Gestational trophoblastic neoplasia – is a collective term for hydatidiform mole (molar pregnancy), chorionadenoma, choriocarcinoma, malignant trophoblast teratoma, and placental site trophoblastic tumor.
There are no methods to accurately predict the malignancy of molar pregnancies. Clinical development is determined by the patient's serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) curve after mole removal.
In 80% of patients with benign molar pregnancies, serum hCG levels steadily decrease to normal within 8-12 weeks after mole evacuation. In the other 20% of patients with malignant transformation, serum hCG levels either increase or remain at the same level. For more information about trophoblastic neoplasia read the article estet-portal.
Gestational trophoblastic neoplasia symptoms
Most cases of gestational trophoblastic neoplasia are diagnosed when serum hCG levels rise in the absence of a fetus on ultrasound.
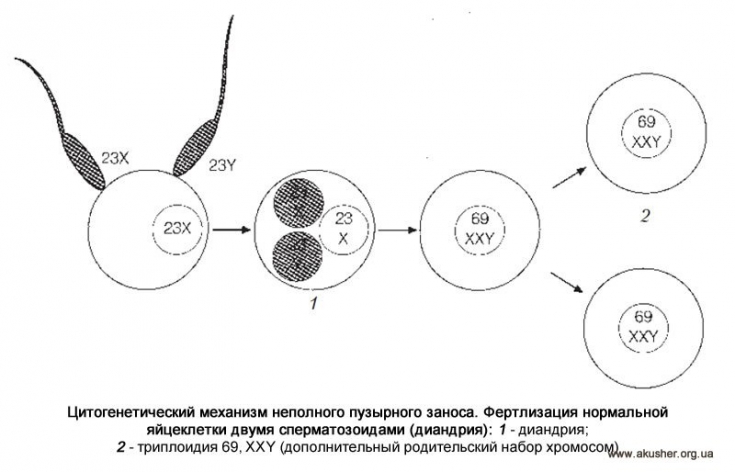
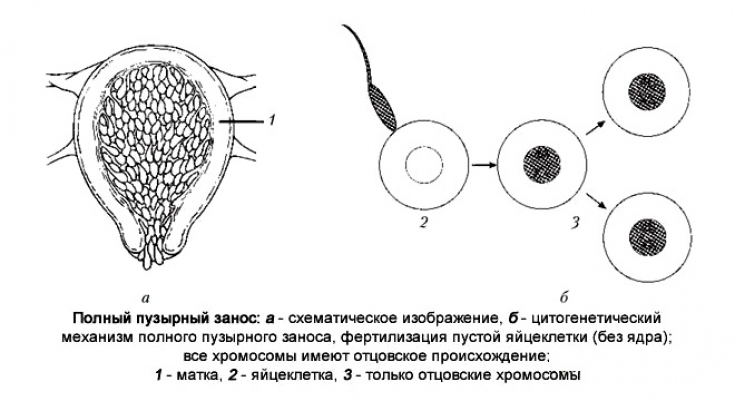
Bubble skid — it is a product of conception in which the normal development of the embryo does not occur, and the chorionic villi grow in the form of bubbles filled with liquid.
When metastases form, the following signs and symptoms appear:
1. bleeding of lower genital tract metastases, which are purple, blue-black papules or nodules;
2. pain in the abdominal region in case of metastasis to the liver or gastrointestinal tract;
3. Defense of the anterior abdominal wall and pain during the development of hemoperitoneum due to metastasis;
4. hemorrhagic shock with profuse bleeding from vascularized metastases;
5. neurological deficit if brain metastasis has occurred;
6. jaundice if liver metastases cause biliary obstruction.
Follow us on Telegram
Diagnostic route for a patient with gestational trophoblastic neoplasia
Laboratory tests used in the diagnosis of GTN are as follows:
• quantitative analysis of hCG serum – to assess the response to therapy and the course of the disease;
• complete blood count – to detect anemia,
• liver enzymes – to detect liver metastases.
What are the symptoms of a tubal pregnancy
Imaging methods:
• pelvis ultrasonography – detection of molar pregnancy in the uterine cavity;
• chest x-ray – detection of metastases in the lung tissue;
• CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast – detection of metastases in the liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract;
• MRI of the brain with contrast– detection of brain metastases.
It is necessary to carry out a therapeutic and diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity, followed by a histological examination.
A hydatidiform mole is complete, in which there are no embryonic tissues, and incomplete, in which the embryo or its individual elements are present.
Treatment tactics for gestational trophoblastic neoplasia
Patients with gestational trophoblastic neoplasia are divided into 2 groups: those with a WHO score of less than 7 (low risk) and patients with a score of 7 or higher.
Peculiarities of management of multiple pregnancy and childbirth
Low-risk patients (WHO score less than 7) are treated with single-agent chemotherapy with methotrexate, but actinomycin D may be used in patients with hepatic impairment.
Switching from methotrexate to actinomycin D occurs if serum hCG levels rise or remain constant and the WHO score remains below 7.
During treatment, serum hCG levels are monitored weekly. An additional six weeks of chemotherapy is given after normalization of hCG levels.
Treatment in patients with a WHO score of 7 or higher:
• EMA-CO is a combination of etoposide, methotrexate and actinomycin D administered in the first week of a two-week cycle, and cyclophosphamide with vincristine administered in the second week.
• EMA-EP - cisplatin and etoposide in the first week of therapy, which are replaced by cyclophosphamide and vincristine in the second week.
Radiation Therapy:
• Patients with liver metastases are considered for liver radiotherapy (2000 centiGray).
• Whole brain irradiation (3000 cGy) given in combination with chemotherapy; dexamethasone is given to reduce brain swelling (the most common approach in the US).
Surgical Care:
1. may require uterine ligation or vascular embolization to control bleeding;
2. hepatic artery embolization has been successfully used to control hemorrhage from liver metastases;
3. A hysterectomy may be required in case of uncontrolled vaginal bleeding.
Modern diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy will help prevent a catastrophe
Prognosis for a patient with trophoblast neoplasia
Molar pregnancy has 100% sensitivity to chemotherapy. Trophoblastic diseases with metastasis in 75% of cases are cured by chemotherapy. After 12 months of normal hCG levels, less than 1% of patients relapse.
Thus, trophoblastic diseases develop as a result of a violation of the fertilization of the egg by the spermatozoon. As a consequence, the haploid tissue begins to divide uncontrollably in the uterine cavity. Such a pathological condition can be complicated by bleeding and malization with the formation of metastases to distant organs. Modern medicine has a sufficient arsenal of medical, radiation and surgical therapy for trophoblastic neoplasia.
You may be interested in an article on our website estet-portal.com in the section "Gynecology" What are the signs of an ectopic pregnancy
Adapted from Medscape







Add a comment