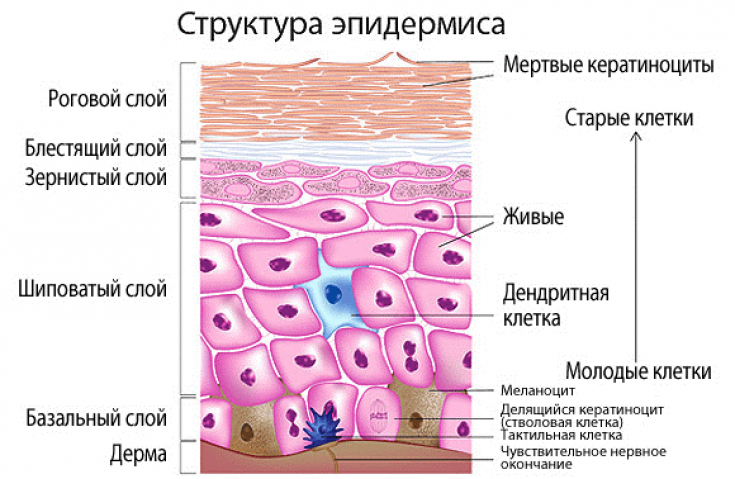
Innate skin immunity includes: skin physical barrier structures, immune cells (neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, natural killers, etc.) and antimicrobial peptides (AMPs). The synthesis of the latter is the primary mechanism of protection against harmful environmental factors and microbial invasion. In addition, these AMP groups stimulate the proliferation of keratinocytes and their migration, which is necessary for the healing of skin defects.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com how the immune function of the skin and vitamin D are related.
- factors that provide immune function of the skin
- suppression of immune function of the skin and vitamin D
- the role of vitamin D in certain inflammatory skin diseases
Factors that provide immune function of the skin
More than 20 proteins with antibacterial functions are found in the skin, but the main groups are β-defensins and cathelicidins.
Subscribe to our page on Facebook!
These proteins mediate antimicrobial activity by directly destroying the bacterial cell membrane and the virus envelope, as well as triggering various signaling pathways to initiate the host's immune response.
Sex hormone dysfunction in the development of acne
In intact skin, the level of antimicrobial peptides is low, however, when the integrity of the skin is broken or infection develops, it increases.
At the same time, there is an increase in local synthesis of vitamin D.
Many studies have shown that after treatment with vitamin D, the expression of defensins in keratinocytes and sebocytes increases. Vitamin D has also been reported to regulate AMP synthesis in several indirect ways, including by regulating the activity of serine proteases that break down these proteins. Suppression of immune function of the skin and vitamin D
In addition to regulating AMP synthesis in the skin, calcitriol (an analog of vitamin D) mediates local immunosuppression
by inhibiting antigen presentation, directly affecting Langerhans cells,or indirectly modulating cytokine production by keratinocytes. Recent studies have shown that vitamin D mediates local immunosuppression in the skin by inducing CD4 + CD25 + T-regulatory cells, preventing further antigen-specific proliferation of CD8 + T-lymphocytes and the production of interferon (IFN) γ.
Vitamin D plays an important role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis, which has been proven in many studies,
where deficiency or low levels of this substance were found in patients with this disease. Several case-control studies reported an inverse relationship between serum 25(OH)D levels and psoriasis severity. However, in a population study by Wilson , no difference was found in serum vitamin D levels between individuals with and without psoriasis.
Skin lesions in systemic lupus erythematosus It should be noted that the concentration of 25 vitamin D depends on race, nutrition, exposure to UV rays, therefore, the results of studies on this issue need
careful interpretation. The role of vitamin D in certain inflammatory skin conditions
Psoriasis is a chronic multifactorial pathology in which the leading role
is played by dysregulation of the skin's immune system, including infiltration of the skin with innate immune effector cells, abnormally high levels of AMP and intolerance to one's own DNA.
Neutrophils and natural killer cells present in psoriasis lesions are involved in the secretion of antimicrobial peptides and pro-inflammatory cytokines. The focus of psoriasis is also characterized by increased infiltration by T-cells, primarily
CD4 + T-helpers of type 1 (
Thus, in response to cytokines released by T-lymphocytes, keratinocytes secrete AMPs, pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6 and TNF), various chemokines and proteins. These soluble mediators act as chemoattractants for neutrophils and other immune cells. Excessive functioning of T-lymphocytes in conditions of psoriasis and a decrease in their suppressive & nbsp;
function lead to a stable inflammatory process.Emollients and food allergies: what's the connection?
Vitamin D treatment can effectively reduce the symptoms of psoriasis, which has been confirmed by many clinical studies. Finamor et al. showed that in patients with psoriasis treated with 35,000 IU of vitamin D3 1 r / day for 6 months, there was a significant improvement in the index of area and severity of psoriasis (Psoriasis area severity index score, PASI) concomitant with a marked increase in serum vitamin D levels.
Many studies have also shown excellent efficacy and safety, concomitant with a marked increase in serum levels of vitaminD, as well as the safety of the use of vitamin D analogues ( calcipotriol, tacalcitol, maxacalcitol) in the treatment of psoriasis. More useful information on our YouTube channel






