Alopecia – this is a serious problem that both women and men often face. To combat this disease, new drugs are constantly emerging, as for many patients with alopecia, their diagnosis becomes a real curse. Women especially suffer from hair loss, and this is not surprising, because society constantly stigmatizes this problem. On estet-portal.com read about basic preparations for the treatment of alopecia and their mechanism of action on the hair growth cycle.
- Estradiol: a hormone that guards hair beauty
- Progesterone to combat alopecia
- Spironolactone in the treatment of hair loss
- Finasteride for hair loss
- Latanoprost for hair improvement
- Minoxidil: the most famous drug for the treatment of alopecia
Estradiol: a hormone that guards hair beauty
Estradiol inhibits the conversion of testosterone to the metabolite dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by inhibiting 5AR activity. In addition, by inhibiting 17β-dehydrogenase, it prevents the conversion of androstenedione to testosterone, which leads to a decrease in the synthesis of testosterone and DHT.
DHT is believed to be the main cause of hair loss in both men and women.
In addition, estradiol accelerates the conversion of testosterone to estradiol, stimulating aromatase, lowering testosterone levels and leading to a decrease in DHT. This drug has been reported to stimulate the formation of hair follicular matrix cells.
One study from 2012 showed a positive effect of estradiol on 53 women with female pattern hair loss. Subjects used topical estradiol for eight months and the results showed a significant improvement in hair count and hair diameter.
Alopecia areata: fractional laser therapy and topical corticosteroids
Progesterone to combat alopecia
Progesterone is a natural 5AR inhibitor – an enzyme that converts testosterone to DHT. Without the presence of progesterone (or not enough), 5AR can do its job of converting. This means that more DHT is produced, which causes further thinning and hair loss in people with androgenetic alopecia.
The most optimal concentration of progesterone for topical application is about 2%.
For example, a 1987 study showed that 10 male patients suffering from androgenetic alopecia were treated for one year with a lotion containing 1% hydroxyprogesterone. After treatment, patients saw an increase in the number and average diameter of the hair shaft at the hair roots.
Read the most interesting articles in Telegram!
Spironolactone in the treatment of hair loss
Spironolactone acts as an androgen antagonist by competitively blocking androgen receptors and also inhibiting ovarian androgen production. This reduces the concentration of DHT, which inhibits hair growth.
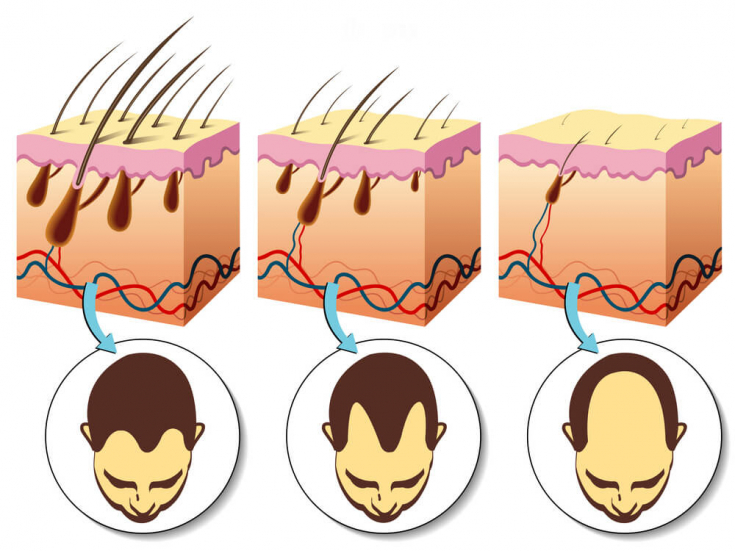
One study in 1988 found that spironolactone worked locally without much systemic absorption. However, its effect on estrogen-dependent malignancies when taken orally remains controversial. In this connection, it is necessary to prescribe this drug systemically with very great caution Finasteride for hair loss
Finasteride works by inhibition of the 5AR enzyme
, which is responsible for catalyzing the conversion of testosterone to the much more active DHT.A 2014 study on 24 healthy men evaluated a newly developed finasteride 0.25% topical solution versus commercially available finasteride 1 mg tablets. As a result, it was found that strong and similar plasma DHT inhibition was found after one week of treatment with both topical and systemic finasteride. Since oral finasteride is associated with a number of complications, its topical application is particularly relevant for the treatment of alopecia.
Hair loss and nanotechnology perspectivesLatanoprost for hair improvement
In 2012, a double-blind scientific study showed that latanoprost, a drug that mimics prostaglandins
, significantlyincreases the density of hair (by 22%) on the scalp after 24 weeks of treatment in young men with mild hair loss. Although the study sample size was small (only 16 subjects), the researchers found that 50% of the subjects had significant differences in hair density in terms of increased pigmentation and hair thickness.
Latanoprost has also been used to treat eyelash alopecia.Androgenetic Alopecia: An Injectable with Proven Effectiveness
Minoxidil: the most famous drug for the treatment of alopecia
Topical minoxidil has been used since the 1990s to treat male and female pattern baldness. The mechanism of action of this drug is quite complicated. First, it plays the role of a vasodilator that increases blood flow and hair trophism.
It is a recognized safe and effective treatment when used early in the onset of alopecia.
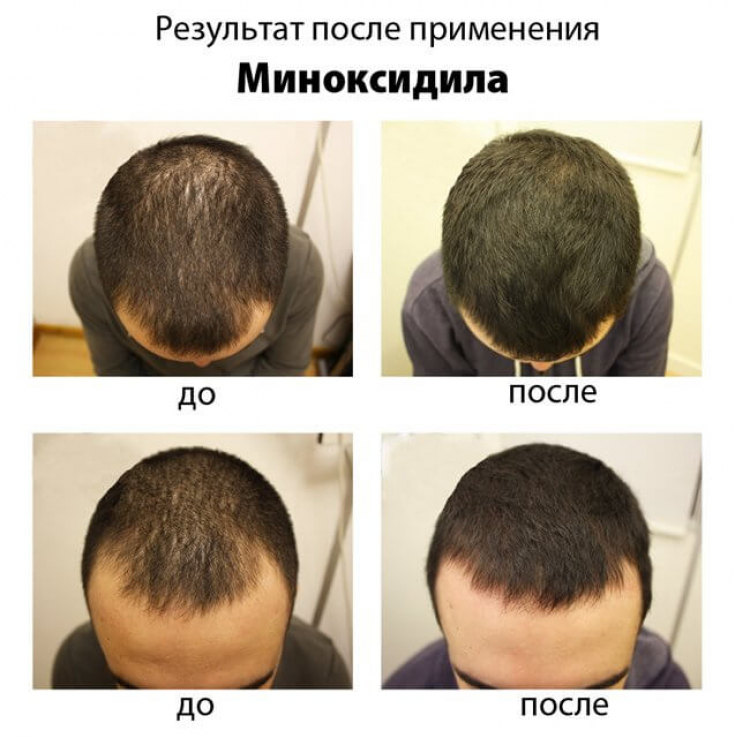 The most effective concentrations of minoxidil are 2% and 5%.
The most effective concentrations of minoxidil are 2% and 5%.
Genetic predisposition to aplopecia has been found









Add a comment