Prostatovesiculitis is an infectious disease that affects the prostate gland and seminal vesicles. The most common cause of its occurrence — gonococcal infection. The causative agent can penetrate into the affected area by a descending hematogenous route, or, more often, infection occurs through the urethra. Blood stasis in the pelvic organs, chronic infectious lesions of the genitourinary system, as well as factors associated with metabolic disorders can contribute to the development of the disease. Read more about the clinical picture and treatment of prostatovesiculitis on estet-portal.com in this article.
The main causes contributing to the development of prostatovesiculitis
Prostate vesiculitis is always preceded by an infection. This can be facilitated by a number of factors, among which the most significant are the presence of chronic diseases of the genital organs and disturbance of microcirculation of the prostate, which occurs with physical inactivity and overweight.
Perine injuries are a risk factor for the development of prostate vesiculitis.
This disease can occur as a result of metabolic disorders, due to malnutrition and lack of physical activity.
Prostatovesiculitis:
• basic methods for diagnosing acute and chronic prostatovesiculitis;
• clinical picture of acute and chronic course of prostatovesiculitis;
• prostate vesiculitis: an effective treatment regimen for the disease.
Basic methods for diagnosing acute and chronic prostatovesiculitis
Diagnosis of prostatovesiculitis begins with a general blood and urine test, which determines the increased content of leukocytes. At the second stage, a rectal examination of the prostate is performed, in which an enlarged and painful prostate gland will be palpated. The most informative diagnostic method — this is an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, including the study of the blood flow of the prostate. Among the mandatory studies for prostate vesiculitis are & nbsp; bacterial seeding of prostate secretion, on the basis of which an antibacterial drug can be selected for etiotropic treatment.
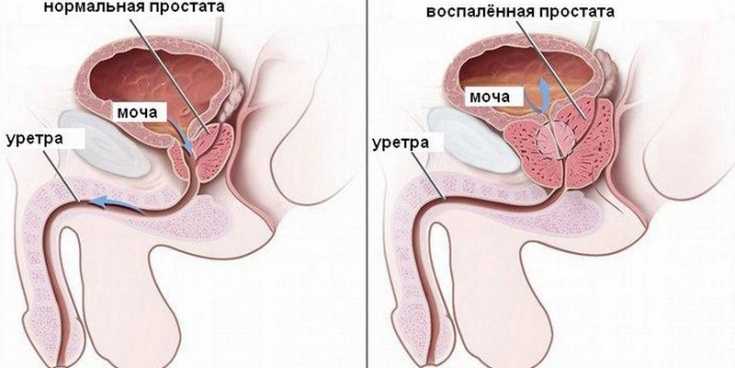
Clinical presentation of acute and chronic course of prostatovesiculitis
The development of prostatovesiculitis can be suspected on the basis of a characteristic clinical picture, which is manifested by such symptoms as:
• pain in the groin, which can radiate to the rectal area and increase with the act of defecation;
• violation of urination, which is accompanied by pain and a burning sensation in the bladder area;
• erectile dysfunction, the main manifestation of which — it painful ejaculation.
With chronic simple vesiculitis absent intoxication, and the symptoms of the disease are less pronounced.
Prostatovesiculitis: an effective treatment regimen for the disease
Prostatovesiculitis requires long-term and complex treatment. If fever is present, strict bed rest and broad-spectrum antibiotics are recommended. Mandatory point of treatment — this is the prescription of laxatives to relieve pressure on the prostate.
If a complication develops in the form of empyema of the seminal vesicles, a puncture is performed with the removal of pus and subsequent drainage.
Prostatovesiculitis is dangerous because in the absence of proper treatment, the disease becomes chronic.







Add a comment