Microdermabrasion – it is a minimally invasive procedure, mechanical peeling of the skin, which is carried out at the level of the epidermis.
This technique is used to correct uneven skin tone/texture, to correct signs of photoaging, stretch marks, melasma and scars, including post-acne scars.
This is a widely available and one of the most common non-surgical cosmetic procedures.
This procedure can be performed on an outpatientby an aesthetic medicine specialist without the use of anesthesia.
On estet-portal.com read more about the features of microdermabrasion and the main advantages and disadvantages procedures.
- Microdermabrasion in the practice of a specialist in aesthetic medicine
- Indications for Microdermabrasion
- Contraindications and complications of microdermabrasion
- Microdermabrasion techniqueand
Microdermabrasion in the practice of a specialist in aesthetic medicine
Microdermabrasion was first introduced in 1985 by Marini and Lo Brutto as a less aggressive alternative to chemical peels and dermabrasion.
During a microdermabrasion procedure, abrasive crystals cause a gentle mechanical peeling of the skin, which ultimately leads to the removal of the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
The technique is considered safe for all Fitzpatrick skin phototypes and complications from microdermabrasion are minimal.
In addition to improving the skin, microdermabrasion improves skin permeability and improves transdermal delivery of cosmetics.
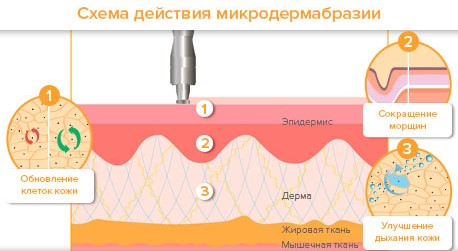
Microdermabrasion:
- removes the stratum corneum;
- affects the deeper layers of the epidermis and dermis;
- causes rearrangement of melanosomes in the basal layer of the epidermis;
- increases the density of collagen fibers at the dermal-epidermal level;
- stimulates the growth of blood vessels in the reticular dermis;
- causes activation of wound healing transcription factors and matrix metalloproteinases in the cellme.
Very clear skin: why mechanical peeling is needed
Indications for Microdermabrasion
Patients often report skin 'radiance' and reduction of pore visibility after microdermabrasion.
Sebum levels are also reduced after the procedure, and biomechanical analysis shows a decrease in skin stiffness, an increase in skin elasticity and thickness.
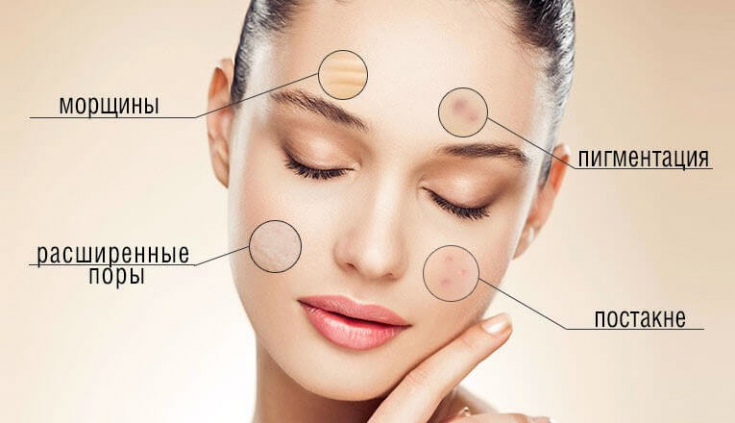

Cosmetic indications for microdermabrasion:
- scars, including post-acne scars;
- uneven skin tone/texture;
- stretch marks;
- melasma;
- photoaging;
- seborrheic skin;
- small wrinkles;
- enlarged pores.
Microdermabrasion has been shown to improve transdermal drug delivery.
Methods to increase transdermal delivery often target the stratum corneum of the epidermis, as it is the main barrier that limits transdermal diffusion of molecules.
Microdermabrasion has been shown to improve transdermal delivery of insulin, vitamin C, lidoca, and
Telegram!
Microdermabrasion Contraindications and ComplicationsMicrodermabrasion
is contraindicated in areas of active infectionsuch as herpes simplex virus, varicella-zoster virus, human papillomavirus and impetigo. People with a contact allergy to abrasive crystals (i.e. allergic to aluminium) should use a different crystal or non-crystal system.
Rosacea and telangiectasias are considered relative contraindications for microdermabrasion.
Side effects of microdermabrasionare minimal
and are absent in most patients.
Common complicationsinclude:
soreness;- edema;
- redness;
- Petechiae.
- Conjunctival crystals may cause
Because the stratum corneum is removed during microdermabrasion, the skin becomes
more susceptible to photodamagewithin a few days after treatment.
Dermabrasion of the skin: how to avoid side effects Microdermabrasion technique
Microdermabrasion devicesare categorized into systems with or without crystals.
Crystal systemadvances abrasive crystals over the skin surface at a predetermined flow rate. The most common crystal used is –
aluminum oxide. Sodium chloride, magnesium oxide and sodium bicarbonate crystals are less commonly used.
In
systems without crystals, diamonds embedded in the tip cause abrasion. Required
area is cleaned with a gentle agentprior to the procedure. Wet gauze is placed over the eyes to prevent contact with abrasive crystals.
Using
negative pressure, the device draws the skin into the handpiece. The device then releases abrasive crystals at a controlled flow rate. Surface debris and stratum corneum cells are removed and particles accumulate in the reservoir.
Remaining crystals and debris are removed and
humidifieris applied. The degree of stratum corneum removal depends on
the crystal flow rateand exposure time of the procedure. The pressure generated by the vacuum device has little effect on the removal of the stratum corneum.
The entire microdermabrasion treatment typicallytakes 30-60 minutes
. Patients often require
4-6 treatments per weekto achieve desired results.






