Frostbite is not a distant past at all, like a frightening shot from an old movie about polar explorers. Experts note that mild degrees of frostbite of the nose, ears or cheeks, fingers and toes can be obtained even while standing at a bus stop waiting for transport. This is especially true if severe frost is accompanied by damp strong winds. The symptoms of frostbite are quite distinct, and if the problem is recognized in a timely manner and adequately provided with assistance, the skin will practically not suffer. But running this problem and not paying attention to the loss of skin sensitivity is not worth it – this is fraught with unpleasant complications.
Why frostbite happens and what happens to the skin
Frostbite is a reaction of the skin to the action of low temperature, when a spasm of blood vessels occurs from the cold and the blood supply to an organ or, for example, to a limb is cut off. Most often, noses, ears and cheeks suffer from frostbite, further in the list of suffering areas of the body – feet and palms.
It is difficult to determine the temperature at which frostbite necessarily occurs, since many factors can influence this process: for example, in children, frostbite occurs faster and at relatively high temperatures. Frostbite will occur more quickly with strong winds or high humidity. An important role is played by the state of the person – The following factors can provoke frostbite:
- weakening of the body's defenses,
- old age,
- insufficient nutrition,
- presence of cardiovascular pathologies,
- clothing not appropriate for the weather.
These factors also affect the degree of frostbite, which is determined by the area and depth of the skin lesion:
- I degree – the blood flow in the capillaries is disturbed, the skin does not die, there are no irreparable pathologies;
- II degree - the surface layer of the skin dies, but is able to quickly recover due to the preserved germ layer;
- III degree – all layers of the skin perish, healing is difficult and fraught with the formation of scars, the death of subcutaneous fatty tissue is possible;
- IV degree – characterized by the death of all layers of the skin and underlying tissues, up to damage to the bones.
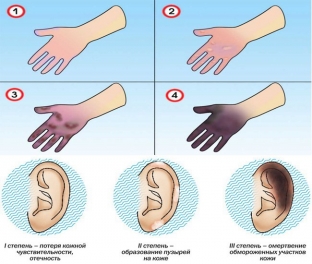
Frostbite is characterized by the fact that its signs appear immediately, in the very first hours of skin damage by cold, which allows you to immediately take action without waiting for the development of extreme stages of the lesion.
What are the signs of frostbite of the skin
Due to the violation of blood flow in the capillaries damaged by cold, first of all, the sensitivity of the skin is disturbed. She becomes pale to marbling. Then a red spot appears on it at the site of the cold lesion, which over time can become bluish-purple. The skin swells and feels tighter to the touch. When moving from a cold to a warm room, the patient complains of pain in the affected area, itching and burning sensation.
Depending on the depth of the lesion, small blisters appear on the frostbitten area of the skin, which coalesce and burst with a yellowish liquid flowing out. The sensitivity of the skin is practically absent, so that the nail plates are painlessly removed on the affected fingers.
In the extreme stages of frostbite, the bandages are soaked through with liquid flowing from the blisters, the epidermis peels off like dark tissue paper and exposes a pale, thinned dermis. Bone damage develops, the radiograph shows a complete absence of a capillary network. The fourth stage is characterized by the dark color of the dermis and the mummification of the frostbitten area.
What measures are taken for frostbite of the skin
It is impossible to immediately intensively warm the frostbitten area, because the heat intensifies metabolic processes and expands the area of the lesion. A thermal bandage is being used.
The treatment of frostbite is to restore blood flow in the affected area as much as possible. For this, drugs are used that dilate blood vessels and increase energy production in the body. The criterion for the success of therapy is the restoration of sensitivity in the affected area, the disappearance of heat and burning.
In severe lesions, obligatory excision of non-viable tissues is performed, antibiotic therapy is prescribed against infectious complications, if necessary – corticosteroid therapy. Much attention should be paid to the full nutrition of the patient, vitamin therapy, physiotherapy procedures.







Add a comment