Minoxidil was created as an antihypertensive drug and the discovery of hypertrichosis side effect from its use paved the way for a great future for this drug.
Today, topical minoxidil is the primary treatment for androgenetic alopecia and is used as an off-target treatment for other hair growth disorders.
Despite its widespread use, the exact mechanism of action of minoxidil is still not fully understood.
In this article on estet-portal.com we will look at the mechanism of action, clinical efficacy and side effects of topical minoxidil.
What is Minoxidil Solution
Minoxidil 2% solution was first introduced to the market in 1986, followed by 5% solution in 1993.
Despite its worldwide recognition for over 30 years, the mechanism underlying the action of minoxidil in promoting hair growth remains to be elucidated.
Minoxidil Solution contains inactive ingredients, includingwater, as well as ethanolandpropylene glycol, which are used to enhance solubility minoxidil.
Propylene Glycol is effective in delivering drugs to the hair follicles, but it often leads to local irritation.
In this regard, a new form of the drug was developed and launched - minoxidil foam, which does not contain propylene glycol.
This foam provides increased delivery of the active ingredient to the target site and easy penetration of the drug with less irritation.
Read the most interesting articlesand in Telegram!
Minoxidil is a potent arteriolar vasodilator that enhances cellular DNA synthesis and cell proliferation.
Mechanism of action of minoxidil
Minoxidil has been used to treat hair loss for several decades.
The drug acts on follicular cells, increasing hair growth and reducing hair loss.
Treatment discontinuation results in progressive hair loss over weeks 12 and 24.
Scientists suggest that minoxidil stimulates the secondary germ cells of hair follicles in the telogen phase, resulting in a rapid transition to the anagen phase.
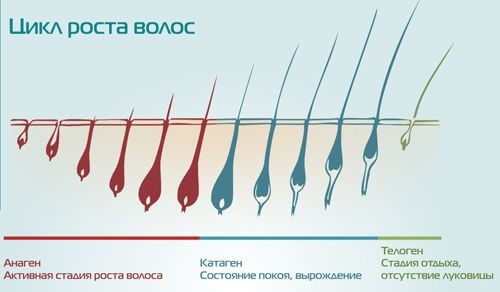
An experimental study has shown that minoxidil prolongs the anagen phase in the dermal papilla by inducing β-catenin activity, stimulating proliferation and differentiation of follicles.
Histologically, increase in follicle size and percentage of follicles in the anagen phase were noted.
A beacon of hope for alopecia areata patients
- Use of topical minoxidil for hair growth disorders.
FDA Approved Indications for the use of the drug:
- androgenetic alopecia;
- baldness in women.
Off-label minoxidil usage:
- Alopecia areata;
- improve the growth of beard, eyebrows;
- scarring alopecia;
- chemotherapy-induced alopecia;
- fibrous alopecia;
- anagen alopecia;
- telogen alopeciaia.
Alopecia Treatment: Basic Preparations
Adverse effects of minoxidil
Topical minoxidil is considered safe. However, some patients experience a range of side effects.
The most common of these is contact dermatitis which is accompanied by itching and flaking.
Allergic dermatitis can also be caused by the propylene glycol in the solution or minoxidil itself.
If the patient is allergic to propylene glycol, minoxidil foam, which does not contain this ingredient, should be given.
It is also possible to develop hypertrichosis, which depends on the concentration of minoxidil, with the highest frequency of unwanted hair growth observed in patients using a 5% solution.
Alopecia areata: fractional laser therapy and topical corticosteroids







Add a comment