For a long time, the main function of vitamin D was considered to be the maintenance of calcium and phosphorus homeostasis, but now vitamin D is considered a prohormone and the range of its studied functions has greatly expanded. According to the recommendations of the American Society of Endocrinologists vitamin D deficiency is considered to be its level in blood serum in the form of 25(OH)D (50 nmol/l). It dose-dependently affects the differentiation and proliferation, apoptosis of skin cells, thereby participating in the pathogenesis of dermatological diseases.
- The role of vitamin D in the processes of skin physiology
- Psoriasis and vitamin D deficiency
- How does vitamin D affect the development and course of atopic dermatitis
The role of vitamin D in skin physiology
The skin is the source of vitamin D in the body. Keratinocytes synthesize it from 7-dehydrocholesterol, which is a precursor of vitamin D. Keratinocytes are also targets for the action of the biologically active form of the vitamin, calcitriol.
Subscribe to our Instagram!
At a low concentration, vitamin D enhances proliferation keratinocytes, at a high concentration, on the contrary, it inhibits, stimulating differentiation. In physiological concentration, the vitamin prevents apoptosis caused by UV radiation, a tumor necrosis factor. At the same time, in high concentration, it is able to stimulate apoptosis keratinocytes.
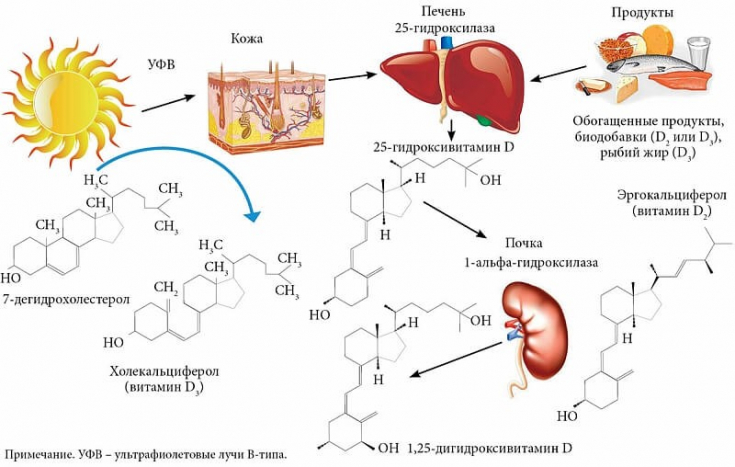
Vitamin D has an effect on the barrier function of the skin. It strengthens the epidermal barrier, by stimulating the synthesis of structural proteins and glycosylceramides, which are necessary for the formation of the lipid protective layer.
Read also: The ABC of the skin for a cosmetologist (Part 1): the structure of the epidermis
Local immunity of the skin is carried out with the help of physical barrier structures, immune cells and antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrobial peptides -
β-defensins and cathelicidins - destroy the bacterial membrane cells, the envelope of the virus, stimulate the proliferation of keratinocytes and their migration to the area of violation of the integrity of the skin for healing.Vitamin D regulates the synthesis of those same antimicrobial peptides by regulating the activity of serine proteases that destroy them.
In addition, the active form of the vitamin directly affects undifferentiated and inactivated T-helpers, T-regulators, activated T-cells
.Vitamin D has a photoprotective effect on skin cells, reducing DNA damage, reducing
keratinocyte apoptosis.Psoriasis and vitamin D deficiency
According to numerous studies, in patients with psoriasis in the blood revealed deficiency or insufficient level
vitamin D.There is a relationship between the degree of the course of the disease and the concentration of the vitamin in the blood serum: with vitamin deficiency, a more severe course of psoriasis is noted.
Vitamin D can reduce the severity of psoriasis symptomsby reducing the infiltration of psoriatic foci with T-lymphocytes, slowing down the effect of pro-inflammatory cytokines
(IL-12, ІL-23, ІL- 1α, ІL-1β, FNT), which are contained in excessive amounts in the area of psoriatic skin lesions.Read also: Psoriasis of the scalp: diagnosis and treatment
Vitamin D inhibits the action of chemoattractants
, psoriasin and coebnerisin, which increase inflammation of psoriatic areas.
In addition to anti-inflammatory action
, in patients with psoriasis, the vitamin can act on the affected epidermis, affecting the expression of genes that are hereditary risk factors for psoriasis.According to some studies, skin damage in psoriasis and a violation of its functions may well be the cause of inadequate synthesis of vitamin D. In this case, a vicious circle is formed: psoriatic skin lesions , increased proliferation and impaired differentiation of keratinocytes, which will lead to a decrease in the synthesis of vitamin D, which, in turn, will worsen the course of the disease.
How does vitamin D affect the development and course of atopic dermatitisThere is a clear association between vitamin D deficiency and deficiency and
an increased risk of developing atopic dermatitis. The severity of the disease is inversely correlated with vitamin D deficiency.
According to studies, patients with atopic dermatitis had lower vitamin D levels than controls.
Read also: Atopic Dermatitis Skin Care
Vitamin D is able to positively influence the pathogenesis and course of the disease,due to the normalization of the level of proinflammatory cytokines (ІL‑2, ІL‑4, ІL‑6, IFN‑γ), reduction IgE, restoration of the epidermal barrier, activation of the synthesis of antimicrobial peptides, and inhibition of mast cell activation.
Follow us on Facebook!
The beneficial effect of phototherapy in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis can also be explained by the correction of vitamin D levels.
Calcitriol regulates the proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis of keratinocytes, affects the barrier function of the skin and local immunity. Understanding and using the anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive activity of vitamin D will help to better and more effectively build tactics for the treatment of skin diseases. Vitamin D deficiency can be safely considered a potential risk factor, and possibly and pathogenetic link development of allergic and chronic inflammatory dermatoses.
More interesting stuff on our YouTube channel:







Add a comment