Urticaria is one of the most common dermatological diseases, which is characterized by rashes on the skin with blisters, accompanied by itching of varying intensity. In this case, the skin reaction is usually associated with edema. Since histamine, which is released from mast cells, is the basic mediator of the pathogenesis of urticaria, H1-antihistamines (AHP) of the 2nd generation are considered the basis of modern therapy.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com what are the current approaches to the treatment of allergic urticaria.
- reasons for the ineffectiveness of antihistamines in the treatment of urticaria
- data on the use of bilastine in the management of urticaria
- bilastine efficacy on urticaria model
Reason for the ineffectiveness of antihistamines in the treatment of urticaria
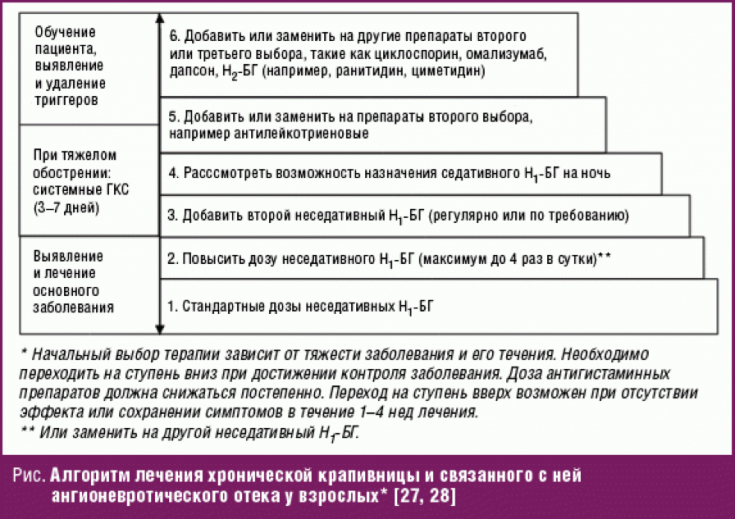
Standard doses of antihistagmine drugs (AHP) are not always sufficient to completely eliminate the symptoms of urticaria.
Subscribe to our page on Facebook!
This is due to the fact that histamine can reach very high concentrations in the skin, due to its poor ability to diffuse in the dermis. For such situations, EAACI / GA2LEN / EDF / WAO recommendations advise to increase the dose of AGP by 2-4 times. At the same time, even with a fourfold increase in the standard dose, control of skin symptoms can be achieved in 78% of patients.
Atopic dermatitis: a studied disease with a mysterious history
Furthermore, although 2nd generation antihistamines, unlike 1st generation antihistamines, only cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in small concentrations, most of them can only be called "minimal sedative", but not "non-sedating". For example, studies of subjective patient response to treatment have shown that 2nd generation antihistamines in chronic spontaneous urticaria (COD) have sedative effects in more than 20% of patients.
Thus, when prescribing antihistamines for the treatment of urticaria, it is necessary to take into account the presence of two fundamentally important characteristics in them.
Firstly, it is the optimal safety profile, namely, minimal sedation; secondly, it is clinical efficacy, i.e. rapid onset and duration of action.
Data on the use of bilastine in the management of urticaria
Bilastin, a methylpropanoic acid, is a novel antihistamine indicated for the treatment of allergic rhinoconjunctivitis and urticaria. Like other antihistamines, bilastine is an inverse agonist. Preclinical studies have shown that the drug is highly selective for histamine H1 receptors, with little to no affinity for other receptors, including other histamine receptor subtypes, muscarinic and serotonin receptors.
Bilastine is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, followed by an exponential decrease in plasma levels over the next 48 hours. After a single dose of 20 mg to healthy volunteers, bilastine reaches a mean peak plasma concentration of 220 ng/mL in 1.3 hours; the volume of distribution is 1.29 l / kg, and the half-life is 14.5 hours; plasma protein binding reaches 84-90%.
Emollients and food allergies: what's the connection?
The results of preclinical in vivo studies were found to be comparable to those obtained in previous in vitro experiments. These studies confirmed the fact that in preclinical models of histamine-induced urticaria, bilastine demonstrated antihistamine and antiallergic properties with activity similar to that of cetirizine and exceeds that of fexofenadine.
Efficacy of bilastine in a model of urticaria
Perhaps the most relevant model for evaluating the potential effect of H1 antihistamines in urticaria is wheal and flare response ─ W & F. To date, 4 such studies are known. The first compared the onset of action after a single dose of 20, 40 and 80 mg of bilastine and 25 mg of hydroxyzine in 20 healthy volunteers.
What elements of the rash may be accompanied by symptoms of vasculitis
Answer W & F was induced by intradermal histamine injection. The results showed that bilastine reached its maximum activity within 1 hour after administration of 40 and 80 mg and within 2 hours after administration of 20 mgcompared to 4 hours with hydroxyzine. The drugs were continued daily for 7 days, after which the test was repeated. A re-study was completed with similar results.
More useful information on our







Add a comment