Polycystic ovary syndrome – this is a pathology of the structure of the ovaries, which develops against the background of hormonal changes in the female body, as a result of which the function of the ovaries is disturbed in the form of manifested anovulation and hyperandrogenism. Pathology is quite common, more than 10% of women of reproductive age are diagnosed with this.
Polycystic ovaries – this is the most common cause of menstrual irregularities that leads to infertility.
There are three forms of polycystic ovaries: with "typical" form pathology occurs directly in the ovaries and is accompanied by hyperandrogenism, with "central" form, dysfunction of the central parts of the reproductive system and neuroendocrine disorders come to the fore, with a "mixed" form, both ovarian and adrenal hyperandrogenism are manifested.
Causes of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Among scientists there is no consensus on the account of the trigger mechanism for the development of polycystic ovaries, so research in this area is still ongoing today. It is known that with polycystic ovary syndrome in a woman's body, the amount of the pancreatic hormone insulin increases significantly.
In this case, insulin receptors do not undergo any changes, but the utilization of glucose by the cell is significantly reduced. It has been experimentally proven that insulin affects the proliferation of granuloma cells, thus significantly increasing the production of androgens.
Learn: Modern ways to solve infertility. What Doctors Can Offer to Patients
In addition, disorders of the nervous system, as well as genetic predisposition, play a role in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome.

Clinical presentation of polycystic ovary syndrome
The main manifestations of polycystic ovaries are signs of a violation of the menstrual and reproductive functions of a woman. There are certain features of symptoms in different forms of polycystic ovaries.
For a "typical" forms are characterized by oligomenorrhea, secondary amenorrhea is much less common. In this case, the cycle is broken even from the period of menarche, which occurs at the normal age of 11-13 years. From the same moment, manifestations of hirsutism begin in the form of excessive hair growth on the face and along the white line of the abdomen. From adolescence, body weight increases significantly with a uniform distribution of subcutaneous fat.
When the "central" form» polycystic ovarian menarche also occurs at a normal age, but the cycle is irregular, characterized by oligo- and amenorrhea. Pregnancy may occur, but ends in spontaneous abortion in the early stages, which leads to secondary infertility.

Hirsutism appears no earlier than 3 years after the onset of disorders, symptoms of adrenal pathology are also characteristic – stretch marks on the skin, brittle nails, hair loss. Obesity is the main complaint in this form of polycystic ovary syndrome, fat deposits are concentrated in the lower abdomen, on the hips, shoulder girdle.
Find out: Emergency contraception. Why You Shouldn't Abuse
"Mixed" the form of polycystic ovary syndrome is characterized by a late onset of the first menstruation, the cycle is disturbed by the type of secondary amenorrhea, while infertility is most often primary, that is, pregnancy does not occur. Hirsutism is observed in absolutely all patients with this form of polycystic ovaries and begins along with the period of menarche. Excessive hair appears on the thighs, legs, abdomen and face. Obesity is extremely rare.
Methods for diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome
The first and, of course, an important point in the diagnosis of polycystic ovaries is a thorough history taking. It is necessary to find out when the patient had menarche, what was the nature of the menstrual cycle, whether the pregnancy occurred and, if so, how it ended.
Since what period did the signs of hirsutism begin to appear and body weight increase. All this information helps determine the form of polycystic ovary syndrome. Using laboratory methods, the hormonal panel is determined. A ratio of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones of more than 3.5 indicates polycystic ovaries. For "mixed" a form of polycystic ovaries is characterized by an increase in the levels of adrenal hormones.

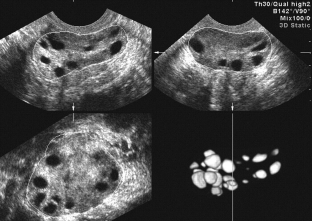
In all forms, the concentration of freely circulating testosterone increases, as directly indicated by the severity of hirsutism. An important point in the diagnosis is the determination of insulin and blood glucose. For polycystic ovaries, the value of the index of the ratio of glucose to insulin is more than 3. A very highly informative method is transvaginal ultrasound of the ovaries.
Read: Erogenous Zone Sensitization: Female Sensitivity Fillers
Ultrasound criteria for polycystic ovary syndrome
- increase in ovarian volume (up to 20 cm³);
- ovarian stromal hyperplasia (25% of volume);
- the presence of more than 10 atretic follicles, located on the periphery and covered with a thickened capsule.
Methods of treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome
There are two main methods of treatment for polycystic ovaries: conservative and surgical. Before starting any of them, normalization of body weight is an obligatory moment, since reducing excess weight is often enough for the onset of ovulation and normalization of hormonal levels.
The effectiveness of the conservative method of treatment is no more than 50%, while the effectiveness of the surgical one reaches 90%. Conservative treatment is mainly used to eliminate the symptoms of PCOS, such as excessive hair growth and acne.
Learn more: Ovarian dermoid cyst: to remove or not
Oral contraceptives with antiandrogenic action are recommended, against which, after 3 months of use, ovarian function should be restored. If the method turned out to be ineffective, a developed therapy regimen is used, in which for six months a woman takes hormones selected for each phase of the cycle, the main purpose of which is to stimulate ovulation.
Among the surgical methods of treatment, the most widely used now is electrocoagulation of the ovaries with laparoscopic access, which reduces the likelihood of adhesions in the abdominal cavity. During the operation, the electrode makes several incisions on the ovarian capsule in different places, which contributes to the release of the mature follicle. The wedge resection method, in which a small part of the ovaries is removed bilaterally, is now much less common.
The prognosis for restoration of reproductive function is very favorable, subject to effective treatment. It is important to establish the diagnosis and start therapy as early as possible in order to save the patient from the terrible diagnosis – infertility.
Find out: Aesthetic Gynecology: How Procedures Improve Patients' Quality of Life







Add a comment