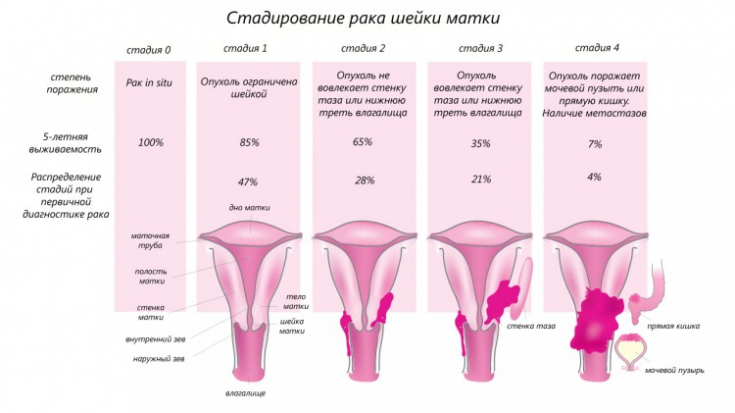
Cervical cancer is one of the most common pathologies in women after breast cancer. Planning the volume of irradiation, in which the primary tumor and the areas of its regional distribution are subject to maximum destructive influence with a minimum load on critical organs (rectum, bladder), is the main task of therapy for cervical neoplasms.
However, the radiotherapy program for these patients involves large volume irradiation with high therapeutic doses on the verge of tissue tolerance.
Learn in the article on estet-portal.com about the main methods of preventing radiation complications in cervical cancer radiotherapy.
Radiation therapy for cervical cancer
The radical radiotherapy program for patients with cervical cancer involves large volumes of radiation with high therapeutic doses.
Follow us on Instagram!
The results of such treatment often remain disappointing. Patients with cervical cancer mainly die from the progression of the underlying disease in the pelvic area, secondary obstruction of the ureters, which leads to renal failure, and in 4.4% of cases, distant metastases develop.
Characteristics of methods for diagnosing breast neoplasms
Combination of radiation therapy with radiomodulating cytostatic drugs or with systemic polychemotherapy (PCT) has a positive effect on the results of complex treatment.
However, such interactions can lead to increased manifestations of both general and local toxicity over time.
The number of unpredictable individual reactions may also increase.
Complications of cervical cancer treatment
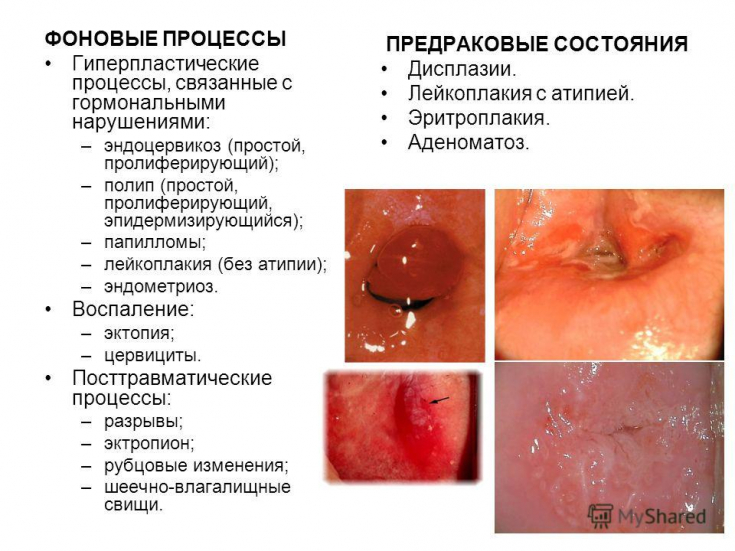
According to clinical signs, complications of radiation therapy for cervical cancer are divided into general and local. Indicators of general toxicity include: the degree of myelosuppression, the level of liver enzymes and blood coagulation indicators, the dynamics of the level of bilirubin, creatinine and urea in the blood serum, as well as the severity of symptoms such as malaise, nausea, vomiting. Local toxicity is characterized by the frequency and manifestations of dermatitis, cystitis, rectitis, colpitis.
Polycystic ovary syndrome increases the risk of developing neoplasms
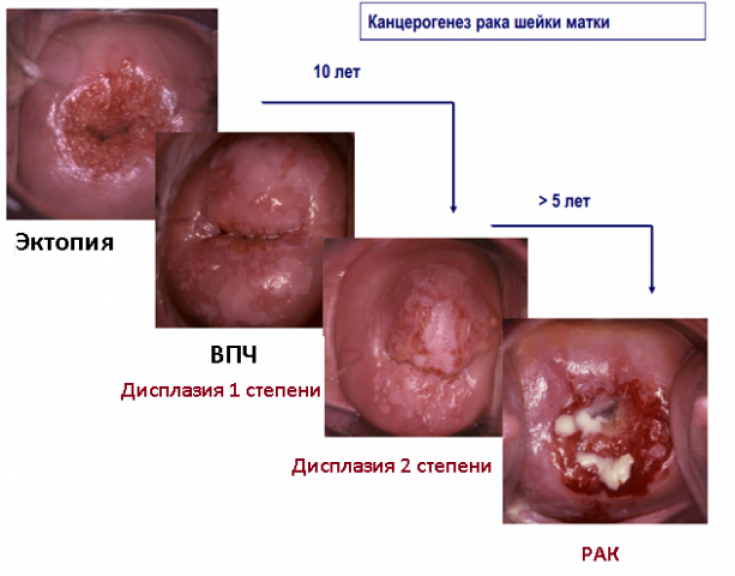
Local complications of radiation therapy are divided into early and late complications according to the time of occurrence. Early − these are the consequences of the influence of radiation on the genetic apparatus of cells undamaged by the tumor process, slowing down of reparative processes and functional disorders, primarily circulatory disorders that develop during radiation therapy and / or in the next 90-100 days after its completion.
Such reactions are usually temporary and reversible.
The mechanism of development of late radiation injuries is the dysfunction of the circulatory and lymphatic systems, namely, vascular damage during radiation therapy. Due to deep histochemical and histological changes, late radiation complications tend to progress.
The frequency of early radiation catarrhal and membranous epitheliitis of the bladder, rectum and vagina, according to the world's leading cancer clinics, is 10-80%. Radiation injuries of the small pelvis and rectum form the basis of late radiation pathology in this group of patients and determine the quality of their future life. The frequency of late radiation reactions of the bladder and rectum, according to different authors, ranges from 5-10% to 45-50%.
Chronic endometritis: is it a factor in IVF refusal?
Prevention of radiotherapy complications
The risk of radiation complications naturally increases with the increase in the dose received during treatment. A dose fractionation regimen is very important in predicting late radiation complications. Increasing the single focal dose (SDO), reducing the time intervals between irradiation sessions increases the risk of radiation complications. On the contrary, a decrease in the ROD, its fragmentation during the day, the use of split courses of radiation reduces the likelihood of the formation of late radiation damage.
Prevention of complications after radiation therapy should include a set of radiological measures combined with local and systemic therapeutic effects. Most often, radiation cystitis occurs.
Such patients are recommended anti-inflammatory, analgesic, decongestant, antioxidant and fibrozolytic therapy (instillations into the bladder with antibiotics, dexamethasone and lidocaine), and for the prevention of infectious complications − systemic antibiotic therapy.
A new group of solutions for instillation is being intensively studied in radiation cystitis, capable of strengthening the tissue frame of the bladder wall, thereby creating conditions for self-restoration of the physiological barrier properties of the urothelium.
One of the most commonly used representatives of this class of drugs are hyaluronic acid preparations, which is part of the urothelium, participates in the process of cell proliferation and is the basis of the connective tissue, ensuring the integrity and basic physico-chemical properties of the lamina propria and submucosa , thereby preventing damage and ensuring the restoration of all components of the bladder mucosa.
Preoperative diagnosis of breast neoplasms
For the purpose of prevention and treatment, it is recommended to use accompanying therapy, which includes: antiemetics, bladder instillations, therapeutic fat microclysters with vitamin mixtures, detoxification, hemostimulating and symptomatic therapy in the course of radiation therapy.
A complex of therapeutic and preventive measures, including a combination of local and systemic effects, should be included in the multipurpose prevention of complications of radiation therapy.
Preservation of reproductive function in gynecological pathology







Add a comment