There are several organs in the human body that can form stones if their function is impaired. These organs include the salivary glands. This pathology is called salivary stone disease or sialolithiasis. Stones in the salivary gland are single or multiple mineral formations that lead to blockage of the ducts of the salivary glands. This pathology occurs in young people. In dentistry, among the pathologies of the salivary glands, sialolithiasis is diagnosed in approximately 75% of cases. More often, stones form in the submandibular glands. What are the causes of the formation of stones in the salivary gland?
What does the stone in the salivary gland consist of, estet-portal.com knows.
- Causes of stone formation in the salivary gland
- Mechanism of stone formation in the salivary gland
- Clinical manifestations of a stone in the salivary gland
- Diagnostics and methods of stone treatment in the salivary gland
Causes of stone formation in the salivary gland
When small stones form, they are easily washed out with saliva, but large stones block the duct of the gland, which leads to the development of clinical symptoms.
Follow us on Instagram!
Stones in the salivary gland are formed against the background of a combination of general and local factors. Among the local causes, congenital anomalies of the ducts of the salivary glands, as well as a change in their secretory function, are important.
In the presence of stones, an inflammatory process always develops in the salivary gland. But the question remains – what is the primary process – stone formation or infection?
Common factors include lack of vitamin A and impaired calcium metabolism.
Salivary gland stones are more likely to form in patients with the following pathologies:
- diabetes mellitus;
- Urolithiasis;
- hyperparathyroidism;
- gout;
- hypervitaminosis D.
Also, taking antihypertensive, antihistamine, psychotropic, diuretic drugs and smoking increase the risk of developing a stone in the
A salivary stone forms around a nucleus that is non-microbial or microbial in nature. In the second case, the stone is a conglomerate of microorganisms (actinomycetes), and in the first case, the stone is represented by an accumulation of desquamated epithelium, leukocytes and foreign bodies that accidentally got into the gland duct.
Read also:Depulped tooth: 5 rules for caring for a tooth without a nerve

The stone consists of components of mineral and organic origin. The chemical composition of the stone in the salivary gland is close to that of tartar. The further formation of a stone in the salivary gland is affected by the rate of saliva secretion, its acidity
and composition. Clinical manifestations of a stone in the salivary gland
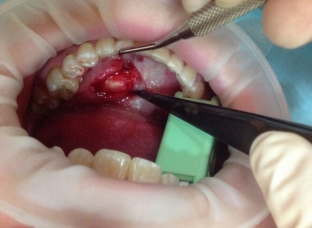
When the stone is in the parenchyma of the salivary gland, it is not accompanied by subjective complaints. In this case, stones in the salivary gland may be accidentally detected on x-rays for another pathology. Complaints in the patient appear when the stone reaches a large size, which contributes to blocking the duct of the salivary gland. The patient feels swelling, a feeling of fullness when eating and an unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth.
A characteristic sign of the presence of a stone in the salivary gland is "salivary colic"; - an acute attack of pain, which is associated with the retention of saliva and a sharp increase in the duct.
Read also:If the stone has blocked the submandibular duct, pain occurs when swallowing, which radiates to the ear or temple.
Avoiding complications after tooth extraction: current recommendations Sometimes you can feel the presence of a stone in the salivary gland. Exacerbation of sialadenitis is manifested by an increase in body temperature and symptoms of intoxication. With a reduced reactivity of the body, the patient may develop
cellulitis or abscesses. Diagnosis and treatment of salivary gland stone
Diagnosis can be suspected by history taking and clinical examination. The diagnosis of a stone in the salivary gland is confirmed by radiography with contrasting of the excretory ducts of the salivary glands. Stones in the salivary gland are differentiated from lymphadenitis, maxillary phlegmon, tumors of the oral cavity and phleboliths.
Read also:Is teeth whitening dangerous at home: a dentist's opinion Sometimes stones can come out on their own. Contribute to this conservative methods of treatment – warm procedures, massage, salivary diet and bougienage of the ducts of the salivary glands. Acute sialadenitis requires antibiotics. When the stone is located near the mouth of the duct, it can be removed with tweezers or by extrusion. Of the surgical methods for treating stones in the salivary gland, sialendoscopy, extracorporeal lithotripsy, intraductal litholysis are used, which is carried out by chemical dissolution of the stone in the salivary gland by introducing a solution of citric acid into the duct.
More useful information on our channel in







Add a comment