Papillomavirus infection has a very high prevalence, with at least three out of four people becoming infected during their lifetime. The infection is most often registered at the age of 20-25 years.
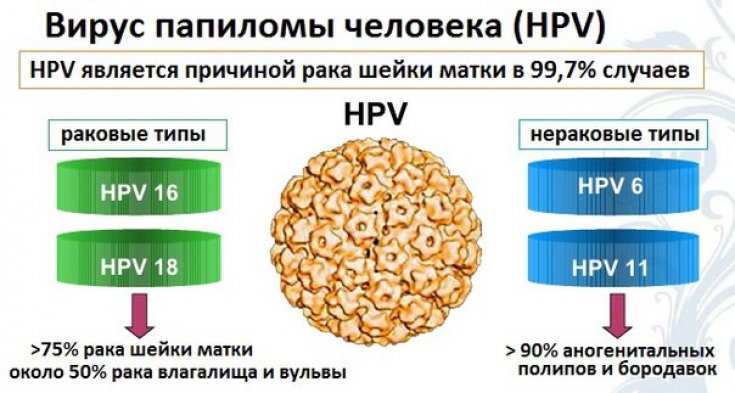
The key role of highly oncogenic human papillomaviruses in the development of oncological diseases, in particular cervical cancer, has been proven. Therefore, prevention of development and competent treatment of human papillomavirus infection are topical issues of our time.
In this article on estet-portal.com, read about the principles of treatment and prevention of papillomavirus infection, which meet international recommendations and postulates of evidence-based medicine.
Papillomavirus infection is most often asymptomatic
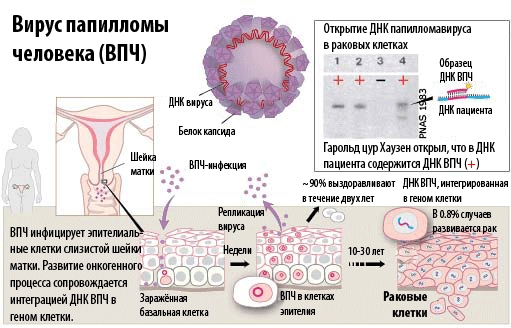
Human papillomavirus has over 200 different strains. The main route of infection transmission is sexual contact. In most cases, human papillomavirus infection is asymptomatic. Warts are most often discovered incidentally during a gynecological examination.
Follow us on Telegram
In rare cases, human papillomavirus infection can manifest itself as intense itching in the vulva, anus and foreskin. The presence of warts in the urethra can cause a burning sensation during urination and even cause hematuria.
For more information about modern approaches to the treatment of human papillomavirus infection, read later in the article.
Drug treatment of warts caused by human papillomavirus
In the treatment of viral infections, including warts and genital warts caused by the human papillomavirus, it is necessary to use drugs with proven efficacy. These include Podophyllotoxin and Imiquimod.
Podophyllotoxin (Evidence A) is used for topical application to visible warts for 3 days. The course of treatment can be repeated with an interval of 1 week. Best suited for the treatment of small solitary warts.
Imiquimod (Evidence B) is used in the form of a cream and has immunomodulatory properties. Imiquimod has no direct antiviral activity. The drug should be applied externally 3 times a week at bedtime, leaving the cream on the skin until morning (for 6-10 hours). Treatment continues until the warts disappear, but no longer than 16 weeks.
You may be interested in: How to suspect intestinal endometriosis and confirm the diagnosis
Physical destructive methods in the treatment of human papillomavirus infection
Physical destructive methods used in the treatment of human papillomavirus infection include cryotherapy, electrocoagulation, and laser excision.
Cryotherapy is the method of choice in the treatment of warts of various localization due to its effectiveness and safety.
At the same time, when using the electrocoagulation method, it is quite difficult to control the depth of exposure.
Laser excision is the best treatment for warts that are located in the urethra, vagina or anus.
According to the Finnish protocols for the treatment of papillomavirus infection, changes that correspond to CIN 1 do not require the use of specific therapy. Their spontaneous disappearance is very likely.
Read also: Contraceptives and lactation: effective and safe methods
Vaccination is an effective method of preventing human papillomavirus infection
Currently, there are two effective vaccines for the prevention of human papillomavirus infections. Both vaccines are aimed at preventing infection with papillomavirus types 16 and 18, but also provide cross-immune protection against other highly oncogenic types of the virus.
The vaccine against papillomavirus infection is not therapeutic, it can only be used for the purpose of prevention.
In Finland, the HPV vaccine has been included in the national vaccination program since 2013. It is administered to all girls aged 11-12.
Vaccination guarantees an immune response for an average of 15 years.
Vaccination against papillomavirus infection is an effective method of preventing the development of gynecological cancerous changes in the future. But it is effective only when it is carried out until the moment of contamination with papillomavirus, that is, even before the onset of sexual activity.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Gynecology" section. You may also be interested in: What are the current methods of conservative treatment of uterine fibroids.
Based on the EMB Guidelines "Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection"






Add a comment