Given the main airborne route of transmission of the coronavirus, which causes the rapid spread of an infectious agent through physical and social contact, health authorities in most countries have introduced restrictive quarantine measures in order to stop the spread of the virus, reduce the number of cases of complicated course of the disease and reduce the burden on the medical system . However, there remains an unexplained relationship between the time during which the carrier or the patient after clinical recovery can still be dangerous to others and spread the virus.
Read more about this study at estet-portal.com
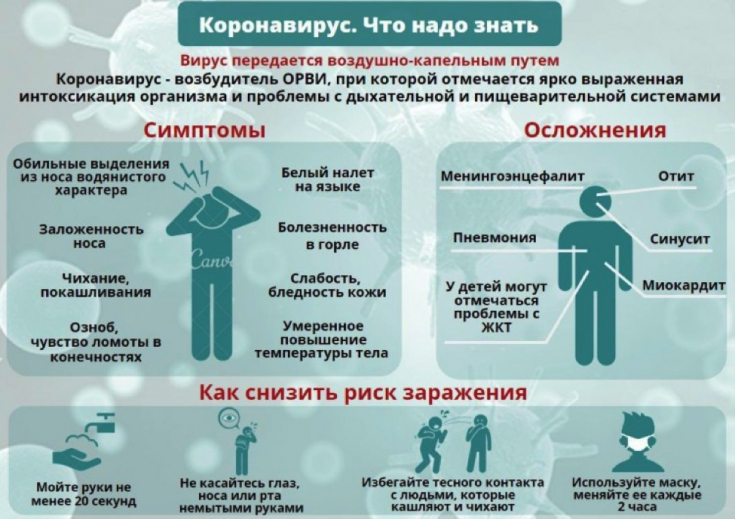
- Clinical presentation of coronavirus infection
- incubation period and timing of spread in case of coronavirus
- Characteristics of protective equipment for coronavirus infection
Clinical picture of coronavirus infection
The American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine published a study involving 16 patients with COVID-19 (mean age of patients was 35.5 years).
Follow us on Instagram!
The studies were conducted from January 28 to February 9, 2020 in a Beijing hospital. The main symptoms of the disease in the study group of patients were: fever (in 14 of 16 patients), cough (11/16), sore throat (5/16) and shortness of breath (2/16). Patients were treated with various drugs, depending on the clinical picture, as well as indications and contraindications for a particular patient: 15 patients received alpha-interferons along with antiviral drugs and antibiotics: oseltamivirin (1/16), lopinavir / ritonavir (11/16) , acyclovir (1/16), moxifloxacin (5/16), methylprednisolone (2/16), gamma globulin (2/16), vancomycin (1/16) and meropenem (1/16).
Read also: What determines the body's susceptibility to viral diseases?
Patients were discharged from the hospital with confirmed virus-negative status using two consecutive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests .
Incubation period and timing of spread in coronavirus
The time from infection to the onset of symptoms (incubation period) averaged 5 days (IQR 1-6 days) for 15 out of 16 patients. The duration of symptomatic viral illness was 8 days (IQR 6.25-11.5 days ). Half of the patients (8/16) remained "virus-positive"; for more than 8 days, even after symptom relief.
Study author Lixin Khe, MD, professor at the College of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, recommends continuing quarantine for an additional 2 weeks after recovery, as patients with COVID-19 may remain contagious even after they recover.
Asymptomatic patients and those who have recently recovered should be treated with the same care as symptomatic patients.
The researchers noted that the patients who participated in the study had moderate and mild forms of coronavirus infection and recovered in a fairly short time, therefore, it has not been proven at the moment, whether similar results will be true for a more vulnerable cohort patients, which includes, for example, older people and people with impaired immune systems.
Characteristics of protective equipment for coronavirus infection
In connection with these data, even when in contact with patients who are clinically healthy or have confirmed results of a coronavirus infection, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment, in particular when providing cosmetic and dermatological services.
Follow our news on Facebook!
These tools must have the following characteristics:
- Surgical masks: Made from odorless, hypoallergenic non-woven material. The outer and inner surfaces should be of different colors, fastened with elastic bands, with a retainer on the bridge of the nose. Masks should not obstruct free breathing.

- Respirator: must be made of non-woven filter material, equipped with a nose clip (nose clip) and nose obturator. The inside of the respirator must be made of soft, hypoallergenic non-woven material.
- Safety goggles: clear plastic lenses with an anti-fog and anti-scratch coating. Protective goggles for multiple use must be resistant to cleaning and disinfection.
Read also: Viral pneumonia: what is typical for different types of viruses. Part 1
Open UV irradiators can only be used as an additional method after surface treatment with disinfectant solutions. The use of shielded UV irradiators is an effective means for air disinfection in case of infectious diseases transmitted by air. The SARS-CoV-2 virus is contained in rather large droplets of mucus, is released during sneezing and coughing, therefore, for disinfection in foci of possible infection, it is recommended to use disinfectants with specific activity against RNA-containing lipophilic viruses.
This activity is determined during the state registration of a disinfectant. The disinfectant concentrations and exposure times recommended by the manufacturer should also be observed.
More relevant information on our YouTube-channel:







Add a comment