Plastic surgery – these are not only aesthetic operations, with the help of which doctors can significantly improve the appearance of the patient. A large percentage of surgical interventions in plastic surgery are reconstructive operations that allow you to restore the lost anatomy and physiology of certain parts of the body. To restore the integrity of the skin, artificial grafts or skin flaps are used. One of the most common complications that occur after such operations is graft rejection. On estet-portal.com read about the main reason for this condition – acute circulatory disorders in transplanted tissues.
Acute circulatory disorders as a cause of graft rejection
Acute circulatory disorders – one of the most common causes of poor outcome after reconstructive surgery.
Depending on the mechanism of occurrence, acute circulatory disorders can develop according to the peripheral and central type.
In the first case, blood supply disturbances occur in those areas of transplanted tissues that are the most distant from the place where the vascular pedicle enters. This occurs as a result of a critical decrease in perfusion pressure in them, while the inflow and outflow of blood through the central vascular highways is preserved. Disorders of the central type are characterized by blockade of the vessels feeding the flap, which may be associated with thrombosis of superimposed anastomoses, vasospasm, or mechanical compression of the feeding pedicle. In all cases, the result of the cessation of nutrition of the transplanted tissue is their acute ischemia and necrosis.
Acute circulatory disorders during flap transplantation:
- causes of acute circulatory disorders of the central type;
- causes of acute circulatory disorders of the peripheral type;
- methods of treatment of acute circulatory disorders in the transplanted flap.
Causes of acute circulatory disorders of the central type
Acute circulatory disorders of the central type occur during transplantation of tissues with an axial blood supply. They begin with mechanical compression of the veins, which ensure the outflow of blood from the transplanted tissue areas. The main reasons for this condition are as follows:
- development of postoperative tissue edema, resulting in compression of the vascular pedicle;
- compression of the graft and its vascular pedicle under the weight of the limb itself;
- mechanical pressure of dressings or plaster splints;
- Tissue displacement and compression of the vascular pedicle as a result of a change in the position of the limb joints close to the graft.
Acute circulatory disorders of the central type are manifested by rapidly developing edema of transplanted tissues, cyanosis of the skin, as well as a sharply accelerated symptom of a disappearing spot.
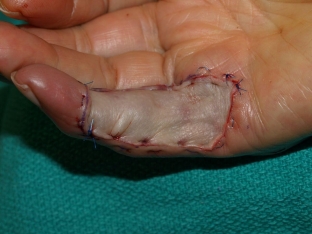
Causes of acute circulatory disorders of peripheral type
Acute circulatory disorders of the peripheral type develop in such cases:
- when taking too large a flap, as a result of which the main vascular bundle extends beyond the pool;
- in case of insufficient perfusion pressure in the artery supplying the flap;
- in case of violation of vascular connections between parts of the tissue complex as a result of incorrect surgical technique;
- in case of excessive hypoxia of skin flaps;
- when creating excessive tension during suturing the surgical wound.
Clinically, these circulatory disorders may present with pallor and cyanosis of the transplanted tissues, as well as a delayed or absent symptom of a vanishing spot.
Methods for the treatment of acute circulatory disorders in the transplanted flap
The choice of treatment for acute circulatory disorders in transplanted tissues depends on many factors. With a peripheral type of violations, it is necessary, first of all, to completely eliminate them & nbsp; cause, & nbsp; as well as to treat metabolic disorders that develop in poorly supplied tissues. The possibilities of treatment of acute circulatory disorders according to the central type are determined by the timing of their diagnosis. With early detection, removal of sutures or incision of a tight bandage is often sufficient to restore normal blood flow to the graft. If simple procedures are ineffective, it is necessary to conduct a revision of the vascular bundle with the restoration of the patency of its elements.
Timely detection and elimination of the causes of acute circulatory disorders in the transplanted flap is the basis for the treatment of such conditions.
Early and effective prevention of such complications will help to avoid their occurrence.







Add a comment