Ectopic pregnancy is a dangerous condition that has recently become increasingly common in gynecological practice. About 2% of all pregnancies are just such an ectopic pregnancy. The high prevalence of infectious diseases is one of the factors that can lead to signs of ectopic pregnancy. Unfortunately, despite the widespread information about ways to protect against diseases that tend to be sexually transmitted, the number of such diagnoses and established ectopic pregnancy does not decrease. In this regard, practicing gynecologists should be aware of the signs, basic methods of diagnosis and treatment of ectopic pregnancy. If the surgical treatment of an ectopic pregnancy is not carried out in time,
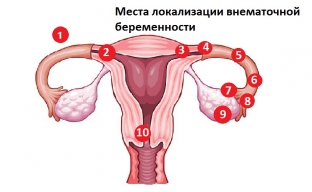
Classification of ectopic pregnancy: localization and clinical courseAn ectopic or ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy in which a fertilized egg is mounted and develops in a non-physiological place. In normal pregnancy, fertilization of the egg occurs in the cavity of the fallopian tube, then the egg, due to the peristalsis of the fallopian tube, moves into the uterine cavity and is implanted in the endometrium. Factors that disrupt the normal exit of a fertilized egg from the fallopian tube into the uterine cavity are the causes of the development of an ectopic pregnancy. In 98% of cases, an ectopic pregnancy is localized in the cavity of the fallopian tube. Ovarian, cervical and even abdominal pregnancy is much less common. According to the clinical course, two forms of ectopic pregnancy are distinguished: progressive ectopic pregnancy and tubal abortion.
Infectious processes leading to the formation of adhesions in the fallopian tubes are the main cause of ectopic pregnancy. Gonorrheal, tuberculosis and chlamydial infection most often lead to the development of adhesions. Endometriosis is also a disease that can develop adhesions and disrupt the patency of the fallopian tubes. Tumors and neoplasms of the internal genital organs are mechanical factors that disrupt the patency of the fallopian tubes and contribute to the occurrence of an ectopic pregnancy. The hormonal background of a woman affects the peristaltic activity of the fallopian tubes, and its violations are also factors leading to the development of an ectopic pregnancy. Stress and smoking can affect the peristalsis of the fallopian tubes, causing them to spasm,
 Clinical signs of progressive ectopic pregnancy
Clinical signs of progressive ectopic pregnancy
Progressive early ectopic pregnancy follows the pattern of a normal pregnancy and may not have any symptoms. An early sign of an ectopic pregnancy is a missed period. With an ectopic pregnancy, against the background of a delay in menstrual bleeding, pain syndrome appears. The pain is quite intense, localized in the lower abdomen and is aching, paroxysmal in nature. The development of an ectopic pregnancy can be masked by bleeding that occurs at the time when menstruation should be, as a result of rejection of the decidua. An enlarged soft uterus is determined by palpation, but its size does not correspond to the term of the expected pregnancy. At the same time, in the area of the appendages, on the side where an ectopic pregnancy develops,
Diagnostic signs of progressive ectopic pregnancyDiagnosis of progressive ectopic pregnancy is based on laboratory and instrumental research methods. In the blood and urine of the patient, chorionic gonadotropin, the hormone of pregnancy, is determined. In the urine, chorionic gonadotropin is determined using special test systems, in the blood - mainly by the enzyme immunoassay method. The main method for diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy is ultrasound. There are the following ultrasound signs of an ectopic pregnancy:
absence of the amniotic sac against the background of hyperplasia of the uterine mucosa;
- free fluid in the recto-uterine space;
- the presence of a fetal bladder outside the uterine cavity.
- Histological examination of the endometrium helps in the diagnosis and especially in the differential diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy, since against the background of decidual transformations of the uterine mucosa there will be no chorionic villi, which speaks in favor of an ectopic pregnancy.
An ectopic pregnancy that has terminated may follow the type of tubal abortion, which is more common, or rupture of the fallopian tube. In such a patient, there is a clinic of an acute abdomen, which causes difficulties in the differential diagnosis of acute conditions of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis. The main signs of a tubal abortion are acute paroxysmal pain that can radiate to the rectum, shoulder, shoulder blade, and collarbone. The pain may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, impaired defecation, dizziness and general weakness. Scanty dark red blood clots are secreted from the genital tract, which do not stop on the background of drug therapy. Palpation is determined by a dense formation in the fallopian tube on the side of the lesion, with clear contours.
The clinical picture of a fallopian tube rupture is quite typical. The patient spontaneously has an acute attack of pain in the lower abdomen with irradiation to the rectum, shoulder or shoulder blade. Cold sweat, pallor appears, loss of consciousness occurs and blood pressure decreases, which is associated with blood loss. Gynecological examination should be carried out very carefully so as not to provoke a deterioration in the patient's condition. On the side of the lesion, a tumor-like formation without clear contours, sharply painful, is palpated. After an attack of pain, scanty bloody discharge from the genital tract appears.
Diagnostic signs of aborted ectopic pregnancy
The main method for diagnosing an interrupted ectopic pregnancy is the puncture of the abdominal cavity through the posterior fornix of the vagina. The blood obtained by puncture is dark in color with small clots, and, characteristically, does not clot. A characteristic feature is the “areola” symptom: a dark homogeneous spot is observed around the blood spot. There are also some palpatory signs of an interrupted ectopic pregnancy:
Solovyov's symptom: on bimanual examination, the uterus is "floating", slipping out of the hands;
- Promtov's symptom: a sharp pain that occurs when trying to move the cervix to the womb;
- Proust symptom: sharp pain when jerking a finger in the posterior fornix of the vagina.
- Treatment of ectopic pregnancy: surgical methods






Add a comment