Angioedema is a consequence of the reaction of the vessels of the deep layers of the skin and mucous membranes, which is accompanied by local expansion and increased permeability of blood vessels due to the release of certain mediators. The specific mechanisms in cells that contribute to the increase in the permeability of their walls are not fully understood. & nbsp; The main mediators causing angioedema are histamine and bradykinin. Angioedema caused by the release of histamine is similar to urticaria in etiology, mechanism of development and treatment. What is the mechanism of development and symptoms of angioedema?
What is the mechanism of development of hereditary angioedema?
Bradykinin is a nanopeptide secreted upon activation of a contact system capable of increasing vascular permeability by binding to its receptor on endothelial cells. Depending on the pharmacological properties, there are 2 types of receptors for bradykinin – BKR1 and BKR2. Bradykinin is formed from high molecular weight kininogen with the participation of plasma kalikrein. Kalikrein is produced from the zymogen during the activation of coagulation factor XII during the activation of the contact system. The mechanism that activates this system has not yet been studied. Inhibitor XII, plasma kalikrein and C1 – the inhibitor is involved in the control of activation of the contact system.
If C1 function is violated – inhibitor, a release of bradykinin can occur, leading to the development of symptoms of angioedema.
As a result of the action of the initiating factor, C1 deficiency – inhibitor leads to inadequate and excessive secretion of bradykinin. This is how vascular permeability increases, which contributes to the expansion of smooth muscles, notes estet-portal.com. Further accumulation of fluid in the tissues provokes symptoms of edema. Thus, in the plasma of patients with angioedema, an increase in the level of bradykinin is observed against the background of insufficiency of C1 – inhibitor.
There are 2 forms of hereditary angioedema:
- hereditary angioedema due to C1 deficiency – inhibitor;
- angioedema with normal amount of C1 – inhibitor.
Clinical manifestations and main symptoms of angioedema
Generalists should be aware of the clinical manifestations and symptoms of angioedema for early detection of pathology and for timely referral of patients to an allergist – immunologist.
Most often angioedema occurs in the first two decades of life. In most cases, the first symptoms of the disease debut in childhood, the frequency of attacks is very variable. Some factors lead to exacerbations of the disease.
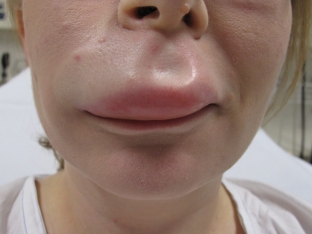
Provoking factors for the development of symptoms of angioedema:
- mechanical injuries of varying intensity;
- Minimally invasive diagnostic procedures;
- tooth extraction;
- surgical intervention;
- infections;
- stress;
- alcohol.
For bradykinin angioedema, the gradual development of symptoms of the disease is characteristic. Edema slowly builds up over 12-36 hours and resolves within 2-5 days. Abdominal symptoms disappear after a day. Angioedema is present on different parts of the body – neck, torso, facial skin, extremities. Paroxysmal abdominal pain is characteristic of angioedema in the gastrointestinal tract.
Severe attacks last 72 – 96 hours, worsening the quality of life and significantly reducing the ability to work. Almost all patients experience at least one episode of upper airway angioedema with a risk of asphyxia during their lifetime.
Most attacks of angioedema symptoms begin with sensations of trembling, skin tingling, fatigue and weakness.
Rashes and itching are not typical for angioedema, however, many attacks are accompanied by the presence of a giant & nbsp; annular erythema. With angioedema of the organs of the stomach – of the intestinal tract, patients complain of colic and diffuse pain in the peritoneum. The clinical picture often resembles "acute abdomen" or intestinal obstruction. Early diagnosis of symptoms of angioedema will prevent dangerous complications. Read the main aspects of the diagnosis of hereditary angioedema in our next article.







Add a comment