Seborrheic dermatitis – This is a chronic inflammatory skin disease with a relapsing course associated with a qualitative and quantitative change in sebum. Most often develops in areas rich in sebaceous glands – on the face, chest, interscapular region and scalp.

Ekaterina Alekseevna Bardova candidate of medical sciences, dermatovenereologist,
Seborrheic dermatitis: are hormones or a fungus to blame
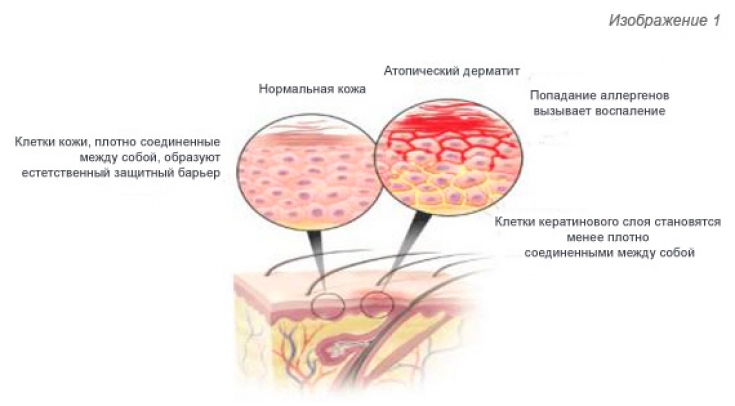
The etiology and pathogenesis of the disease are still unknown. Due to hereditary predisposition, hormonal disorders, neurohumoral, metabolic and immune failures in the body, a qualitative and quantitative change in sebum occurs, as well as a violation of the barrier function of the skin, which leads to the activation of conditionally pathogenic flora and the development of rashes characteristic of this pathology on the skin. .
At present, an important role in the etiology of seborrheic dermatitis is assigned to the lipophilic yeast-like fungus Pityrosporum ovale (Malassezia furfur), which is an opportunistic pathogen living in the stratum corneum of the epidermis and a constant component of the microflora of healthy skin in most people.
The microflora of the scalp normally contains 30-50% P. ovale, dandruff consists of 75% of these microorganisms, and in moderate and severe forms of seborrheic dermatitis, the concentration of P. ovale reaches 90%. Some authors are inclined to believe that seborrheic dermatitis – this is a hypersensitivity reaction to this type of fungus.
How to get rid of seborrheic dermatitis: effective treatments? Causes of seborrheic dermatitis
Of great importance in the development of seborrheic dermatitis are diseases of internal organs, primarily diseases of the endocrine system. The sebaceous glands are simple alveolar glands with a holocrine type of secretion. They begin to function even in the prenatal period. In infants, they are already fully formed and developed.
Seborrheic dermatitis first appears in the neonatal period and can be seen as a reaction to maternal hormone stimulation. It resolves on its own and does not require treatment.
In the pubertal period, the sebaceous glands increase in size, their secretory activity increases, reaching a maximum by 18 & ndash; 25 years. It is during this period that the next peak in the development of the disease is observed.
The fact that men suffer from seborrheic dermatitis more often confirms the assumption that the activity of the sebaceous glands is under the control of androgens. Sebum production in men is stimulated by testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone and androstenedione. In women, sebum production is affected by even slight increases in circulating androgen levels.
It is known that in patients with diseases of the central and autonomic nervous system, as well as on the background of emotional stress, seborrheic dermatitis develops more often, is more severe and difficult to treat.
Some authors among the provoking factors of seborrheic dermatitis pay special attention to the state of the gastrointestinal tract (unbalanced nutrition, decreased motility, changes in the enzymatic activity of the stomach and intestines), the presence of foci of chronic infection and the negative impact of the external environment (the use of alkaline detergents).
There are three clinical forms of seborrheic dermatitis:
1. Dry;
The dry formis characterized by the appearance of small floury white scales on the skin of the scalp, or peeling can take on a large-lamellar character, without signs of visible inflammation. Patients often have thinning and thinning hair. Subjectively, patients complain of a burning sensation and itching. 2. Oily;
The fatty formis characterized by the appearance of large-lamellar yellowish scales against the background of excessive sebum secretion. Hair with this form is greasy, shiny, sticks together in strands. 3. Mixed;
The mixed formis characterized by the appearance of inflamed spots of a pinkish–yellowish color with clear boundaries and peeling.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face: methods of treatment of the disease?
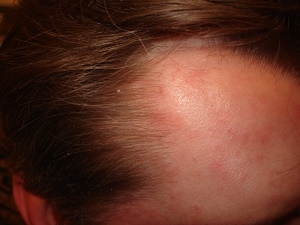
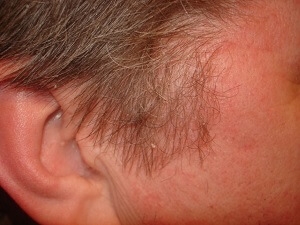
Contact dermatitis: inflammation from irritation
Contact dermatitis – it is an inflammatory disease caused by direct skin contact with an irritating agent.
Contact dermatitis can be caused by both immune and non-immune mechanisms.
In the first case, we are talking about allergic contact dermatitis, and in the second – about simple contact dermatitis. The clinical picture is usually represented by slight hyperemia and peeling.
Simple contact dermatitis is caused by irritants. In the practice of a dermatologist, it is not uncommon for cases when contact dermatitis of the scalp can develop after the use of certain shampoos or products used to treat head lice, low-quality hair dyes and hair care products.
Cracks in the skin between the fingers: is it contact dermatitis? Psoriasis. Characteristic symptoms
Psoriasis – chronic dermatosis of a multifactorial nature, characterized by a violation of keratinization and hyperproliferation of epidermal cells, followed by the development of inflammation in the dermis.
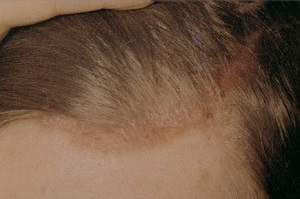 Psoriasis often develops on the scalp, and can exist in isolation for a long time. Often the first manifestation of it is profuse peeling without pronounced inflammatory changes on the skin.
Psoriasis often develops on the scalp, and can exist in isolation for a long time. Often the first manifestation of it is profuse peeling without pronounced inflammatory changes on the skin.
In the differential diagnosis with seborrheic dermatitis, if there is no family history, the absence of hair thinning or baldness, despite many years of flaking of the scalp, and the appearance of plaque elements that have a number of features compared to rashes located on other parts of the body, help.
 So, along the border of the hair, they are less clear than the outlines of the foci on the body, and are covered with grayish-yellow scales that fit more tightly, and therefore the psoriatic triad does not always have a classic appearance, and instead of pinpoint bleeding, weeping bleeding can form surface.
So, along the border of the hair, they are less clear than the outlines of the foci on the body, and are covered with grayish-yellow scales that fit more tightly, and therefore the psoriatic triad does not always have a classic appearance, and instead of pinpoint bleeding, weeping bleeding can form surface.
Psoriasis news: What is the immune system and its effects? The characteristic signs of psoriasis of the scalp, on the basis of which it can be differentiated from seborrheic eczema, is a skin lesion on the border with the scalp - the so-called "psoriatic crown", the absence of hair loss, less tendency to follicular arrangement of elements, greater dryness scales, rare occurrence of pityriasis peeling.
Some authors distinguish a special form - sebo-psoriasis, which is considered as a transitional form between psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis or as a combination of two pathologies.
Peculiar psoriatic rashes on other seborrheic areas of the skin: on the face and in the sternum, especially in persons prone to seborrhea. Sebo-psoriasis is characterized by the presence of plaques with difficult to detach scales, but they have a more oily texture and yellowish coloration.
In addition, sebo-psoriasis is characterized by a greater tendency to exudate, not as clear-cut boundaries as with ordinary plaque forms.
In the differential diagnosis of psoriatic rashes from seborrheic eczema, one should take into account the color of the rashes (more yellow in seborrheic eczema), the vagueness of the foci, weeping, especially after scratching, more frequent itching, and the absence of the psoriatic triad. Family history should also be taken into account.
Three main modern methods of treating psoriasis? Seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis are chronic dermatoses therefore, along with systemic treatment, it is necessary to use topical preparations.
Source estet-portal.com







Add a comment