Chronic cystitis – it is a problem that deprives the normal life of many people. Pathology, which occurs with periodic exacerbations, is accompanied by extremely painful and unpleasant sensations. Moreover, sometimes patients constantly experience pathological symptoms.
In 1/3 of all cases, chronic cystitis is the result of incorrect or insufficient treatment of an acute process in the bladder.
Read on estet-prtal.com about the causes of chronic cystitis, methods for diagnosing the disease, as well as the difference in the clinical picture of this pathology in men and women.
- Methods of diagnosis of chronic cystitis
- What are the causes of chronic cystitis
- Clinical presentation of chronic cystitisa
Methods for diagnosing chronic cystitis
Diagnostic measures for chronic cystitis begin with a detailed history taking, including screening of information about the genitourinary area of the urological patient.
Laboratory diagnostics consists in the appointment of a general and bacteriological examination of urine, determining the sensitivity of the flora to antibiotics.
To verify the diagnosis, instrumental diagnostic methods are required. These include:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, bladder;
- x-ray with contrast agents;
- endoscopic examinations.
When diagnosing a disease in men, it is mandatory to examine all the reproductive organs: the urologist palpates the scrotum, conducts a digital examination of the prostate gland. This helps to link inflammation in the bladder with phimosis, prostatitis and/or orchiepididymitis.
Chronic cystitis is classified into 3 forms:
- latent;
- persistent (actually chronic);
- interstitial.
Latent cystitis is characterized by a complete absence of symptoms and changes in laboratory tests.
Persistent – undulating course, when the period of remission replaces the period of exacerbations.
Interstitial – this is the persistent presence of symptoms of pathology with a deterioration in the reserve functions of the bladder.
Even chronic cystitis is divided into primary and secondary chronic.
Cervical, diffuse and focal cystitis – This is a classification of the disease, taking into account the degree of prevalence of the pathological process. Among chronic infectious cystitis, nonspecific and specific are distinguished.
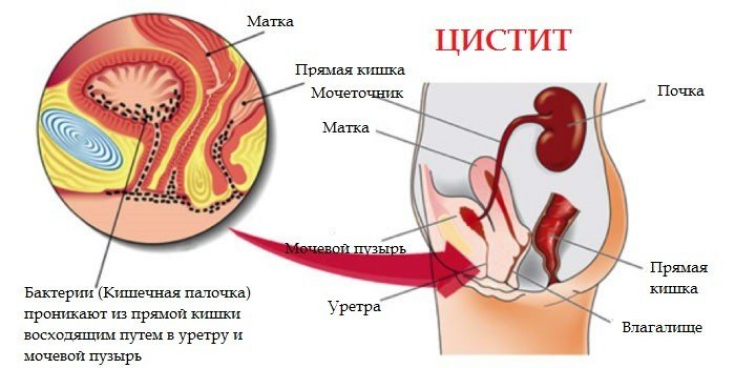
Not a step away from the toilet: treatment of overactive bladder For what reasons does chronic cystitis occur? When analyzing the incidence statistics, it is clear that chronic cystitis has a clear gender identity – women from 25 to 45 years old are sick more often than the male population. The anatomical features of the female body are to blame.
The short urethra in women serves as an ascending pathway for many types of pathogenic flora.The root causes of chronic cystitis are:
agents of bacterial nature: gram-negative enterobacteria, staphylococci; fungus of the genus Candida;
protozoa;
herpetic and adenovirus contamination.
-
Chronic cystitis
- can cause calculi
- of the genitourinary system, benign and malignant tumor processes
- , hormonal changes
Poor urine flow, frequent urinary retention, non-compliance with hygiene rules, nutritional errors, stress – this is an incomplete list of factors that can provoke a chronic form of cystitis.
Read the most interesting articles in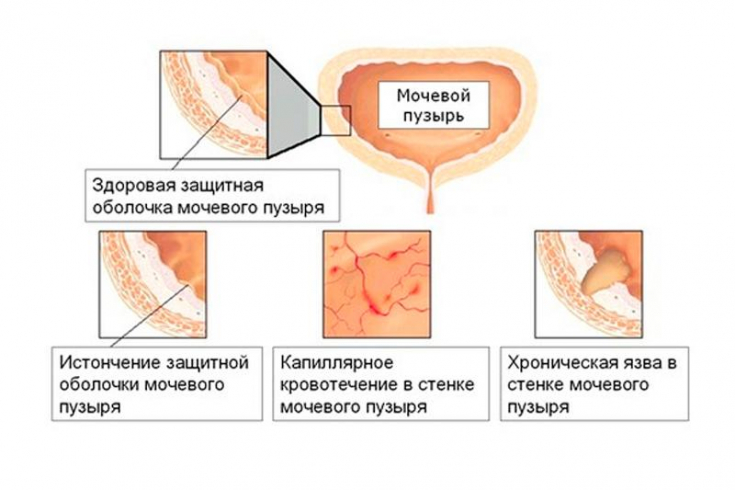
! Clinical presentation of chronic cystitis The symptoms of the disease and the severity of the main symptoms depend on the form of chronic cystitis. The clinical picture of the disease varies somewhat in men and women.
Exacerbations of the disease manifest themselves as acute or subacute inflammation: urination becomes more frequent, accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and along the urethra.Then urine may become cloudy and blood is recorded in it. In severe inflammatory processes, there is an increase in temperature and the appearance of signs of intoxication: the general state of health worsens, nausea and sometimes vomiting appear.
Efficacy of fluoroquinolones in the treatment of urinary tract infections
Features of chronic cystitis in women
In women with chronic cystitis, pain often radiates to the lower back, and the urge to urinate is difficult to control. Signs of skin irritation quickly join, pathological vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor appears. During sexual intercourse, a woman experiences unpleasant, and even painful sensations. In chronic cystitis, women very often experience exacerbations. Therefore, any hypothermia can provoke a recurrence of symptoms of chronic cystitis: pain when urinating, abdominal discomfort and dyspareunia.
Features of chronic cystitis in men
 In the period between urination, urological patients feel diffuse pain in the phallus, in the groin and pubis.
In the period between urination, urological patients feel diffuse pain in the phallus, in the groin and pubis.







Add a comment