As you know, pyoderma is staphylococcal etiology, streptococcal and mixed. In previous articles, we considered the causes of the development of pyoderma, as well as options for the course of streptococcal pyoderma. What are the features of the manifestation of staphylococcal pyoderma, read further on estet-portal.com. Staphylococcal pyoderma can occur in the form of folliculitis, carbuncle, furuncle, furunculosis and hidradenitis. In children, the course of staphylococcal pyoderma has its own characteristics. Learn more about the course of staphylococcal pyoderma in our article.
Manifestations of staphylococcal pyoderma of the scalp
The most superficial form of staphylococcal pyoderma is ostiofolliculitis. A pustule appears at the mouth of the follicle, the size of which ranges from a pinhead to the size of a lentil. It has a hemispherical shape, penetrated by hair. The cover of the pustule is dense, its contents — purulent. On the periphery there is a small hyperemic corolla. The bottom of the pustule is located in the upper sections of the outer root sheath of the hair follicle. Purulent exudate shrinks into a crust. After 3–4 days, the element resolves without scarring.
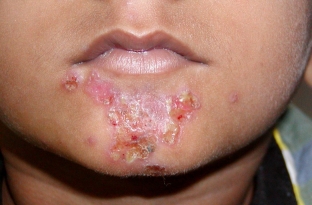
Folliculitis — acute purulent inflammation of the hair follicle. Unlike ostiofolliculitis, it is accompanied by infiltration, severe pain. The pustule opens with the release of pus and the formation of erosion or shrinks into a crust. The element of staphylococcal pyoderma is resolved either by resorption of the infiltrate, or with the formation of a scar, according to estet-portal.com. The duration of the course of folliculitis — 5–7 days.
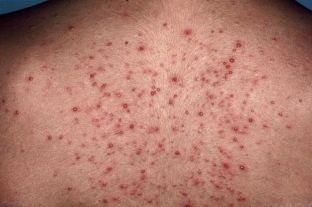
Deep folliculitis differs from typical folliculitis in its significant extension into the dermis. It is allowed only with the formation of a scar, the duration of the course — 7–10 days.
Features of the course of staphylococcal pyoderma with the development of furuncle and carbuncle
Furuncle is an acute purulent-necrotic lesion of the follicle, sebaceous gland and surrounding subcutaneous fat. Often there is a development of a boil from ostiofolliculitis or folliculitis. The growth of the pustule is accompanied by the spread of sharply painful infiltration. After opening the pustule and separating the pus, a necrotic rod is clearly visible, which is gradually separated along with the pus. An ulcer forms in place of the separated necrotic rod.
When a boil is localized on the face, scalp, there is a risk of developing sepsis or thrombosis of superficial and deep veins that have direct anastomoses with the sinuses of the brain.
Furunculosis — recurrent form of a boil with staphylococcal pyoderma. Conventionally, local furunculosis is distinguished, when rashes are observed in limited areas, and disseminated, in which elements appear on different parts of the skin.
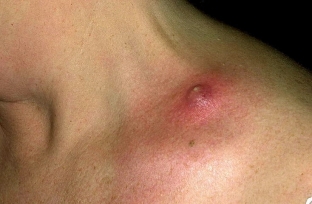
As a rule, furunculosis with staphylococcal pyoderma develops against the background of a pronounced immune imbalance, for example, in HIV-infected patients with diabetes mellitus.
Vulgar sycosis is a chronic recurrent inflammation of the follicles in the growth zone of short thick hair . Most often, the disease occurs in men with signs of an imbalance of sex hormones and is localized in the area of beard and mustache growth. Carbuncles are the most common manifestation of staphylococcal pyoderma.
Clinical signs of carbuncle in staphylococcal pyoderma:
- Carbuncle is characterized by purulent-necrotic lesions of several hair follicles with the development of staphylococcal pyoderma.
- The inflammatory infiltrate increases as a result of its spread deep into the underlying tissues.
- On palpation, there is a sharp pain.
- Gradually, deep skin necrosis occurs in several places around the follicles.
- The focus acquires a slate-blue, black color, melts in one or more places (the name "carbuncle" comes from carbo — coal).
- At the next stage of this staphylococcal pyoderma, multiple holes appear, from which a purulent-bloody fluid flows out.
- After rejection of necrotic masses, a deep, irregularly shaped ulcer with bluish, flaccid, undermined edges is formed.
- The ulcer is gradually cleared of plaque, filled with granulations and scarred within 2-3 weeks.
The nature of the course of hidradenitis with staphylococcal pyoderma
Hydradenitis — purulent inflammation of the apocrine sweat glands, observed in young and adulthood, the cause of which is staphylococcal pyoderma.
In children before puberty and in the elderly, hydradenitis is not observed, since the apocrine sweat glands do not function.
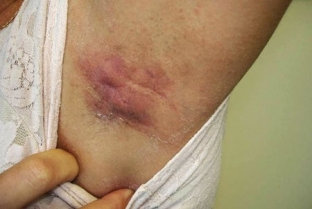
The most frequent localization of inflammation in this disease — axillary areas, sometimes the process develops on the chest around the nipples, navel, genitals, anus. The disease develops slowly, accompanied by discomfort, pain in the lesion, in some cases itching, burning, tingling in the lesion.
At the onset of the disease, the surface of the skin is of a normal color. With further development, the area increases to 1–2 cm, the surface of the skin becomes bluish-red. The formation of conglomerates protruding above the level of surrounding healthy areas is characteristic (the old name is "bitch's udder"). At autopsy, one or more fistulous passages are formed, necrotic rods do not occur. With the regression of hidradenitis with staphylococcal pyoderma, retracted scars are formed. Individuals with immune imbalances often experience relapses of the disease. Timely treatment of staphylococcal pyoderma will prevent the appearance of cosmetic skin defects.






Add a comment