The course of a normal pregnancy suggests that the fertilized egg develops in the uterine cavity, however, there are cases when the pregnancy does not develop in the uterus.
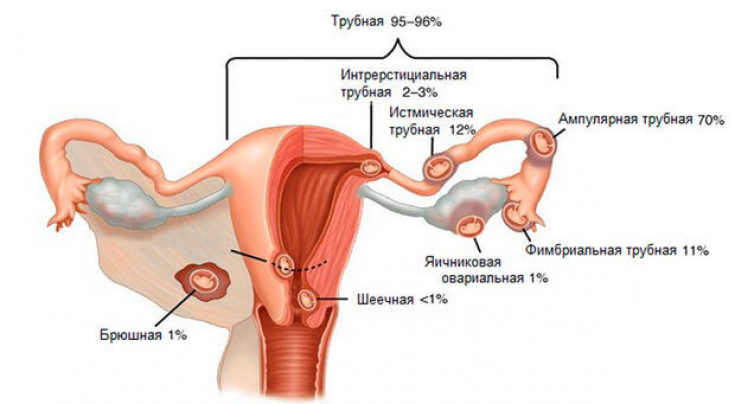
0.4% of ectopic pregnancies are precisely abdominal pregnancies.
In such cases, the embryo is implanted on the surface of the abdominal organs, peritoneum or omentum, which can have different consequences.
Read more on estet-portal.com what are the risk factors and causes of abdominal pregnancy.
- What is the mechanism of development of abdominal pregnancy
- Main causes and risk factors for abdominal pregnancy
- What are the features of the course of abdominal pregnancyand
What is the mechanism of development of abdominal pregnancy
During fertilization, a spermatozoon enters the ampulla of the fallopian tube, resulting in the formation of a zygote with an ovum membrane.
Further, the zygote advances under the influence of peristalsis of the fallopian tubes and fluctuations of the cilia of the tubular epithelium, while dividing processes occur simultaneously in the zygote.
Undifferentiated cells of the zygote are located near the common membrane.
Next, the cells divide into 2 layers: outer – trophoblast, and internal – embryoblast.
The embryo passes into the stage of blastocyst, goes to the uterine cavity, shedding its membrane, and the trophoblast plunges its villi deep into the endometrium, that is, implantation takes place.
What you need to know about your first IVF procedure
Main causes and risk factors for abdominal pregnancy
Abdominal pregnancy can develop in two cases.
1. If the embryo first attaches in the cavity of the fallopian tube, then rejection according to the type of tubal abortion, and while in the peritoneum, implants again on the surface of the omentum or other abdominal organs.
2. Also, abdominal pregnancy can develop if at the time of implantation, the ovum is in the abdominal cavity.
Main risk factors for abdominal pregnancy:
- presence of adhesions and/or disorders of the contractile activity of the fallopian tubes after surgical interventions;
- slow tubal peristalsis or tubal elongation in genital infantilism;
- inflammatory processes in the fallopian tubes and ovaries;
- Tubal endometriosis;
- long-term use of intrauterine devices and IVF;
- mechanical compression of the fallopian tubes by the tumor;
- some pathological processes in the thyroid gland and adrenal glands;
- an increase in the concentration of progesterone, which can slow down the peristalsis of the tubes.
Women who smoke have a 3.5 times greater risk of abdominal pregnancy than non-smokers. The reason for this is a decrease in the immune forces of the body, a high frequency of delayed ovulation when smoking, as well as a violation of the peristaltic activity of the fallopian tubes when smoking.
Many researchers single out stress as one of the main reasons for the development of abdominal pregnancy.
Stress conditions affect the contractile activity of the tubes, provoking anti-peristaltic contractions in them, in which the embryo remains in the tube, attaching to its wall.
Further after the tubal abortion it is again implanted on the organs in the abdominal cavity.
In the modern world, over the past decades, doctors have observed a tendency to postpone the birth of a child to 30 years or more, which significantly increases the incidence of abdominal pregnancy.
This happens because with age, the hormonal background changes, neurovegetative disorders appear, and the peristaltic abilities of the fallopian tubes decrease.
Women aged 35 have a 4 times higher risk of developing an abdominal pregnancy than women aged 25.
Read more of our statson Facebook!
What are the features of the course of abdominal pregnancy
The course of abdominal pregnancy depends on the place of attachment of the embryo.
If a fetus is implanted in a place where there ispoor blood supply, it will immediately die.
When a fetus is implanted in a site withan extensive network of capillaries and vessels, it develops as in normal gestation.
But, since the fetus is not protected in this case by the wall of the, the likelihood of congenital defects is much higher. Abdominal pregnancies quite rarely
are carried to term.The germination of the chorionic villi of large vessels contributes to the development of internal bleeding.
The introduction into the parenchymal and hollow organs of the placenta leads to serious damage
to these organs.Find out in our next article the main manifestations and symptoms of abdominal pregnancy,
as well as methods for its earlydiagnosis and treatment.
Pregnancy with endometriosis: the real possibilities of modern medicine







Add a comment