Anatomical features and factors such as skin quality, environmental influences, genetic predisposition and weight fluctuations cause difficulties in the aesthetic correction of the submental zone.
As a rule, a double chin and a turkey neck – characteristic problems in this area, which most often become a source of psychological discomfort for patients and the reason for seeking help from a specialist in aesthetic medicine.
In this article, Dr. Marc Pacifico discusses the available submental correction techniques.
When is it better to refer a patient to a plastic surgeon
Surgical lifting of the lower part of the face/neck – the gold standard for solving aesthetic imperfections in the submental area due to the appearance of excess skin as a result of age-related changes or weight loss.
Also, surgery remains one of the most effective methods of removing fat deposits under the chin, as it provides access to both deep and superficial fat compartments.
While subcutaneous fat reduction is possible with other methods, deep fat deposits can only be corrected through surgical procedures.
Plasty of the neck and chin: an effective combination of two techniques
Assessment of the state of the submental zone: how to choose a correction method
Before choosing a submental zone correction method, it is important to make a correct assessment, which includes:
1. Skin condition
The best results for localized fat removal are achieved with firmer, more elastic skin without signs of photodamage.
If it is difficult for a specialist to determine what caused the problem in the submental zone – excess skin or fat, the author recommends comparing the prone and standing profiles of the patient (Figures 1 and 2). If, in the supine position, fullness in the submental zone persists, this indicates the presence of fatty deposits. Otherwise, the reasons for the aesthetic defect – laxity of the skin and subcutaneous muscles of the neck.
Non-surgical techniques work with pre-platysmal (subcutaneous) rather than sub-platysmal fat.
2. Fat distribution
This step of the assessment allows you to determine the depth of excess fat deposits (in the pre-platysmal or sub-platysmal compartments). When working with deep fat pads, only surgical methods of correction are effective.
Pinch the submental tissue between thumb and forefinger (Figures 3 and 4) and ask the patient to take a sip. During this process, the subplatysmal fat will return to its original position, and the superficial adipose tissue will remain in the grip.
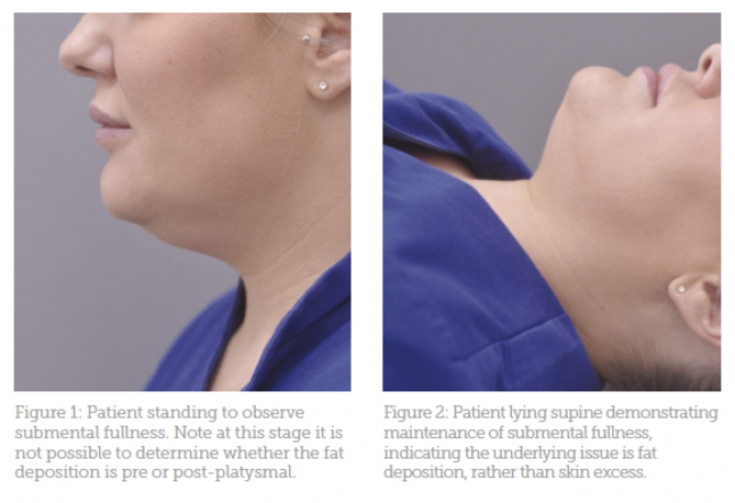
Fig. 1: Patient in standing position (fat depth cannot be determined)
Fig. 2: Patient in supine position (fullness under chin persists, indicating excess body fat)
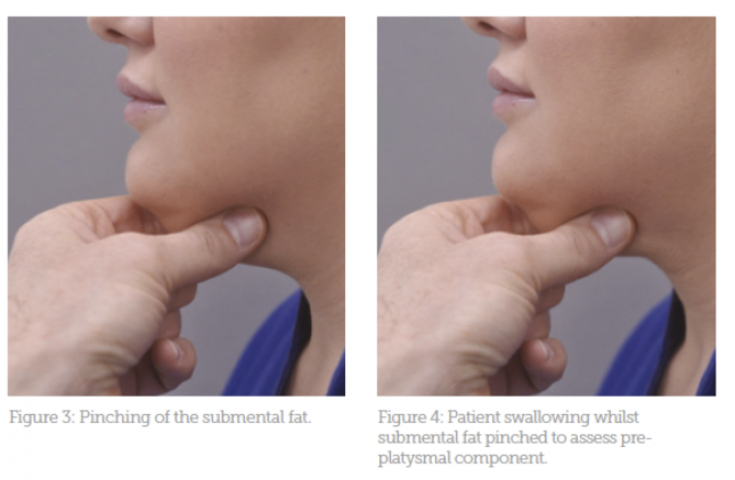
Fig. 3: capturing submental fat
Fig. 4: assessment of the severity of preplatysmal fat during swallowing
Non-surgical methods of correction of the submental area
Laser Therapy
Initially, laser therapy was used to improve the results of surgical liposuction. However, in a study by Jackson et al. the effectiveness of this method as a monotherapy was demonstrated: a decrease in body fat with a subsequent decrease in triglycerides and total cholesterol levels 2 weeks after the procedures.
The process of removing fat from the body is accompanied by local redness and a temporary increase in regional lymph nodes.
Cryolipolysis
Reduction of the subcutaneous fat layer during controlled exposure to cold is provided by natural thermal diffusion; surrounding tissues are not damaged during the procedure.
Cryolipolysis has been shown to achieve a 2-3.7 mm fat reduction without raising serum lipids or compromising liver function. Undesirable phenomena after the procedure: redness, numbness and sensitivity of the treated area. Cases of paradoxical adipocyte hyperplasia followed by the need for surgical liposuction have also been documented.
Injectable lipolysis
Small doses of purified synthetic deoxycholic acid can achieve the effect of focal cytolysis of fat cells.
Based on my experience, the author claims that a course of 2-5 treatments is required to obtain the desired result, which are carried out with an interval of 1 month. Possible adverse effects: swelling, bruising, numbness and, in rare cases, temporary paralysis of the marginal mandibular nerve.
Double Chin Opportunities: How the Neck Contour is Corrected
Radiofrequency
The fight against fat deposits in the submental zone using radiofrequency therapy occurs due to heating of adipose tissue, which stimulates the destruction of adipocytes.
The best results are achieved with moderate to moderate fat removal in patients with high skin quality.
Side effects are localized and include erythema, pain, swelling, and vesicles.
Case Study
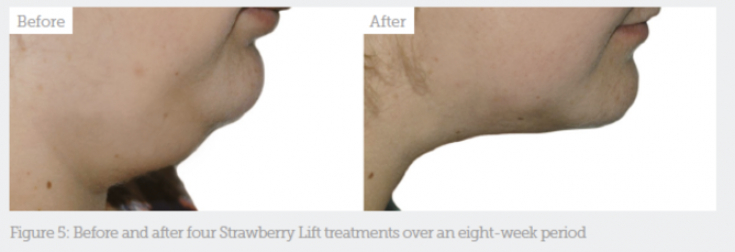
Fig. 5: before and after 4 Strawberry Lift treatments over 8 weeks
A patient (22 years old) with polycystic ovary syndrome came to the author's clinic with a complaint of fullness in the submental area. During the examination, a zone of preplatysmal fat was revealed. The patient underwent 4 procedures with the Strawberry Lift laser device with an interval of 2 weeks. The patient was satisfied with the results of the correction.
Adapted from Aesthetics







Add a comment