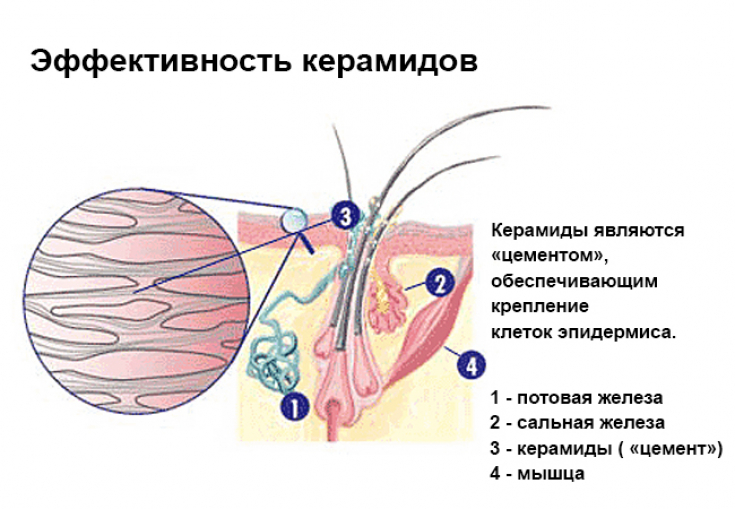
Imagine our skin cells − these are bricks. What does it take to transform individual bricks into a solid structure that will perform its functions? Of course − cement. Such a natural "cement" for our skin are ceramides.
Ceramides or ceramides − it is a component of the skin barrier − lipids (i.e. fatty, waxy molecules) that help the skin retain moisture and function properly. They are − a natural body moisturizer and a barrier that prevents dehydration.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com about the function and classification of ceramides in cosmetology,as well as their effect on the skin.
- Classification of ceramides in cosmetology
- Ceramides in skin care products
- The effect of ceramides on the skin
Classification of ceramides in cosmetology
In addition to providing moisture and elasticity to the skin, ceramides, or as they are also called ceramides, play another important role.
Follow us on Instagram!
Ceramides protect against the negative effects of external factors − bad ecology, pollution, dry air, temperature changes, aggressive detergents and the like. After all, one of the main functions of our skin − protect us from negative environmental factors.
Another function of ceramides is signaling − they determine the time for the death of old cells and the formation of new ones.
Ceramides perform the following main functions for skin and hair:
1. moisture retention;
2. improvement of skin elasticity and structure of the stratum corneum;
3. improvement of regeneration processes;
4. protection against negative external factors;
5. acting as signaling molecules that determine "lifespan" cells.
A revolution in the fight against wrinkles and skin aging
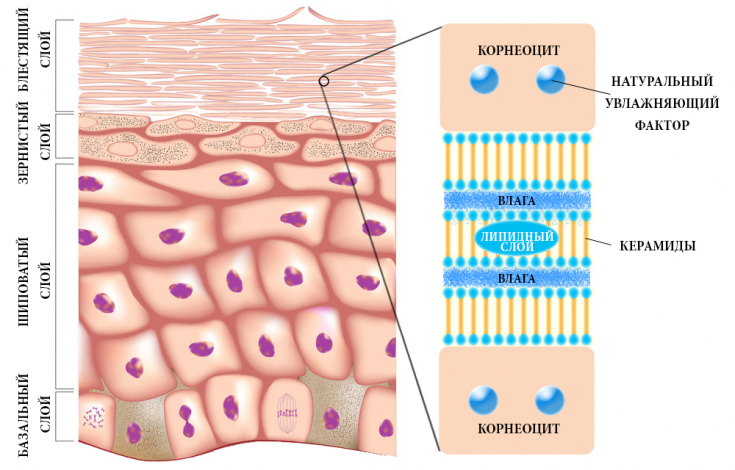
There are 9 types of ceramides, which are usually denoted by numbers from 1 to 9:
- Ceramide 1 / Ceramide EOS;
- Ceramide 2 / Cermamide NS / N-stearoyl sphinganine;
- Ceramide 3 / Ceramide NP / N-stearoyl phytosphingosine (most used in cosmetology);
- Ceramide 4 / Ceramide EOH (also common in cosmetic formulas);
- Ceramide 5 / Ceramide AS;
- Ceramide 6 / Ceramide AP / α-hydroxy-N-stearoylphytosphingosine;
- Ceramide 6 II / Caproyl sphingosine;
- Ceramide 7 / Ceramide AH;
- Ceramide 8 / Ceramide NH;
- Ceramide 9 / Ceramide EOP.
Ceramides, which are used to make skin and hair products, can be obtained from plants, but the most common are synthetically synthesized. So far, there is no study that would prove the greater effectiveness or safety of one of the species. The advantage of synthetic − in the ability to make them "more appropriate" for skin cells.
Ceramides in skincare
There are also two specific "predecessors" ceramides to look out for are phytosphingosine/Phytosphingosine (eg Caprooyl Phytosphingosine) and Sphingosines (eg Hydroxypalmitoyl Sphinganine, or Caproyl Sphingosine). Instead of simply restoring the lack of ceramides, these components help the skin cells synthesize them on their own.
Injection technologies in cosmetology
It is possible to increase the amount of ceramides / ceramides in the body with the help of food. Ceramides can be found in many nutritional sources, but predominantly in plants. Phytoceramides − in the composition of beets, wheat, rice. Eggs and soy are rich in sphingolipids, which help the skin replenish its ceramides on its own. Of course, internal use will not provide an instant wow effect, but together with the use of products with ceramides, it will bring you closer to the desired result.
Ceramides for cosmetic products are obtained in one of three ways:
1. enzymes "manufactured" ceramides from many similar molecules;
2. using enzymes, sphingolipids are broken down into ceramides;
3. with sphingomyelin (a type of sphingolipids), by hydrolysis (under the action of water) or enzymatically.
Influence of ceramides on the skin
How do you know if your skin lacks ceramides? Everything is very simple − the skin itself will give signals. There will be a feeling of dryness, peeling, redness, irritation, allergic manifestations, and even eczema. Manifestations of premature aging and a decrease in local immunity will be noticeable. Cosmetics and hair products with ceramides in the composition will be useful for everyone, because it is always better to prevent a problem than to overcome it. However, there are cases when products with ceramides are critically needed.
The use of ceramides is especially recommended for: dry, irritated skin with redness and flaking; age mature skin; problem skin with manifestations of acne, sensitive skin; skin prone to allergic reactions; for recovery after cosmetic procedures; for skin care around the eyes; for the care of damaged hair, after dyeing and chemical procedures, to restore shine and "reconstruction" hair; as part of UV protection products.
Toxin at gunpoint: the mechanism of action of botulinum toxin
The human body is able to independently generate ceramides in the stratum corneum of the epidermis. However, under the influence of certain factors, this ability deteriorates. Therefore, it is so important to replenish the supply of these important components of the skin.
The new generation of UV filters in the field of aesthetic medicine







Add a comment