Legionellosis – an acute infectious disease characterized by a wide range of clinical manifestations.
The causative agent of legionellosis is a natural inhabitant of groundwater and open water. Favorable conditions for their life are created in the water for air conditioning systems, evaporative condensates, artificial thermal reservoirs and even in the shower head.
The most common form of transmission is by inhalation of contaminated aerosols. The disease is most often registered in the warm season, mainly among men.
For more details about the clinical picture of legionellosis, as well as modern diagnostic methods and effective therapeutic schemes, read on estet-portal.com in this article.
- Legionnaires' disease: gastrointestinal and respiratory symptoms
- Pontiac Fever, Pittsburgh Pneumonia, Fort Bragg Overview
- Diagnosis of legionellosis: radiography and specific methods of examination
- Effective treatment of legionellosis: principles of antibiotic therapy of the disease
Legionnaires' disease: gastrointestinal and respiratory symptoms
The causative agent of legionellosis – Legionella pneumophila – is the cause of not one but several types of infections: Legionnaires' disease, Pontiac fever, Pittsburgh pneumonia and Fort Bragg fever.
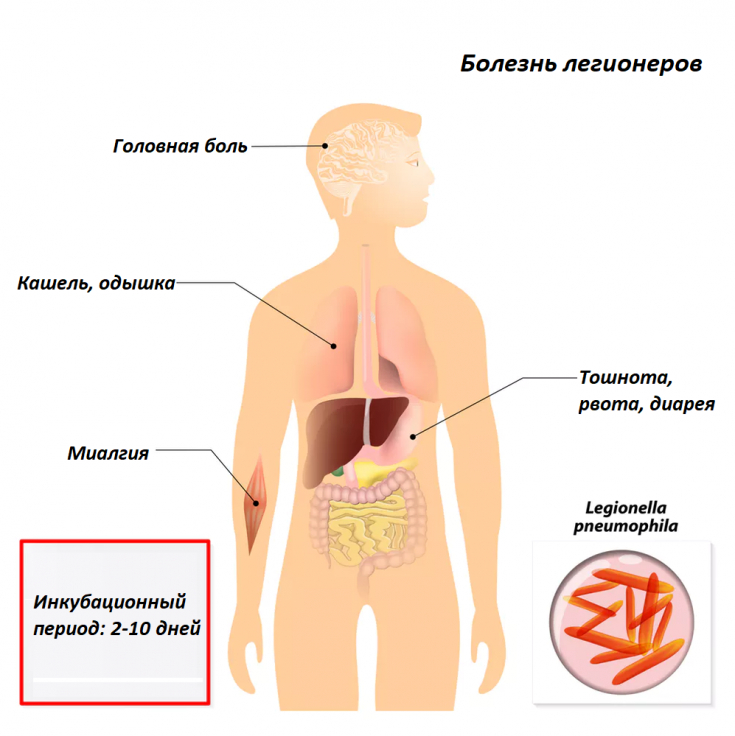
Legionnaires' disease is characterized by an acute onset with headache, myalgia, and arthralgia. The temperature rises to 40 degrees and cannot be reduced by antipyretics.
Gastrointestinal syndrome (diarrhea, vomiting, pain in the epigastric region) is typical.
Already on the first day of the disease, scanty mucopurulent sputum may appear. Subsequently, the patient's condition worsens, respiratory failure increases, the lungs (usually the right one) and the pleura are drawn into the process.
Follow us on Facebook
With a favorable course of the disease, the symptoms begin to gradually resolve in the second week. The convalescence of patients lasts a very long time: up to 10 weeks or longer.
Pontiac Fever, Pittsburgh Pneumonia, Fort Bragg Overview
Pontiac fever is clinically very similar to influenza – for differential diagnosis, completely different seasonality of diseases should be taken into account.
Another name for Pontiac fever – non-pneumonic legionellosis. Characteristic symptoms: myalgia, arthralgia and headache.
In most cases, the disease resolves spontaneously within 3-5 days. Fort Bragg fever clinically resembles Pontiac fever, but is characterized by the development of a polymorphic rash from the first days of the disease, self-resolving without a trace after a few days.
Principles for the diagnosis and treatment of mycoplasma respiratory infections
Pittsburgh pneumonia is most commonly seen in immunocompromised patients. It is characterized by a severe course of pneumonia, a tendency to develop
X-ray of the chest organs is performed to identify infiltrative changes characteristic of legionellosis.
Dangerous city pigeons: principles of diagnosis and treatment of psittacosis
Serological tests play a predominantly supporting role in
Effective treatment of legionellosis: principles of antibiotic therapy of the disease Etiotropic treatment of legionellosis consists in the use of antibiotic therapy. The drugs of choice are fluoroquinolones and macrolides. Among the fluoroquinolones, levofloxacin, which is administered at a dose of 750 mg 1 r / day orally or intravenously for 7-14 days, has the greatest effectiveness.
Among the macrolides, the drugs of choice are:1. Azithromycin 500 mg po or iv for 7-10 days; 2. Clarithromycin 500 mg po bid for 14-21 days.
Legionellosis can cause severe pneumonia, which is characterized by the development of severe hypoxia, hypercapnia, sepsis, etc. In such cases, international protocols recommend the appointment of combined antibiotic therapy with fluoroquinolones and macrolides.The physician prescribing combination antibiotic therapy should be aware of the potential toxicity of the combination of these groups of drugs, in particular the risk of developing "torsades de pointes" arrhythmias.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Infectology" section. You may also be interested in Fever and coughing can be signs of pneumonia







Add a comment