Hematological diseases make up the majority of chronic pathologies that are quite difficult to cure, since the cause to be eliminated is very difficult to find. Thus, the main cause of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) has not yet been clarified. But timely detection and treatment greatly increases the chance for effective treatment and long-term remission. Read how thrombocytopenic purpura manifests itself at estet-portal.com
- When can thrombocytopenic purpura develop?
- Mechanism of development of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Main clinical manifestations of thrombocytopenic purpura
- Main features of the rash in thrombocytopenic purpura
- Methods of diagnosing idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- The main directions in the therapy of thrombocytopenic purpura
When can thrombocytopenic purpura develop
Thrombocytopenic purpura belongs to the group of hemorrhagic diathesis. There are primary and secondary forms of purpura. The primary form can be hereditary or acquired, develops after an infection. The secondary form is a sign of other diseases. Due to unclear reasons, there is a failure in the bone marrow megakaryocytes, which is manifested by a violation of their functioning.
The development of thrombocytopenic purpura is also possible at the stage of platelet circulation in the blood, when antibodies are formed on them.
Subscribe to our Instagram!
Causes of platelet antibodies in thrombocytopenic purpura:
- Surgical intervention.
- Severe overheating or hypothermia of the body.
- Recent trauma.
- Recent vaccinations.
- Development of individual intolerance after taking medications.
- Permitted bacterial or viral infection.
Mechanism of development of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
If there are antibodies to their own platelets in the blood, they begin to stick together. This process of intense agglutination leads to the formation of microthrombi and clogging of small vessels. At the same time, platelets stop producing the proper amount of serotonin, which constricts blood vessels. Therefore, the walls of the vessels remain expanded and easily pass blood, contributing to the development of bleeding and hematomas. Against the background of the overlapping of small vessels by microthrombi, less oxygen enters the tissues of the organs, and ischemia of the organs develops.
Read also: Psoriasis of the scalp: diagnosis and treatment
Thrombocytopenic purpura is characterized not only by a decrease in the number of platelets and their inferiority, but also by disturbances in the blood coagulation system. At the same time, the blood clot that is formed does not have the property of retraction (tightening of the edges of the wound, spontaneous compression), the clot is very loose, which contributes to repeated bleeding. With the development of thrombocytopenic purpura, the development of severe anemia is possible.
Main clinical manifestations of thrombocytopenic purpura
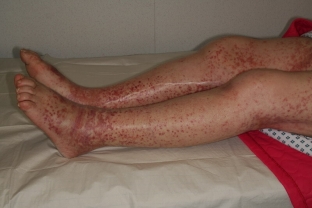
In the acute form of the disease, symptoms develop rapidly and spontaneously. The patient feels a number of non-specific symptoms: nausea, vomiting, weakness, loss of appetite, fever up to 380C, headache, pain in the abdomen or behind the sternum. At the same time, small bruises or hemorrhages are noted on the body, which are not associated with trauma.
Read also: Atopic Dermatitis Skin Care
A little later, these nonspecific symptoms are joined by symptoms of hemorrhagic syndrome:
- heavy menses or uterine bleeding;
- nosebleeds, bleeding of gums and mucous membranes;
- the presence of hemorrhages in the conjunctiva, sclera, retina, vitreous body, fundus or eardrum;
- hematomas or hemorrhages on the skin;
- gastrointestinal bleeding, presence of blood in the stool;
- blood in the urine due to renal bleeding;
- prolonged bleeding after a tooth extraction procedure that cannot be controlled with medication.
These symptoms of hemorrhagic syndrome have their own characteristic when it comes to Werlhof's disease, or thrombocytopenic purpura.
Main features of the rash in thrombocytopenic purpura
After the appearance of a hemorrhagic rash on the body with thrombocytopenic purpura, the general condition of the patient is further aggravated. There is a sharp increase in temperature, and disturbances in the work of the central nervous system develop. This can be manifested by convulsions, deep pathological sleep, retarded speech, tremor, blurred vision, the development of unilateral paralysis, ataxia, disorientation in space, mental disorders.
Follow us on Facebook!
Characteristic of the rash in thrombocytopenic purpura:
- bleeding occurs often at night, for no particular reason;
- if bleeding occurs after an injury, the intensity of bleeding does not correspond to the injury;
- elements of hemorrhagic rash vary from small petechiae to large hematomas;
- The color of the elements of the rash is varied, which has acquired the name "shagreen skin"; or "leopard skin";
- hematomas are painless to the touch;
- rash is not symmetrical.
.Thus, if a patient has many non-specific symptoms or neurological symptoms, it is important to do a complete blood count first. This can help to suspect the disease, which will enable to properly treat the patient.
Methods for diagnosing idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
When patients have complaints and symptoms described in the first part of the article, the doctor conducts a diagnosis, which confirms or refutes the presence of thrombocytopenic purpura. For this, specific methods are used, which consist in conducting a tourniquet, a pinch test, as well as a Konchalovsky-Rumpel test – Leede.
These samples are considered positive if hemorrhages occur at the site of the test, which indicates reduced elasticity of the vascular wall. Laboratory research methods are no less informative.
Read also: Acne treatment: sulfur, zinc, resorcinol
Laboratory results for thrombocytopenic purpura:
- Duke bleeding duration increased to 4 minutes or more;
- blood clot retraction reduced to 60-75%;
- presence of thrombocytopenia below 140х109/l;
- in the bone marrow there are a large number (54-114/µl) of megakaryocytes, which can be morphologically altered;
- presence of antibodies to platelets;
- disturbances in the properties of platelets (change in shape and large sizes);
- the level of bilirubin in the blood is increased;
- elevated blood urea and nitrogen in cases of kidney damage.
What to do before treating thrombocytopenic purpura
Treatment of thrombocytopenic purpura directly depends on the stage of the disease and the severity. Therapy for ITP can be conservative or radical. The acute period implies immediate hospitalization with strict bed rest. The patient needs to eat chilled food in small portions and drink plenty of fluids.
Before starting treatment, it is advisable to check the level of platelets and leukocyte count in the blood. After all, a single detection of thrombocytopenia and other indicators, although it is the main diagnostic criterion, but to make a residual diagnosis, repeat these tests.
The main directions in the therapy of thrombocytopenic purpura
As for medical treatment, it is carried out in four directions: antianemic, hemostatic, hormonal and surgical. Let's take a closer look at the methods of treating thrombocytopenic purpura:
- Antianemic – the appointment of vasoconstrictor agents, iron preparations, intravenous injections of immunoglobulins. Also, transfusion of blood, platelet or erythrocyte mass, polyglucin or dry plasma solution is used.
- Hemostatic – intravenous injections of aminocaproic acid (in the absence of blood in the urine), dicynone or etamsylate. Prescribe drugs to increase blood clotting (atropine, adrenaline, peptone). Local treatment of bleeding is carried out using a fibrin or gelatin film, a hemostatic sponge, tampons with hydrogen peroxide.
- Hormonal – it is advisable to use hormones-androgens in acute and chronic forms of the disease in women with hormonal disorders and uterine bleeding. Corticosteroids are used to increase blood clotting and reduce vascular permeability. When "dry" in the form of purpura (bleeding only on the skin), hormones are not prescribed.
- Surgical – involves the removal of the spleen. This method is resorted to when hormonal treatment has not brought an effect. The operation is performed during the period of remission. If splenectomy fails, immunosuppressive drugs are prescribed along with hormonal drugs.
In addition to these methods of treatment, it is important to recommend that the patient follow diet No. 5, drink hemostatic herbal preparations based on water pepper, corn stigmas, rose hips, nettles and yarrow. It is also recommended to use choleretic drugs. It is important to remember that patients with thrombocytopenic purpura are contraindicated in UV and UHF, chlorpromazine, platelet inhibitors.
Read also: Retinoid side effects: how to control and correct them
With timely initiation of treatment for thrombocytopenic purpura, the prognosis can be very favorable. Cases of persistent remission after an acute onset of the disease are described. After all, the most important thing in the treatment of any process is the right treatment started on time.
More interesting stuff on our YouTube channel:







Add a comment