Among the many antibacterial drugs for the treatment of pyoderma, drugs containing the antibiotic mupirocin with a bactericidal effect against staphylococci, streptococci and many gram-negative microorganisms deserve attention.
This article on estet-portal.com describes the results of using the antibiotic mupirocin in patients with staphylococcal and streptococcal pyoderma (presence of folliculitis, boils and impetigo), as well as with allergic dermatoses complicated by pyoderma.
- The main features of the course of pyoderma
- Antibiotic mechanism of action
- Antibiotic study on pyoderma
- Outcomes of antibiotic use in patients with with pyoderma
The main features of the course of pyoderma
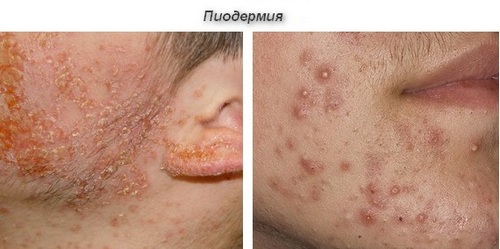
Recently, the incidence of pyoderma (pustular skin diseases) has increased significantly in dermatological practice. These diseases are caused by staphylococci, streptococci, less often by other pathogens.
Eczema Treatment: Whether to Prescribe Antibiotics
Pyoderma may occur primarily or complicate the course of another disease. Under appropriate conditions, pustular skin diseases can cause complications - meningitis, osteomyelitis, purulent processes in various organs, sepsis.
The use of antibacterial drugs recommended for the treatment of patients with pyoderma does not always provide a sufficient therapeutic effect.
The reasons and factors that may have an adverse effect on the effectiveness of antibacterial drugs in patients with pyoderma include: the characteristics of the pathogen, its morphological, biological properties (pathogenicity, virulence, ability to form a microcapsule, transform into L-forms, the state of the macroorganism, its resistance to pyogenic microorganisms, features of nonspecific resistance and immune status, functions of the nervous and endocrine systems, the presence of circulatory disorders, metabolism, and in particular carbohydrate.
Follow us on Instagram!
The occurrence and severe course of pyoderma is caused by the presence of foci of chronic infection, allergic restructuring of the body, diseases of the endocrine glands, digestive tract, hypovitaminosis; environmental factors that cause overheating or hypothermia of the body, which causes a decrease in the barrier functions of the skin, the appearance of microtraumas, maceration and so on.
Antibiotic mechanism of action
In the dermatological treatment of patients with certain skin diseases (streptococcal impetigo, furunculosis, true eczema complicated by pyoderma), antibiotic preparations with mupirocin were used for topical therapy. Its main action – it is a blockage of protein synthesis of bacteria, which thus leads to the bactericidal action of the antibiotic.
Mupirocin − the only representative of its class of antibiotics, the mupirocin class, that is, it has a unique chemical structure, therefore it does not cause resistance in microorganisms. The antibacterial action of the drug is aimed at the main pathogens of skin infections, such as strepto- and staphylococci, Haemophilus influenzae, and β-hemolytic streptococci and others.
Absorption of this drug is low. 30 minutes after applying the ointment to the skin surface, even traces of mupirocin cannot be detected in the systemic circulation.
Is topical treatment of atopic dermatitis effective
The stable advantage of this antibiotic over other drugs of similar action is due to the impossibility of systemic effects and cross-resistance, since there are only local dosage forms of this antibiotic - it does not enter the systemic circulation or into the intestines, where there are favorable conditions for selection resistant to xxxx>microflora antibiotics.
Study of antibiotic action in pyoderma
Patients with various clinical forms of pyoderma and allergic dermatoses were observed. The age of patients is from 18 to 59 years. The diagnosis was established by the presence of typical clinical manifestations of the disease. For local therapy, patients of both groups were prescribed a drug (ointment) containing the antibiotic mupirocin.
Evolution of treatment approaches based on the causes of psoriasis
Applied to the affected areas 2-3 times a day (course 6-10 days). Additional therapy was not carried out. As a control, selected case histories of patients previously treated in the same department using traditional complex therapy (local in combination with systemic antibiotics) were used. Results of antibiotic use in patients with pyoderma
In patients on the 4th day of topical application, a gradual regression of pustules, a decrease in the amount of purulent discharge, the severity of hyperemia and pain were observed. On the 8-10th day of treatment, inflammatory infiltrates and soreness of the skin in the area of inflammation disappeared, the general condition of the patients returned to normal.
Rapid wound healing: dangers of fungal microflora In patients, topical application of the antibiotic contributed to the disappearance of the vesicular-pustular rash and exudation in the affected areas on the 4-5th day of treatment. There was a decrease in the severity of hyperemia and infiltration, subjectively itching, burning and pain. On the 8-10th day of appointment, the patients observed the disappearance of infiltration, crusts and the restoration of the normal state of the skin in the area affected by pyoderma.
No side effects were observed.
When analyzing the results obtained with historical control data, it is assumed that the topical treatment of pyoderma in terms of effectiveness and duration did not exceed, and sometimes was even shorter than, traditional therapy, but only for mild to moderate pustular lesions. Patients with severe pyoderma should be treated with systemic antibiotics.
 The antibiotic mupirocin can be recommended for widespread use both in inpatient and outpatient settings in the treatment of patients with acute and chronic mild to moderate pyoderma as monotherapy, severe − in combination with systemic antibiotics.
The antibiotic mupirocin can be recommended for widespread use both in inpatient and outpatient settings in the treatment of patients with acute and chronic mild to moderate pyoderma as monotherapy, severe − in combination with systemic antibiotics.
Aloe vera in dermatology: impact on wound healing







Add a comment