Many innovations and advances in the beauty industry have been developed through the study of biochemical processes that occur at the molecular level. It is the molecular level that is the initial basic structure of the human body.
The study of the processes of genetic and epigenetic regulation of biochemical reactions is a huge prospect for new discoveries in the field of anti-ageing therapy.
Today, the study of molecular methylation is of great interest. For more information about what this process is, as well as what connection exists between methylation and premature aging, read on estet-portal.com in this article.
Methylation is a biochemical process that occurs continuously in cells
Methylation, also known as one-carbon metabolism, is a biochemical process that occurs continuously in every cell in our body. As the name suggests, it consists in adding methyl groups to the composition of the molecules. Imbalanced methylation is the cornerstone of premature aging and multiple age-related degenerative diseases.
Imbalanced methylation is the cornerstone of premature aging and multiple age-related degenerative diseases.
The process of methylation of molecules is closely related to other biochemical reactions in the body, in particular, such as:
1. Synthesis of DNA and RNA, biosynthesis of purine nucleotides;
2. Expression of genes, as well as their "silence";
3. Neurotransmitter metabolism;
4. Estrogen metabolism;
5. Regulation of the immune system;
6. Biotransformation and antioxidant activity;
For more information about the role of methylation in the synthesis of DNA, RNA and purine nucleotides, and whether there is a link between methylation and premature aging, read further in the article.
Read also: The role of antinuclear antibodies in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
Methylation: synthesis of DNA and RNA, biosynthesis of purine nucleotides
As a result of numerous scientific studies, it has been established that the synthesis of DNA and RNA, as well as the biosynthesis of purine nucleotides, is affected by a chronic deficiency of a methyl phosphate donor, in particular folate (vitamin B9). It contributes to the occurrence of errors in gene expression, the initiation of apoptosis and carcinogenesis.
In a study using a sensitive in vitro model system (transgenic mouse prostate adenoma mimicking prostate cancer), the role of folate in initiating genetic, epigenetic and phenotypic changes in the body was proven.
Follow us on Telegram
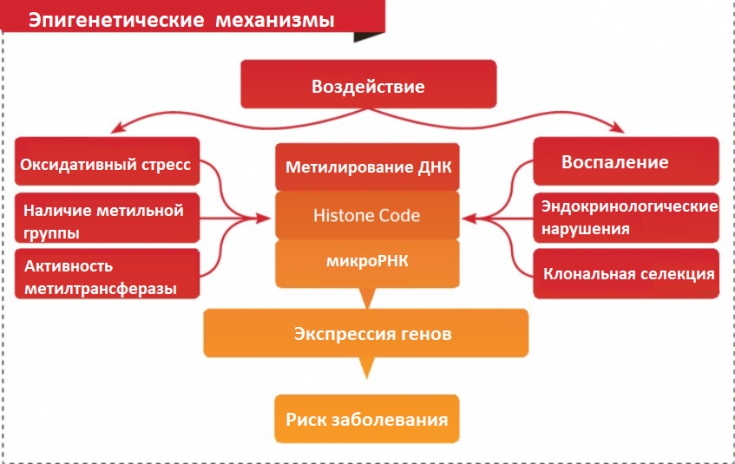
DNA methylation is a well-known epigenetic mechanism
DNA methylation is one of the well-known epigenetic mechanisms that regulate gene expression and human phenotype. In healthy cells, the methylation process ensures the correct regulation of gene expression (without changing the DNA sequence), as well as their "silence".
DNA methylation occurs at so-called CpG sites ("Cytosine base followed immediately by a Guanine"). Those regions where CpG sites are located near gene promoters are known today as CpG islands (CpG islands).
Recent studies have shown that DNA methylation in CpG island regions, histone deacetylation, and histone methylation results in "freezing" genes. Aberrations in gene expression caused by hypermethylation of the epigenetic promoter of CpG islands can lead to carcinogenesis (so-called "inappropriate silence").
Methylation plays a key role in the removal of exogenous toxins
Methylation plays a key role in the removal of exogenous toxins from the human body. This process conjugates methyl groups to toxins, which promotes the binding and elimination of xenobiotics and carcinogens, including heavy metals such as mercury, lead and arsenic.
Follow us on Telegram
In addition, methylation promotes the production of glutathione, taurine and cysteine. These substances are involved in inflammation and regeneration reactions, and are also powerful antioxidants. In particular, glutathione contributes to the neutralization of free radicals and reactive oxygen species, as well as the activation of exogenous antioxidants (vitamins C and E) in their reduced forms.
Methylation deficiency may be a cause of premature aging
Through the results of numerous scientific studies, it has been established that a deficiency in the methylation process, or its imbalance, can be the causes of premature aging, in particular, this can contribute to the appearance of gray hair at a young age.
Read also: Braid to the waist: why our hair is aging
A link has been established between hypomethylation and the development of cardiovascular diseases, arteriosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, neurotransmitter imbalance and other mental disorders.
It has been proven that pathological changes in DNA methylation loci are associated not only with biological aging, but also affect human life expectancy.
Epigenetic drift, which leads to an imbalance in DNA methylation, is a fundamental aspect of the aging process.
Interestingly, both hypermethylation and hypomethylation contribute to the progressive accumulation of epigenetic damage. It is the imbalance of the methylation process that is the reason why phenotypic similarities between young individuals are lost with age. This even applies to twins.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Cosmetology" section. You may also be interested in: Bio-supplements with active ingredients and their impact on health.
Based on Prime magazine.







Add a comment