Disorders of metabolism and metabolism can be genetically determined and manifest depending on the type of inheritance. Metabolic disorders against the background of a lack of the homogentisinase enzyme contribute to the incomplete breakdown of homogentisic acid, which has its own manifestations. This condition is called alkaptonuria. Pathology is characterized by the excretion of homogentisic acid in the urine and its deposition in the tissues. The first signs of alkaptonuria are manifested in childhood with specific symptoms. How does alkaptonuria manifest itself? What is the mechanism for the development of symptoms of alkaptonuria?
Causes and mechanism of development of clinical manifestations of alkaptonuria
Alkaptonuria is also called homogentisin aciduria and hereditary ochronosis. The pathology is based on a violation of the metabolism of tyrosine, which is characterized by the formation of an intermediate metabolite – homogentisic acid. Find out more about the symptoms of alkaptonuria at estete-portal.com. The manifestations of the disease are polysystemic, therefore orthopedists, dermatologists, urologists, rheumatologists, geneticists and cardiac surgeons are involved in the treatment of alkaptonuria.
Alkaptonuria is an enzymopathy that is inherited in an autosomal fashion – recessive type. The mutation occurs on the long arm of the 3rd chromosome.
Homogentisic acid exchange characteristics:
- In a healthy person, homogentisic acid is an intermediate metabolite of phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolism.
- The acid is transformed into maleylacetoacetic acid under the action of homogentinase, with further cleavage to acetoacetic and fumaric acids, which are further involved in the cycles of biochemical reactions.
- When the enzyme homogentisic acid is deficient, it is not metabolized, turning into polyphenols.
- Polyphenols accumulate in connective tissues and are excreted in the urine.
Three main clinical manifestations of alkaptonuria
Alkaptonuria is manifested by the following symptom complex: arthropathy, aciduria and ochronosis. These clinical manifestations appear at different times. Thus, urine staining is observed from birth, joint damage begins after 40 years, and skin staining becomes pronounced by the age of 30.
Even in early childhood, you can notice the first signs of alkaptonuria – on the diapers of the child there are dark stains from urine that are not washed off. When passing urine for analysis, the collected urine in the jar quickly becomes brown.
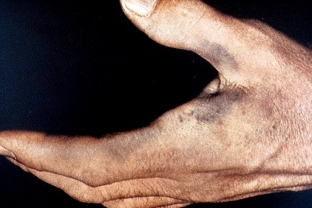
This child is at increased risk of developing pyelonephritis, calculous prostatitis, and urolithiasis. Manifestations on the part of the skin are the appearance of gray – brown pigmentation on the skin of the face, palms, neck, abdomen, groin and axilla.
A typical sign of alkaptonuria is a gray-blue coloration of the ears, their induration, as well as pigmentation of the sclera and conjunctiva.
The pigment is deposited in the cartilage of the larynx, which is manifested by shortness of breath, hoarseness of voice and swallowing disorders. With age, calcification of the valves of the heart and aorta occurs. The musculoskeletal system is affected with the development of deforming spondylosis of the lumbar and thoracic region. This contributes to the growth of lumbar lordosis, pain and stiffness of movements. Further, deforming osteoarthritis develops. Such changes are manifested by swelling, pain, impaired mobility, crepitus and the development of flexion contractures.
There is no etiopathogenetic treatment for alkaptonuria. Only symptomatic treatment is carried out in order to prevent excessive formation of homogentisic acid. A low protein diet is recommended for alkaptonuria.







Add a comment