Treatment of systemic scleroderma for each patient must be selected individually depending on the form, stage and severity of the course of the disease, as well as the localization of lesions, especially in view of the high degree of spontaneous remission of some forms of the disease. The goal of therapy is to prevent further development of sclerosing inflammation. There are indications for therapy, as a rule, in the presence of signs of active inflammation, it is almost impossible to influence the formed scar therapeutically. What are the main principles of treatment of systemic scleroderma?
The use of anti-inflammatory therapy in the treatment of systemic scleroderma
The advisability of prescribing high doses of penicillamine (750-1000 mg per day and above) to patients with scleroderma is currently controversial.
Basic principles of treatment of systemic scleroderma:
- anti-inflammatory therapy;
- systemic therapy;
- physiotherapy methods;
- surgical methods.
Anti-inflammatory therapy. There is good experience with local glucocorticoids (classes II & ndash; III), local calcipotriol. Vitamin D derivatives have an immunomodulatory effect (suppress the activation and recruitment of T-cells) and block the proliferation of fibroblasts. /kg of body weight per day or pulse therapy at a dose of 30 mg/kg of body weight for three days per month).
What can cause systemic scleroderma?
The main methods of treatment of systemic sclerodermaIn linear forms of scleroderma, systemic therapy should be started early to avoid further consequences of the disease. In addition, with a widespread lesion, physiotherapeutic measures are indicated (therapeutic exercises, manual lymphatic drainage). What are the criteria for the effectiveness of the treatment of systemic scleroderma, read further on estet-portal.com. Surgical measures are advisable only in the case of a confirmed inactive stage of the disease. This applies to both orthopedic measures (lengthening
Achilles tendon, epiphyseodesis to equalize the difference in leg length), and plastic surgery measures (for example, with hemiatrophy of the face).
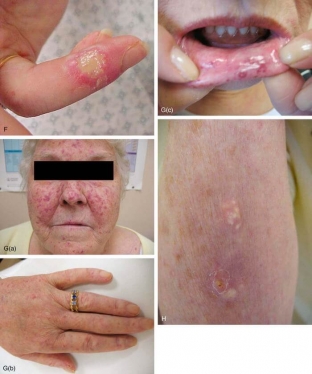
Patients withPhysiotherapy and surgical methods in the treatment of systemic scleroderma:localized scleroderma do not require a special diet. In case of damage to the limbs, it is necessary to avoid excessive physical exertion, sudden movements, shocks and shocks.
- Physiotherapy treatment is carried out under the supervision of a physiotherapist.
- Phonophoresis, hyaluronidase electrophoresis and
- therapy with laser radiation of the red range (wavelength 0.63 & ndash; 0.65 and 0.89 microns) are used. Therapeutic exercises and massage are especially recommended for patients with a linear form of scleroderma with limited movement in the joints and the formation of contractures.
- Surgical treatment of systemic scleroderma is necessary in the presence of
- flexion contractures and deformities of the body (head, joints, limbs). If there are cosmetic defects, plastic surgical correction is indicated.
- Surgical interventions should be performed in the inactive stage of localized scleroderma (in the absence of disease activity for several years).
The criteria for the effectiveness of the treatment of systemic scleroderma are the cessation of disease progression, resolution or reduction of Patients with localized scleroderma should avoid excessive sun exposure, trauma, hypothermia and overheating, colds, stressful situations, unreasonable use of drugs.
The prognosis of the disease depends on the form of scleroderma. Thus, in 50% of patients with plaque forms, the process clinically regresses within about three years, or at least signs of softening of the foci are observed.In the case of deep forms, this occurs on average after five years. After linear and deep forms, ugly scars often remain. The transition to progressive systemic sclerosis occurs only in the case of pansclerotic scleroderma.
Thus, localized scleroderma remains one of the most urgent problems of modern medicine due to its wide distribution, variable clinical course, disease of people of the most able-bodied age and refractoriness to many methods of therapeutic intervention. An individually tailored comprehensive approach to the treatment of systemic scleroderma for each patient, depending on the form, stage and severity of the course of the disease, as well as the localization of lesions, will prevent further development of sclerosing inflammation.







Add a comment