Abdominal wall defects are one of the most common and challenging problems faced by plastic surgeons.
Many patients with abdominal wall defects have comorbidities, which puts them at high risk of complications.
In addition to advanced surgical skills and accurate anatomical knowledge, a plastic surgeon needs a rigorous action plan to optimize pre- and post-op patient care.
In this article on estet-portal.com read about the 4 steps to a successful abdominal wall reconstruction.
- Hernia repair with abdominal wall reconstruction
- Principles for performing safe and effective abdominal wall reconstructionki
Hernia treatment with abdominal wall reconstruction
can be performed on an emergency or elective basis. A patient showing signs of
obstruction of the bowelusually requires urgent surgery. When dealing with such patients, the clinician
has little time for preoperative optimizationas the risks of delaying the operation are extremely high. On the other hand, the vast
most patientswith abdominal wall defects do not show such alarming symptoms. They may experience
occasional discomfortand inability to perform certain activities of daily living due to a large hernia. And in this case, the surgeon has the opportunity to
optimize the patient's conditionto obtain the best result of the operation.
Read the most interesting articles inTelegram!
The ultimate goal of – improving the quality of life of patients.As a result of the reconstruction, the surgeon must obtain a strong, dynamic and durable abdominal wall, which is usually achieved through the use of special meshes.
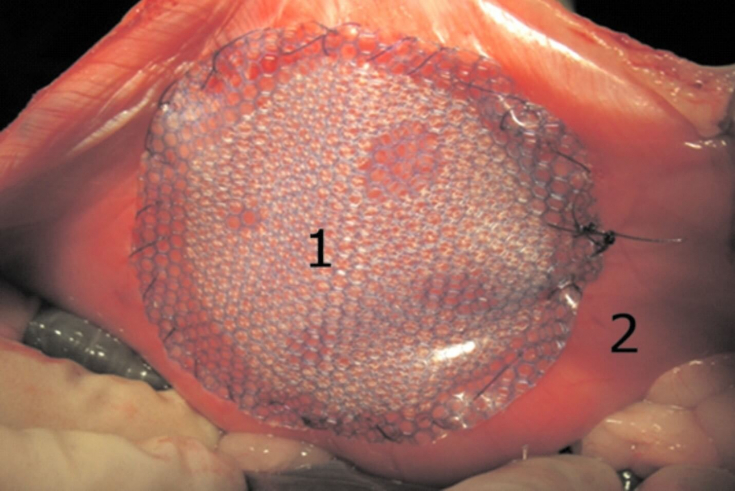
The surgeon should also strive to
minimize complicationswhich can be divided into 3 categories:
recurrent hernia;Ideal tummy: main features of tummy tuck Principles for performing safe and effective abdominal wall reconstruction
Modifiable risk factors:
- Smoking.
- Smoking, by reducing tissue perfusion and oxygenation, impairs wound healing. Quitting smoking 4 weeks before and after surgery significantly reduces the risk of infection and other complications;
- Malnutrition.
- Protein malnutrition, especially arginine and methionine deficiencies, is associated with significantly higher mortality. In addition, low albumin levels are associated with a 10-fold increased risk of infection;
- Obesity.
- Not only does obesity increase the risk of hematomas and seromas, but it has also been shown to increase the risk of hernia recurrence.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Poorly controlled diabetes mellitus is another risk factor for complications. Even infrequent hyperglycemias reduce tissue perfusion and impair immune function.
To minimize the risk of hernia recurrence, it is necessary to achieve
closure of the defect, while removing all non-viable and scar tissues, and fix it with mesh. At the same time,
the fabrics should not be under tension. Excessive tension on the edges of the defect can cause fascial dehiscence and recurrence of the hernia.
As a general rule,the mesh should be under enough tension
to avoid ripples or wrinkles.
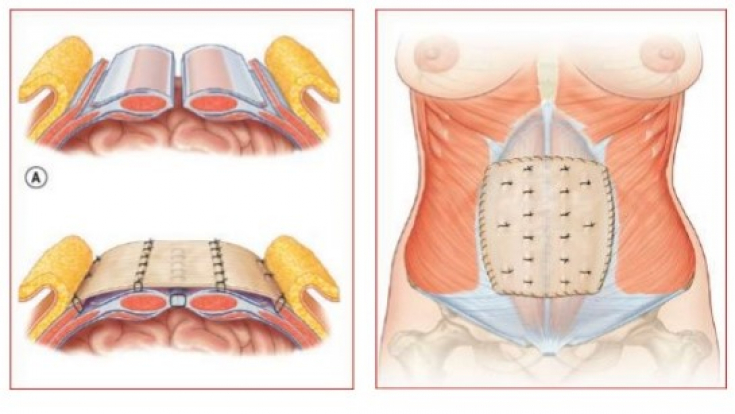
. Meshes can be broadly divided into
syntheticand biological.
Synthetic meshes are more durable, however biological meshes tend to be better embedded and more resistant to infection. Recent data suggest that the porosity and weight of the synthetic mesh are important factors when it comes to integration
: lightweight meshestend to suffer more from failure and heavy microporous meshes more often associated with scarring and infection.
Body plastic surgery: current issues about aesthetic operations on the body
Principle 3: Pay special attention to the skin and subcutaneous tissuePreservation of the vascular system of the skin and soft tissues is important to reduce the risk of complications. Therefore, it is desirable that access be as minimally traumatic as possible.
Principle 4: Careful postoperative care of the patientFor a patient who is undergoing a complex abdominal wall reconstruction,
postoperative treatmentis as important to the final result as the operation itself. Increased intra-abdominal pressure after reconstruction puts the patient at high risk for venous thromboembolism, atelectasis, and pneumonia.
To minimize the risk of venous thromboembolism, the patient mustmove
. It is advisable to start physical activity in the evening after the operation. Adequate
pain controlis important to achieve early patient recovery.






