Pyoderma is a pustular skin disease that occurs when pathogens of a pyogenic infection penetrate and when the overall resistance of the body is weakened. They are among the most common skin diseases, affect various groups of the population, and can be severe. Currently, pustular skin diseases are the most common dermatoses. The occurrence and course of these diseases depends on the relationship of the microorganism and the infected macroorganism. Find out the causes of pyoderma at estet-portal.com.
Which microorganism is the most common cause of pyoderma?
The most common cause of pyoderma (pyon - pus, derma - skin) are microorganisms such as staphylococci, streptococci, less often - Proteus vulgaris, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, mycoplasma, E. coli. In the study of the normal microflora of the skin, the greatest contamination with staphylococci was revealed. Read more about these bacteria on estet-portal.com. At the same time, it turns out that the skin of the folds, subungual spaces, mucous membranes of the nose and throat is contaminated most of all, which can serve as a source of endogenous infection.
Due to the fact that the surface of the skin contains a lot of fatty and protein ingredients, it creates favorable conditions for the vital activity of various microorganisms, the skin is never sterile.
The permanent representatives of the bacterial flora of the skin include white staphylococcus aureus and epidermal staphylococcus aureus. At the same time, to establish the cause of pyoderma, bacteriological studies are carried out, as a result of which the presence of various microorganisms that do not belong to the permanent bacterial flora is often detected on the surface of skin. The most common non-permanent representatives of the bacterial flora of the skin surface include various varieties of staphylococci and streptococci, pseudodiphtheria bacilli.
Staphylococcus aureus is the main cause of pyoderma. Characteristics of Staphylococcus
Staphylococci are currently well studied. They are cells of a regular spherical shape with a diameter of 0.5–1.5 µm. Staphylococci are Gram-positive and do not form spores. In the process of life, staphylococci secrete an exotoxin that has the ability to lyse human erythrocytes. The pathogenicity of staphylococcal cultures is always associated with coagulase activity.
Coagulase is an exoenzyme that is easily destroyed by proteolytic enzymes, inactivated by ascorbic acid. Coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative pathogens can be found in pyoderma. Coagulase-negative pathogens, in addition, are currently considered as probable causative agents of gram-positive sepsis.
When developing therapeutic and preventive measures, after establishing the cause of pyoderma, it must be taken into account that staphylococci have a high degree of survival in the external environment.
Staphylococcus characteristic:
- they tolerate desiccation well, keep in dust;
- spread with airflow;
- suppress the functions of the reticulohistiocytic system;
- The ways of transmission of staphylococci are very diverse: transmission by airborne droplets and contact-household routes, etc. is possible;
- carriage of streptococci is much less common;
- facultative anaerobes form endo- and exotoxins, enzymes;
- exotoxins have cytotoxic, immunosuppressive and pyogenic effects, erythrogenic activity.
Streptococci produce deoxyribonuclease, hyaluronidase, streptokinase and other enzymes that provide optimal conditions for the nutrition, growth and reproduction of microorganisms, which is the cause of pyoderma.
What are the contributing factors for the development of pyoderma?
In the pathogenesis of pyoderma, a decisive role is played by a decrease in local and general antibacterial resistance of the organism. The integrity of the stratum corneum, the presence of a positive electrical charge between the bacterial cells and the skin provide a mechanical barrier to the introduction of pyococci. The discharge of sweat and sebaceous glands with a high concentration of hydrogen ions (pH 3.5–6.7) has bactericidal and bacteriostatic properties. Such a "chemical mantle" is regulated by the autonomic nervous system and endocrine glands. Disruption of its work to some extent is the cause of pyoderma.
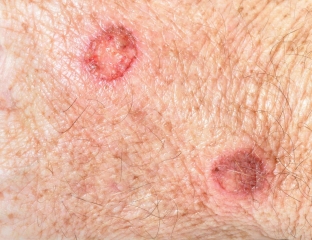
The most significant exogenous factors provoking the development of pyoderma are: skin pollution, especially when in contact with grass, dry skin, aggressive chemical agents, temperature irritants, etc.
Endogenous factors and causes of pyoderma include overwork, unbalanced nutrition, especially leading to hypovitaminosis, chronic intoxication, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, foci of chronic purulent infection, immune imbalance, endocrine diseases.
In particular, it is known that pyoderma is most severe and torpid in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Other factors that weaken the protective, antibacterial function of the skin include metabolic disorders that reduce resistance to bacterial agents, diabetic changes in blood vessels, xxxx>trophic disorders associated with diabetic polyneuritis, as well as dry skin, itching and other subjective sensations.
Thus, the main and frequent causes of pyoderma are staphylococci and streptococci, which provoke the development of staphylococcal pyoderma and streptoderma, which you can read more about in the following articles. Also read the treatment of pyoderma on estet - portal.com.






Add a comment