfoliative cheilitis, the scales look like a thin strip on the lip.
Often the dry form of cheilitis turns into exudative: with constant trauma to the surface of the lip.
The exudative form must be differentiated from actinic cheilitis, pemphigus vulgaris and other types of cheilitis.
You may also be interested in: Vulnerable mouth: diagnosis and treatment of exfoliative cheilitis
Glandular cheilitis: causes of development and characteristic features
Glandular cheilitis – this is a disease that develops as a result of hyperplasia of hyperfunction and often heterotopia of the salivary glands in the region of the red border of the lips and the transition zone.
Primary glandular cheilitis is associated by many authors with a congenital anomaly of the salivary glands: patients have enlarged orifices of the salivary glands in the form of red dots from which droplets of saliva are released
The development of secondary glandular cheilitis is due to the fact that the inflammatory infiltrate characteristic of the underlying disease irritates the salivary glands and leads to their hyperplasia and hyperfunction.
Serous and purulent forms of glandular cheilitis are also distinguished: the serous variant of the course is characterized by swelling of the lips and congestive hyperemia.
A viscous secret is released from the dilated ducts of the salivary ducts in the form of drops – dew symptom.
The purulent form often occurs with secondary infection through the excretory ducts of the gland. There is significant swelling, redness and soreness of the lips on palpation.
It is not difficult to make a differential diagnosis of glandular cheilitis with other types of lip lesions: the pathology has clear clinical signs.
Allergen reaction: what can cause allergic cheilitis
Contact allergic cheilitis – This is a pathology that occurs when the allergen comes into direct contact with the mucous membrane of the lips. Cheilitis develops as a result of sensitization of the red border of the lips, less often the mucous membrane to chemicals.
Allergens can be cosmetics, toothpastes and dentures, as well as certain foods (citrus fruits, chewing gums).
Clinically, cheilitis is manifested by burning and severe itching. At the site of contact with the allergen, there is a sharply limited erythema and slight peeling.
In some patients, the disease may be accompanied by the appearance of small vesicles, which quickly open and form weeping areas. There are also cracks and transverse furrows. This disease is differentiated from cheilitis and dry forms of exfoliative cheilitis.
Actinic cheilitis: what causes lip hypersensitivity
Actinic cheilitis is a chronic disease that occurs as a result of increased sensitivity of the red border of the lips to sunlight.
The dry form of cheilitis in the spring is manifested by pronounced hyperemia of the lips and is covered with small dry silver-white scales. In many patients with this form, areas of keratinization and sometimes vercose growths form on the lips. The exudative form of actinic cheilitis clinically resembles the manifestations of acute allergic contact dermatitis. With a long course, a persistent increase in the lips develops – acrochelia.







Add a comment