Treatment of urinary tract diseases during pregnancy requires a careful approach by the clinician, as many drugs have a negative effect on the development of the fetus.
During pregnancy, the size of the uterus increases and the pressure on the ureters and kidneys increases, which contributes to rapid infection of the urinary tract.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com about the features of the treatment of pyelonephritis during pregnancy with positions on the safe effects of drugs on the fetus, as well as risk factors for the development of postpartum urinary tract infections.
- Treatment of acute pyelonephritis during pregnancy
- Drugs for Gestational Pyelonephritis: Evidence-Based Medicine
- Instrumental treatment of pyelonephritis
- Complications of pyelonephritis during pregnancy
- Prevention of acute pyelonephritis in pregnant womenх
Treatment of acute pyelonephritis during pregnancy
Treatment of acute pyelonephritis of pregnant women is based on restoration of the outflow of urine from the kidney.
For this, positional therapy is used: the patient is recommended to lie on a healthy side with the lower end of the bed raised, to take a knee-elbow position.
Follow us on Instagram!
Sometimes this simple procedure can reduce the severity of inflammation in the kidney by reducing pressure on the ureter. In parallel, antibacterial therapy is carried out, for which the least toxic antibacterial drugs are chosen, especially before the 12th week of pregnancy.
After 12 weeks of pregnancy, antibiotics can be more widely used, in particularand aminoglycosides.
This is due to the fact that the laying of the main organs and systems of the fetal body ends before the 12th week.
Drugs for Gestational Pyelonephritis: Evidence-Based Medicine
For the treatment of acute pyelonephritis of pregnant women, according to EAU – European Association of Urology (Evidence A), recommended:
- ceftriaxone (1-2 g IV or IM every 24 hours);
- aztreonam (1 g every 8-12 hours);
- piperacillin/tazobactam (3.375-4.5 g every 6 hours);
- cefepime (1.0 g every 12 hours);
- imipenem/cilastatin (500 mg every 6 hours);
- ampicillin (2 g every 6 hours);
- gentamicin (3-5 mg/kg of body weight per day in 3 divided doses).
Popular aesthetic procedures during pregnancy: pros and cons
If the specified conservative therapy is ineffective, and the examination revealed violations of the outflow of urine from the affected kidney, ureter catheterization.
Usually, the catheter can be passed without interference through the entire ureter to the renal pelvis, and the discharge of urine from it in frequent drops or even a stream begins at a height of 13-20 cm from the bladder, that is, just above that level m, where the uterus presses the ureter to the narrow bone ring of the pelvis.

Instrumental treatment of pyelonephritis
In most pregnant women with acute pyelonephritis, with the help of a catheter or catheter-stent, which is left in the ureter for several days, it is possible to eliminate the obstruction of the upper urinary tract, to achieve sufficient evacuation of urine, which leads to the subsidence of the inflammatory process. If this short-term renal pelvis catheterization fails, only catheter-stent.
Effective treatments for gestational diabetes
The latter is often advisable to leave for several weeks after childbirth. If it does not provide sufficient evacuation of urine, and the kidney bowl remains enlarged, then percutaneous puncture − nephropyelostomy under ultrasound guidance.
Only very rarely, when the catheter fails to drain the upper parts of the TSS, do you have to surgery − pyelostomy or nephropyelostomy.
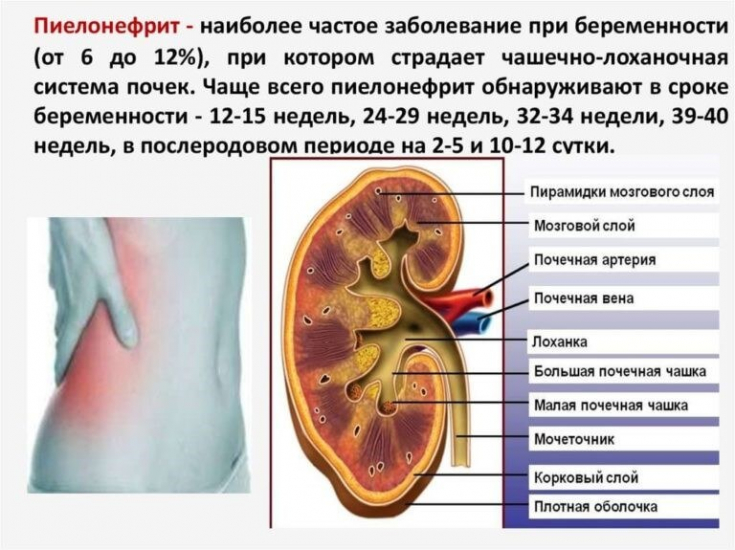
Complications of pyelonephritis during pregnancy
For most women, the physiological changes in the urinary tract caused by pregnancy disappear without any consequences after childbirth.
However, in those who have suffered acute pyelonephritis, urodynamic disturbances do not always go unnoticed.
Chronic pyelonephritis, less frequently – Urolithiasis and others
Methods for diagnosing rubella during pregnancy
So, pregnant women who have had pyelonephritis are much more likely to develop kidney diseases due to a long-term urodynamic disorder.25-30% of them show postpartum pyelonephritis, which can develop in the first days / weeks after birth, when the tone of the genitourinary tract is not yet fully restored.
Risk factors
for postpartum pyelonephritis include:
the effect of hormonal levels during pregnancy (3 months);- dilatation of the genitourinary tract (≈1.5 months);
- inflammatory diseases, primarily of the genital organs;
- complications of the postpartum period (hypotonia of the uterus, bleeding, etc.).
- In case of postpartum pyelonephritis, a
is performed, including X-ray and radioisotope examination, the purpose of which is − determination of the condition of the kidneys and urinary tract, as well as the identification or exclusion of any other causes of pyelonephritis (anomalies of the urinary system, tuberculosis, calculusc).

of acute pyelonephritis of pregnant women aimed at:
preventive treatment of chronic urinary infection;
Improve the flow of urine from the kidneys with positional exercises (intermittent use of the knee-elbow position; lying on the side, opposite side of the predominant expansion of the renal pelvis, with the lower end of the bed raised).- Prevention and treatment of toxoplasmosis: how to protect the unborn child
When performing these positional exercises, professional instruction of the patient by the doctor or obstetrician who is observing the pregnant woman is important.
In all positions indicated:
the pressure of the uterus on the ureters decreases;urine outflow improves;
- significantly reduced expansion of the renal vasculature.
- This
- is confirmed by ultrasound , under the control of which it is desirable to prevent pyelonephritis in pregnant women.








