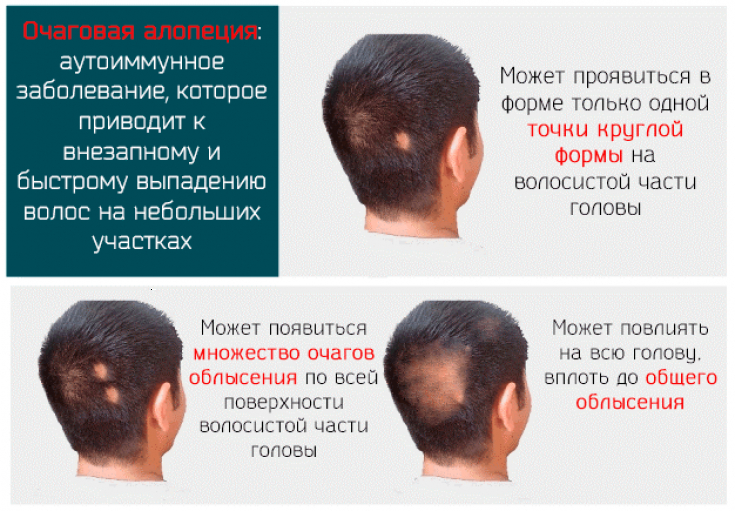
Alopecia areata (OA) − chronic dermatosis, which is characterized by pathological non-scarring hair loss as a result of exposure to the hair follicle of various factors.
This is manifested by the formation of foci with absence of hair on the scalp, in the area of the beard, eyebrows, eyelashes and torso.
Read the article on estet-portal.com what causes are distinguished in development alopecia areata, as well as a practical case combined treatment disease.
- Prevalence and causes of alopecia areata
- The role of the immune system in the development of alopecia areata
- Clinical investigation of the causes of alopecia areata
- Alopecia areata treatment regimen and outcomes
Prevalence and causes of alopecia areata
Alopecia areata − a common hair disease in both children and adults. Among patients who first applied to a doctor−dermatologist with dermatoses alopecia areata occurs from 2 to 5% of cases, the frequency of the disease in the population is 0.2%.
When it's scary to look at a comb: the main causes of hair loss
Today, there are between 2.2 and 4.5 million people who suffer from alopecia areata.
Follow us on Instagram!
The role of the following disorders has been established in the pathogenesis of alopecia areata
|
|

Recent data indicate an increase in the incidence of alopecia areata, while there is a trend towards an increase in the frequency of torpid forms of the disease, resistant
to therapy.The role of the immune system in the development of alopecia areata
A special role in the development of alopecia areata belongs immune disorders
.The involvement of the immune system
in the development of alopecia areata confirms:- transformation of the immune response in patients with various forms of alopecia;
- active migration of cytotoxic lymphocytes to the lesion site;
- development of perivascular and perifollicular infiltration;
- IgE deposits in the papillary dermis.
It is believed that alopecia areata can be considered as a tissue-specific autoimmune disease
mediated by autoactivated T-lymphocytes.An important role in the development of alopecia is played by functional activity of lymphocytes
, which form an infiltrate around the hair follicle.At the same time, a high level of IL - 1, IL – 10; low - FNS - α, IFN - γ.
Hair loss in alopecia areata − the result of both the effect on the hair follicles of activated T - lymphocytes, and the indirect influence of various cytokines.
Clinical study of the causes of alopecia areata
As a result of the
research on the causesof alopecia areata, 10 patients aged 20 to 48 years were examined and treated. A connection between the occurrence of
alopecia areatawith acute or chronic psycho-emotional stress − in 3 patients with acute viral or bacterial infections − in 5 patients, in 2 − cause unknown. All patients with alopecia areata had clinical manifestations
progressive and stationary stages, which were characterized by the presence of single or numerous isolated, rounded outlines of baldness foci on the head.
The area of hair loss on the head was up to 25%, the duration of the disease − 2 ? 4 months. The role of topical drugs in the treatment of alopecia areata and androgenetic alopecia
Concomitant dystrophic lesion
of the nail platewas detected in 7 patients with alopecia areata. The patients underwent a complex
clinical and laboratory examination: blood for RW, toxoplasmosis; consultations of a surgeon, dentist, ENT, neuropathologist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist. 6 patients were diagnosed with concomitant pathology of digestive organs (gastritis, duodenitis
Alopecia areata treatment regimen and results After the final diagnosis was established,
complex treatment- , which included the following drugs:
- Deacura (biotin)
- - 1 tab. 1 r / d for 1 month; Askotsin
- - 1 tab. 1 r / d for 1.5 months; Calcemin
- - 1 tab. 2 r / d for 1 month; Epadol
Local - ointment
Protopic (tacrolimus) 0.1%according to the scheme 1 month 1 time per day in the afternoon, from 2 to 6 months - 2 times a week. Alopecia areata: fractional laser therapy and topical corticosteroids
After the complex treatment, after 4-6 months significant improvement was noted: dense overgrowth of more than 50% of the area of hairless areas and foci of baldness with a large amount of vellus, pigmented and depigmented hair,
no new focibaldness was observed.
The area of loose hair and dystrophic changes in the nails after the course of treatment are absent. There were no recurrences of the process. The proposed
complex methodof treatment of patients with alopecia areata can be administered to patients both in inpatient and outpatient settings. Besides efficiency, the advantages of the proposed method are
the absence of intolerance and complications.Mechanism of activation of hair follicle stem cells in case of damage
More useful and interesting information on our channel on YouTube
!







Add a comment