Fat grafts are stable, autologous and are an integral part of the tissues of the recipient zone. The ability of such material to rejuvenate tissues at the injection site is due to stem cells in the stromal vascular fraction of lipoaspirate. Fat grafting cannot replace HA-based dermal fillers, which remain the staple for soft tissue remodeling, as it requires surgical preparation. However, this procedure is an attractive alternative for doctors who have the opportunity to offer it to their patients. In this article, plastic surgeon Anthony Macquillian talks about the basics of facial fat grafting, indications and contraindications for the procedure.
What is a fat graft procedure
Adipose tissue transplantation – This is the transplantation of fat cells (adipocytes) from one part of the body (donor zone) to another (recipient zone). The transplantation technique involves the complete separation of adipose tissue from the blood supply network in the donor area, and the viability of the transplanted cells in the recipient area is ensured by subsequent vascularization.
The blood supply is critical to the survival of the graft, otherwise necrosis and fat resorption occurs, leading to loss of volume in the recipient zone.
Because the process of capillary ingrowth after transplantation takes several days, the cells survive by diffusion of oxygen and nutrients from the fluid surrounding the tissue. This means that only cells located near the surface of the tissue block will be able to survive due to the intake of the above substances.
The smaller the size of the fat particles, the higher the chance of survival of the transplanted tissue.
Adipose tissue grafting for augmentation
Fat transplantation is increasingly being used to rejuvenate or augment multiple areas of the body, most commonly – chest, arms and face. The two main advantages of this method are:
- complete graft autologous (no risk of allergic reactions);
- very low risk of infection after vascularization.
The graft responds to touch like normal tissue and can be used as a base for future fat injection if needed. According to the author, autologous fat is the optimal material for injectable augmentation.
Thanks to the advent of microfiltration technologies that filter, purify and reduce the size of particles, the creation of nanofat has become possible. Nanofat grafting involves the injection of very small particles, or almost liquid fat, to correct fine lines.
Although the exact mechanism of action of nanofat is unknown, it is believed that its anti-aging effect is due to the stimulating effect of stem cells and growth factors on the synthesis of collagen and elastin.
Indications for nanolipofilling:
- correction of small wrinkles – intradermal nanofat injections;
- skin photodamage – intra- and sudermal nanofat injections;
- discoloration of the skin (for example, in the area of the lower eyelid) – intra- and subdermal nanofat injections.
Adipose tissue transplantation protocol
Fat cells are harvested for transplantation through liposuction, during which, unlike liposuction for body contouring, fat is aspirated by special systems, usually filtering the aspirate and separating living cells from non-viable adipocytes and fat.
The aim of this approach is to introduce only living tissue into the recipient zone in order to avoid its resorption and loss of volume.
Special systems are used to take large volumes of graft (for example, for breast or thigh augmentation). However, when smaller volumes of fat are required, most physicians use a thin liposuction cannula and syringe.
Fat graft work has its own characteristics: unlike HA-based fillers, adipocytes are sensitive to pressure, which must be taken into account during insertion. And the consistency of fat depends on the place of injection.
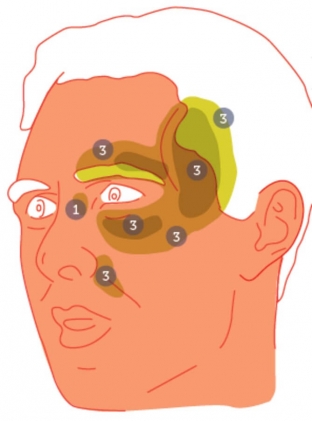
Fig. 1: Target areas of the face for fat grafting. The numbers refer to standard volumes of injected fat in ml.
For augmentation of the zygomatic and temporal region, it is mainly used "dry" (undiluted) fat, however, a more liquid graft is injected into the periorbital area (some practitioners dilute the fat with saline solution in a 70:30 ratio).
Based on my experience, the author claims that the introduction of a liquid graft into the periorbital region reduces the likelihood of induration under the thin skin of the eyelids.
The introduction of fat into the recipient zone can be performed in various ways – they all require the use of a cannula or needle. Many practitioners use a wide-bore needle to inject the graft, but most surgeons use a 0.7-0.9 mm blunt cannula because the needle increases the risk of damaging blood vessels.
For facial fat grafting, the author prefers to use a 0.9 mm blunt cannula.
Most physicians prefer to administer the drug as the cannula is withdrawn in a controlled manner. However, some experienced professionals use other techniques, such as "spraying" (airbrushing) – rapid introduction of very small volumes of material using a very thin cannula and multiple passages.
Adipose tissue harvesting for transplantation: selection of the donor site
As stated above, after vascularization and integration into the surrounding tissues of the face, living fat cells respond to changes in the nutritional status of the patient. Therefore, it is important to remember that:
- The patient's weight must be stable prior to fat grafting (otherwise the result will be unpredictable).
- Further weight gain will affect the appearance of the face.
To reduce the likelihood of the above problems, it is necessary to choose the right donor zone – an area of the body that remains relatively unchanged when weight is gained or lost.
In practice, this means that for facial fat grafting, the first donor site of choice is the inside of the knee, followed by the lateral thigh and abdomen.

Contraindications for fat grafting
Like any other procedure, adipose tissue transplantation has its contraindications. First of all, for it to be performed, the patient must have a sufficient amount of fat in the donor area, which is usually not a problem in the case of facial augmentation.
It is important to explain to the patient that a certain degree of graft resorption – This is normal and may require a second treatment to obtain maximum results.
The author notes that in his practice, smoking is an absolute contraindication to facial rejuvenation with autologous fat.
It is important to explain to the patient that in order to work with the areas in which the scars are located, you will need at least two procedures – to eliminate the scar and form the basis for the further introduction of fat. The introduction of the graft to patients who have undergone surgery on the target area is complicated due to the formation of surgical scars.
Ideally, facial revolu- tion is performed as part of, or prior to, a surgical procedure on the face. In the case of HA-based fillers, it is very important to wait for their complete resorption before injecting fat, since the presence of the filler will prevent the vascularization of adipose tissue, which will lead to the death and resorption of adipocytes.
Complications after fat transplantation for facial rejuvenation
In the past, one of the main problems associated with fat grafting was the appearance of lumps (clumps) in the graft, especially in the periorbital region. Thanks to new technologies, it has become possible to inject fat in a more liquid consistency, which has significantly reduced the incidence of such complications. In the event of lumps appearing in areas that are not amenable to massage, the problem can be corrected by injecting diluted steroids.
The most common complication after fat transfer – loss of graft volumes. However, correct sampling and injection techniques can reduce the likelihood of this phenomenon.
Infections after autologous fat grafting are extremely rare, however, as a precautionary measure, the author always prescribes a weekly course of antibiotics to patients after surgery.
The risk of embolism when fat is injected into a vessel, especially into the ophthalmic artery, can be minimized by using a blunt-tipped cannula and injecting material as the cannula is withdrawn. Traumatization of nerves, blood vessels and the eye itself when using a cannula is also possible, although extremely unlikely, provided that the graft is correctly injected.
After fat grafting: what to warn the patient about
After facial fat transplantation, it is important to warn the patient about the need to minimize pressure on the recipient area, and avoid exposure to cold for at least a week.
High carbohydrate intake for 4 weeks after surgery helps the transplant to take root due to the action of insulin-like growth factor.
It is important to warn the patient that it will be possible to evaluate the effect of the procedure after 3 weeks, and the final result – after about 6 months.
Read also: New methods of lipofilling procedure
Adapted from Aesthetics.







Add a comment