Melasma – violation of skin pigmentation in the form of yellow or brown spots with uneven boundaries, which are localized mainly on sun-exposed areas of the face.
This type of hyperpigmentation is often difficult to treat. In addition to other methods of treating pigmented areas of the skin, there are many topical products, the main purpose of which is to control or eliminate pigment spots.
This estet-portal.com article represents the results of Dr. Leonardo Marini who used a topical cream based on 5% cysteamine for the treatment of melasma.
Disadvantages of topical hydroquinone preparations for the treatment of melasma
The main disadvantages of the previously proposed natural and synthetic formulations for the treatment of hyperpigmentation are the low safety or efficacy profiles of topical preparations.
More interesting articles in Instagram!
Hydroquinone has been considered the gold standard treatment for melasma in the US since the 1960s. In 1975, the Kligman formula (KF – hydroquinone, retinoic acid and dexamethasone) was introduced, which demonstrated the maximum effectiveness in the treatment of melasma.
However, hydroquinone is toxic and with long-term use is associated with the risk of a number of side effects, like KF (skin hypotrophy, ochronosis, irritation), therefore the duration of such therapy is limited.
Cysteamine, unlike hydroquinone, is a non-toxic, non-mutagenic and non-carcinogenic depigmentant.
Cysteamine, introduced in 1966 by Chavin et al., showed more powerful depigmenting properties than hydroquinone, but due to the rapid oxidation of the substance, an unpleasant odor appeared. After solving this problem, cysteamine entered the market for depigmenting agents in a 5% concentration.
Cysteamine in the treatment of melasma: case reports
Patient, 34 years old, with progressive melasma, most pronounced on the forehead and in the area between the eyebrows, above the upper lip and on the cheeks. Minimal spontaneous improvement in winter was replaced by significant deterioration during spring and summer, despite proper use of SPF 50+ sunscreen.
The debut of melasma was preceded by a year of taking oral contraceptives. The patient underwent two six-month cycles of modified KF therapy, which resulted in a minimal depigmenting effect with a high degree of skin irritation.
Female patient, 54 years old, with melasma that persists for six years and is localized mainly in the lateral thirds of the frontal region. The situation worsens after intense ultraviolet exposure. The patient underwent three six-month courses of modified KF therapy, the effectiveness of which in the context of pigmentation control decreased over time.
Actives of the brightening cream and their effectiveness against pigmentation
Both patients reported a lack of adequate photoprotection and intense skin exposure to ultraviolet radiation at an early age. There have been no menstrual irregularities in the last five years.
Topical treatment of melasma with cysteamine-based cream
To enhance and optimize the transepidermal penetration of topical substances, the skin should be properly prepared.
The protocol includes:
1. 4 sessions of microdermabrasion (MegaPeel — Dermamed Solutions, USA) with an interval of 14 days. After the first and last session of microdermabrasion – mask-film based on 5% hydroquinone (LEM— Laboratorio Ecoceutico Magistrale, Italy), exposure time – 20 minutes.
2. Cyspera Intensive Pigment Corrector Cream based on 5% cysteamine (Cyspera – Scientis, Switzerland). Skin Contact Time – 15 minutes. During the first four weeks – daily use in the evening, then – twice a week.
3. Morning: soft moisturizing of the skin with thermal water (La Roche Posay Laboratoires, France); gel based on 15% azelaic acid; then – serum based on Hyalu B5 HA (La Roche Posay Laboratoires, France) and soothing/moisturizing cream (Cream for Intolerant Skin – Avene Laboratoires, France).
4. Daily throughout the course of treatment – sunscreen Fotoprotector 100+ Spot-prevent ISDN (Spain).
Melasma treatment: effectiveness of mono- and combination therapies
Results of treatment of melasma with cysteamine-based cream
During the clinical examination and analysis of before and after photos, a noticeable, almost uniform depigmentation of melasma was observed in the first case and a significant decrease in the severity of localized hyperpigmentation in the second patient.
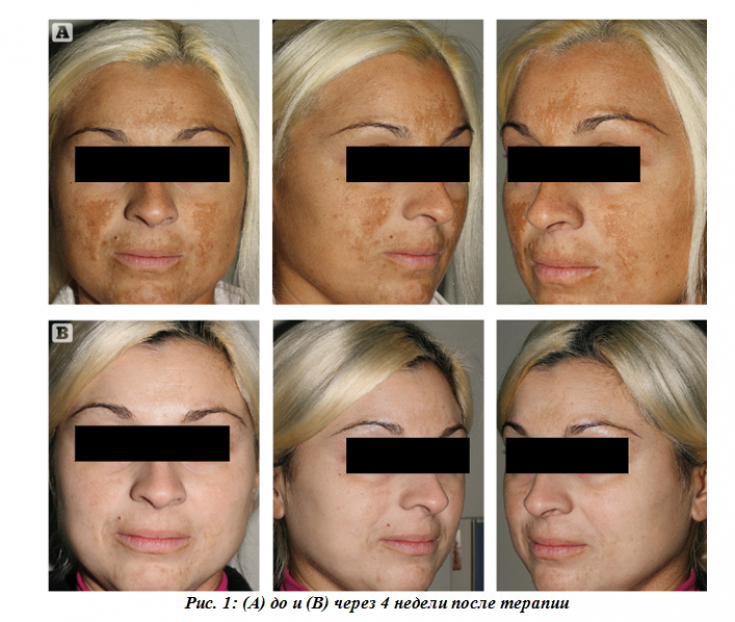
There were no side effects or complications during the course of treatment. The patients rated the therapy based on Cyspera Intensive Pigment Corrector Cream as effective.
There were no side effects or complications during the course of treatment.
The reported cases, despite such a small number of patients involved, have demonstrated that Cyspera cream based on 5% cysteamine is extremely effective, well tolerated and does not cause complications.
Pigmentation removal with laser technology

Cysteamine, unlike hydroquinone, is a non-toxic, non-mutagenic and non-carcinogenic depigmenting agent. Therefore, the author prefers to include this substance in the treatment plan for melasma.
According to Prime magazine







Add a comment