Toxicoderma – acute inflammatory lesions of the skin, sometimes mucous membranes, as a reaction to substances circulating in the blood that have a sensitizing, toxic, dysmetabolic effect. A distinctive factor from dermatitis is the penetration of the allergen into the skin by the hematogenous route.
Direct contact of the skin with the allergen, at the site of the lesion, does not always occur. A toxic-allergic agent can enter the body either by ingestion of food or drugs, or by inhalation.
Further, the allergen spreads in the body through the circulatory system and affects the skin already "from the inside"; organism. Read more in the article estet-portal.com.
Toxicoderma: the etiology of the disease
Drug toxicoderma mainly develops when taking antibiotics, sulfonamides, vitamins, rivanol, the use of novocaine, furacilin, gamma globulins, blood serum products.
Follow us on Instagram!
Food products can also contain toxic-allergic agents. These can be preservatives, dyes, flavors contained in the products. It is also worth considering the possibility of a person having idiosyncrasy – individual intolerance to some substance.
Of the professional factors in the development of toxicoderma, it is worth noting the effect of substances containing chlorine, nickel, cobalt, and iodine in their structure.
Do not forget about the possibility of autointoxication. It is caused by the accumulation of non-typical metabolic products, which arose as a result of a metabolic disorder or a violation of their excretion from the body.
Routes of allergen entry:
1. injection
2. alimentary
3. inhalation
4. transdermal
5. endogenous
Fig. 1 Correlation of etiological factors.
The mechanism for the development of toxicoderma includes two components:
• allergic − according to one of the four types of reaction (anaphylactic, cytotoxic, immunocomplex, cell-mediated);
• toxic – pseudo-allergies, drug side effects, metabolic disorders.
Risk factors, according to studies, are smoking, frequent stress, the use of low-quality products or those containing a large number of additives.
Clinical picture of toxicoderma
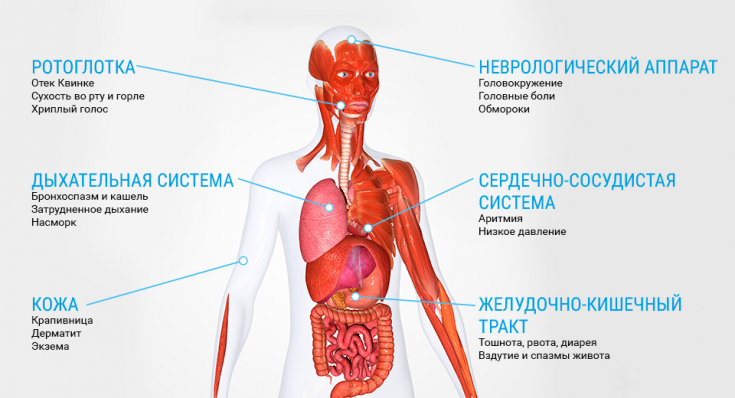
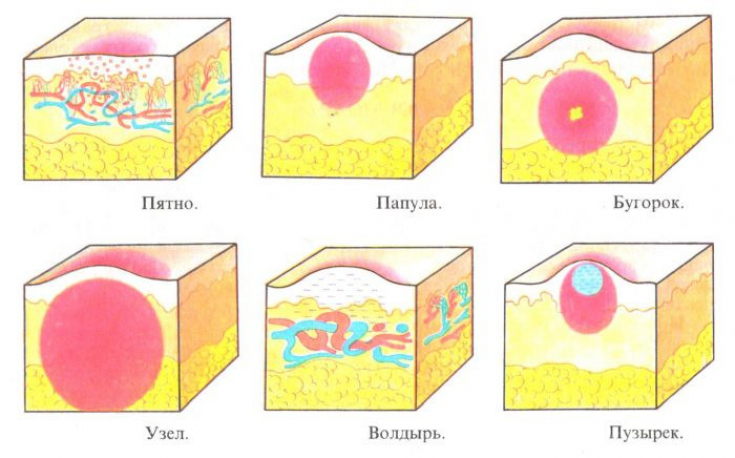
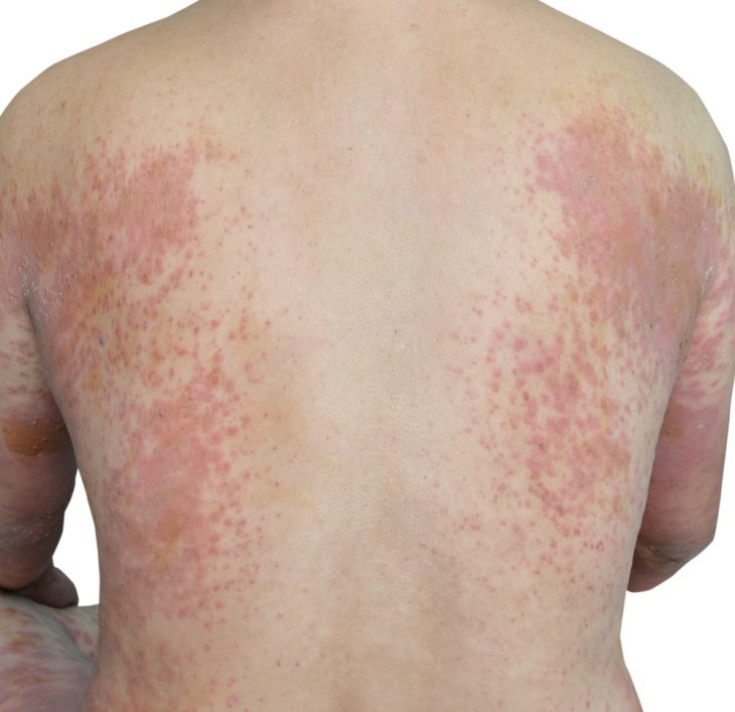
Clinical manifestations of toxidermia can be very diverse. The main symptom is an inflammatory lesion of the skin, which can manifest itself in the form of rashes of the following nature: erythematous spots, urticarial, papular, pustular, bullous, nodular and vesicular rash.
Five skin manifestations requiring urgent diagnosis and treatment
In some cases, the clinical picture is similar to common dermatological diseases and infections accompanied by skin lesions: scarlet fever, erythema intermittent, lichen rosea, measles, etc. Clinical manifestations can have an acute onset, accompanied by a violation of the general condition of the body (fever, malaise, swollen lymph nodes), itching, nausea, vomiting.
Due to the polymorphism of the manifestations of the disease, it is imperative to conduct a differential diagnosis with common dermatological and infectious diseases that have skin manifestations.
Classification by severity:
1. mild
Accompanied by itching, manifestations in the form of erythematous spots, urticaria and papular rashes. Symptoms disappear after a few days, after the intake of the toxic-allergic agent into the body is stopped.
2. moderate
Of the symptoms present: itching of the skin, subfebrile condition is possible. The nature of the rash: urticaria, solitary blisters, widespread erythema, vesicles, nodules. In the general blood test, the following can be detected: eosinophilia, increased ESR.
3. severe
Characterized by a significant rise in temperature (up to 40 ° C), nausea, vomiting. May present with urticaria and Quincke's edema, & nbsp; generalized rash and accompanied by anaphylactic shock. Severe toxicoderma also includes Lyell's syndrome, Stevens-Johnson syndrome. In the general blood test, more pronounced eosinophilia and an increase in ESR are observed.
Read: Severe and rare forms of toxic-allergic dermatitis
Classification by prevalence:
1. limited (the number of elements is not significant, they do not merge, the diameter of the rashes is less than 3 cm)
2. common (there are merging elements, the diameter of the rashes is more than 3 cm)
Treatment of toxicoderma: main directions
First of all, assistance is aimed at stopping the entry of a toxic-allergic agent into the body, removing it from the body and stopping symptoms.
For mild to moderate severity, outpatient treatment is possible. As a rule, in these cases, detoxification, desensitizing and symptomatic therapy is carried out. If the source of the toxin is removed, recovery occurs in a few days.
In cases where there are signs of: severe intoxication, fever, extensive skin lesions, impaired consciousness, shortness of breath, tachycardia – hospitalization, the use of systemic hormonal drugs, antihistamines and more intensive methods of detoxification are required.
The main groups of drugs used in the treatment of toxicoderma: antihistamines, systemic and / or local corticosteroids, sorbents. If the affected areas of the skin are infected with bacteria or fungal flora – prescribe appropriate antibiotics and antifungal drugs.
In the presence of an extensive lesion, it is necessary to monitor the patient's water balance due to the relative loss of fluid due to edema of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. In the most difficult cases, a plasmapheresis procedure can be performed for the purpose of detoxification.







Add a comment