Until recently, all the pathological processes that occur in the nose were evaluated according to the patient's sensations and the results of the rhinolaryngologist's attempts to examine the condition of the nose with a light bulb and a pair of mirrors reflecting it. Today, the doctor is armed with excellent diagnostic equipment, which makes it possible to examine not only the anterior part of the nasal cavity, but and all the details of the state of the respiratory organ up to the nasopharynx. Today, rhinoscopy allows timely diagnosis of polyps, chronic rhinitis and many other problems in the nasal cavity, and is also used in preparing patients for plastic surgery for the correction of the nasal septum or the shape of the nose.
What can rhinoscopy do and when is it prescribed
Rhinoscopy refers to the methods of instrumental diagnostics, which allow you to study in detail the condition of the nasal cavity using a special set of mirrors – bivalve, nasopharyngeal, as well as with the use of fiber-optic and rigid instruments, which make it possible, simultaneously with the examination of the nasal cavity, to photograph its individual sections and even video recording, to conduct a sparing biopsy in the presence of formations deep in the nose.
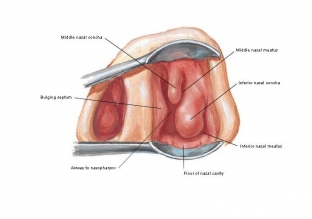
To inspect each of the parts of the nasal cavity – anterior, middle or posterior rhinoscopy – their own mirrors or nasodilators are provided. During this procedure, the doctor can examine in detail not only chronic rhinitis or the presence of polyps, but also the condition of the nasal septum, nasal passages & nbsp; and shells, look into the nasopharynx.
Indications for rhinoscopy may include the following problems, symptoms, and state:
- patient after rhinoplasty or septoplasty – to evaluate the results of plastic surgery;
- complaints of chronic headache of unknown origin;
- disorders of the olfactory function;
- nose injury;
- suspicion of a foreign object in the nose;
- suggestion of deviated septum;
- frequent nosebleeds.
Rhinoscopy is performed for various sinusitis, as well as hay fever, rhinitis of unknown origin, the assumption of the presence of adenoids, synechia, polyps.
If necessary, rhinoscopy can be supplemented by other diagnostic methods – e.g. sinus X-ray, sinus CT scan, diagnostic puncture or biopsy.
Features of different types of rhinoscopy
Anterior rhinoscopy. Performed using a forehead reflector and nasal speculum. Allows you to explore the state of the nasal septum, a large ethmoid vesicle, the anterior sections of the bottom of the nasal cavity and the lower, middle turbinate, nasal passages (common and lower, middle). If there is a furuncle or an exacerbation of eczema in the vestibule of the nasal cavity, the study is temporarily postponed.
Medium rhinoscopy. It is advisable to perform the examination under local anesthesia, since the mirrors are inserted deep enough and may cause the patient to gag. The study allows you to consider the middle nasal passage, semilunar cleft, cells of the ethmoid bone, maxillary sinuses, openings of the frontal sinus. If you move the mirror a little deeper, you can see the opening of the sphenoid sinus and the entire olfactory region. It is advisable to supplement the study with the use of a bellied probe: if necessary, this will reveal polyps, synechiae, foreign bodies, and also assess the density of the mucosa.
Posterior rhinoscopy. Performed with local anesthesia. The nasopharyngeal mirror is inserted behind the palatine uvula, which allows you to examine the choanae, vomer, pharyngeal vaults and pharyngeal pockets, and the posterior edges of the turbinates. Difficulties for examination may be enlarged tonsils, scars, swelling of the mucosa.
In general, rhinoscopy is not difficult, especially if the technique is followed, but it provides good diagnostic capabilities.







Add a comment