Yersiniosis is an anthroponotic intestinal infection that manifests itself as toxic-allergic reactions and is characterized by multifocal manifestations. A person can become infected from pets, dogs and rodents. The symptomatology of yersiniosis consists of many non-specific symptoms and syndromes, the simultaneous identification of which is very important in making a diagnosis. What symptoms of yersiniosis should alert you to the possibility of an intestinal infection caused by yersinia?
How can I get yersiniosis? Risk groups
It is possible to contract yersiniosis by eating animal products that are not processed enough. Infection is also possible through water sources that are contaminated with the feces of infected animals. The contact-household way is implemented in families with a low hygienic culture. Often, infection with yersiniosis is carried out through unwashed vegetables or fruits, as well as against the background of a lack of habit of washing hands before eating.
According to clinical manifestations, yersiniosis is divided into generalized, secondary - focal and gastrointestinal forms. The incubation period of pathogenic bacteria is up to 6 days. The manifestations of the disease are expressed by several syndromes.
What are the main symptoms of yersiniosis? Forms of yersiniosis
Severe intoxication, fever up to 400C, general weakness, chills, headaches, aching joints and muscles are more often detected. Appetite is significantly reduced, damage to the central nervous system may be noted. The fever period lasts at least a week. The gastrointestinal form is characterized by the predominance of dyspeptic phenomena – nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea.
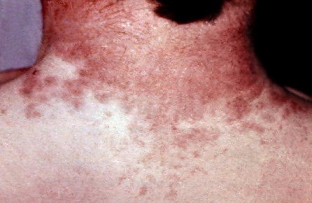
Sometimes exanthema can appear with yersiniosis. The rash has a maculopapular character, large-spotted or small-spotted rashes can appear on different parts of the skin. The most frequent and characteristic feature of the rash in yersiniosis – sock syndrome and «gloves». The rash may be accompanied by a burning sensation in the palms, leaving the skin flaky.
Clinical forms of yersiniosis development:
- Some forms are accompanied by the development of arthropathic syndrome. The joints of the extremities are affected – hands, feet, knees and elbows. They become painful on palpation, edematous, active movements in the affected joints are somewhat limited.
- The gastrointestinal form of yersiniosis is the most common in practice. The disease proceeds very similar to infectious - toxic lesions of the intestine. Intoxication may develop simultaneously or precede dyspepsia. Against the background of severe intoxication, the likelihood of developing hepatosplenomegaly increases.
- The generalized form is characterized by various symptoms. There is a critical level of temperature increase, as well as an intensely expressed general toxic syndrome.
- Approximately 10-20% of cases of yersiniosis occur as erythema nodosum. In this case, subcutaneous nodules are formed on the legs, buttocks and thighs. They are large and painful. Their number can reach more than a dozen. After a couple of weeks, the nodules resolve.
General characteristics of the course of yersiniosis. Possible Complications
A common characteristic sign of damage to organ systems in yersiniosis is an undulating course and a tendency to vegetative-vascular pathologies.
Yersiniosis is dangerous for its complications. These are hepatitis, myocarditis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, the development of surgical pathologies (intestinal obstruction, adhesive disease), perforation of the intestinal wall, appendicitis and peritonitis, pathologies of the nervous system, excretory organs and the musculoskeletal system.
Thus, if a patient has a persistent fever for several days, which is combined with severe intoxication, dyspeptic syndromes or rashes, it is important to clarify the epidemiological history.







Add a comment