To date, the statistics of skin lesions with neoplasms are disappointing. According to the World Health Organization, the incidence of skin melanoma is rapidly increasing, with an average of 132,000 new cases per year.
Melanoma – the most dangerous consequence of the degeneration of nevi. The neoplasm has an aggressive course and often ends in a fatal outcome in the later stages.
Several factors play a role in the occurrence of melanoma: skin phototypes one and two,, red hair and light eyes, a large number of moles, a family history of melanoma, and severe sunburn in childhood.
Melanoma can occur at any age, but is more common in women aged 40-60. On the estet-portal, read about the symptoms of degeneration of nevi into a malignant neoplasm, as well as the classification of melanoma and its predecessors.
Melanoma-dangerous nevi: clinical picture and localization of formations
Very often, melanoma is preceded by pigmented nevi, such as: nevus of Ota, dysplastic nevus, blue nevus, borderline nevus, Dubreuil's melanosis.
Dysplastic nevus precedes melanoma in 30-50% of clinical cases.
Dysplastic nevus is often an acquired formation with clear boundaries and heterogeneous color.
It is localized on the trunk, lower extremities and almost never on the face.
Blue nevus is characterized by small size, smooth edges and blue coloration. Often pigmented formation occurs on the face, upper limbs and buttocks.
Follow us on Facebook
The borderline nevus can be located anywhere, it looks like an irregular brown or black nodule with a purple tint.
Dubreuil's melanosis transforms into melanoma in half of the cases and occurs mainly on open areas of the skin in elderly women. In the case of malignancy of Dubreuil's melanosis, the disease proceeds more favorably and responds well to radiation therapy.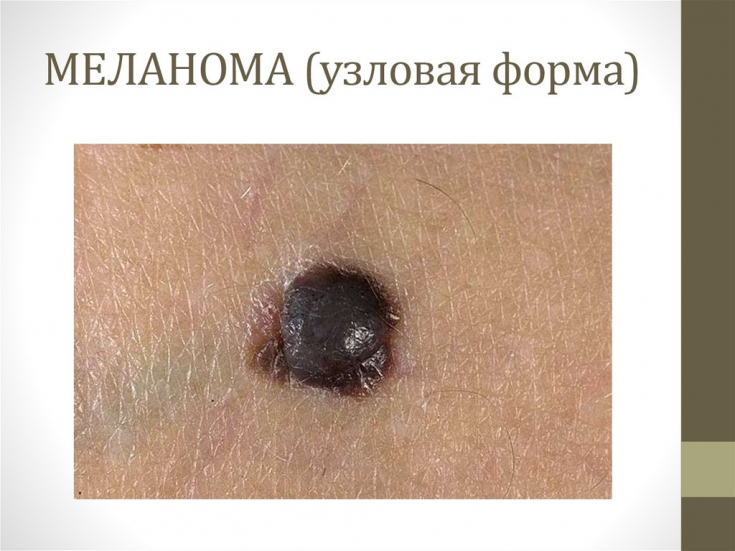
Clinical and anatomical forms of melanoma: features and localization
Melanoma – this is a neoplasm with a malignant course that develops from pigment cells – melanocytes.
There are several main clinical forms of melanoma:
1. surface;
2. nodular;
3. lentiginous;
4. acrolentiginous.
The most common form of melanoma – superficial, which is characterized by a two-phase flow and a favorable outcome.
This melanoma is characterized by exophytic and superficial growth. It is localized, as a rule, in the head and neck, as well as on the lower extremities.
Nodular melanoma is less common (15-30% of cases) and is characterized by a more malignant course. Presented as a flat dark blue or black nodule with frequent ulceration.
Acrolentiginous form is less common and spreads radially on the hands, feet, and under the nails.
Malignant lentigo is characterized by the appearance of small, yellow to black nodules, predominantly in the elderly. The neoplasm grows slowly and radially, the prognosis for this form is favorable.
Signs of malignant transformation of pigmented skin lesions
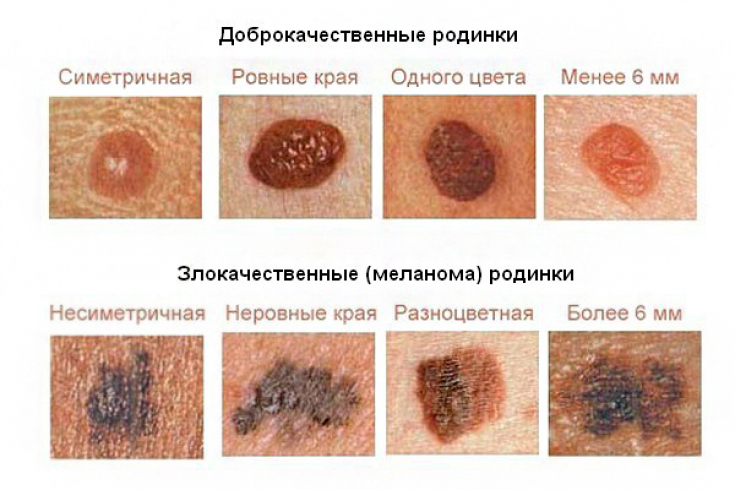
A special scheme (ABCDE) has been developed for the early diagnosis of melanoma.
It presents the main signs of malignant transformations of pigmented skin lesions, including:
• A (asymmetry) –shape change;
• B (borders) –fuzzy borders;
• C (color) - color change;
• D (diameter) - increase in size above 6 mm;• E (evolution) – evolution of the formation.In addition to these symptoms, bleeding, pain, peeling, ulceration and growth of benign formations should be added to dangerous changes.
However, a histological examination of the lesion is necessary to make a definitive diagnosis of melanoma.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Dermatology" section. You may also be interested in:







Add a comment